Dado el recorrido en orden y el recorrido en orden de nivel de un árbol binario. La tarea es calcular la altura del árbol sin construirlo.
Ejemplo:
Input : Input: Two arrays that represent Inorder
and level order traversals of a
Binary Tree
in[] = {4, 8, 10, 12, 14, 20, 22};
level[] = {20, 8, 22, 4, 12, 10, 14};
Output : 4
The binary tree that can be constructed from the
given traversals is:
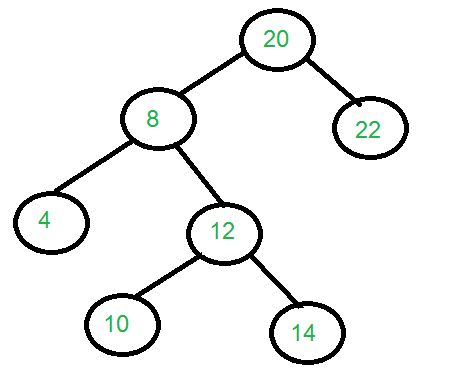
We can clearly see in the above image that the height of the tree is 4.
El enfoque para calcular la altura es similar al enfoque discutido en la publicación Construcción de un árbol a partir de recorridos en orden y en orden de niveles .
Consideremos el ejemplo anterior.
en[] = {4, 8, 10, 12, 14, 20, 22};
nivel[] = {20, 8, 22, 4, 12, 10, 14};
En una secuencia de Levelorder, el primer elemento es la raíz del árbol. Entonces sabemos que ’20’ es raíz para secuencias dadas. Al buscar ’20’ en una secuencia en orden, podemos encontrar que todos los elementos del lado izquierdo de ’20’ están en el subárbol izquierdo y los elementos de la derecha están en el subárbol derecho. Entonces sabemos la estructura debajo ahora.
20
/ \
/ \
{4, 8, 10, 12, 14} {22}
Llamemos {4, 8, 10, 12, 14} como subarreglo izquierdo en el recorrido Inorder y {22} como subarreglo derecho en el recorrido Inorder.
En el recorrido por orden de niveles, las claves de los subárboles izquierdo y derecho no son consecutivas. Entonces extraemos todos los Nodes del recorrido de orden de nivel que están en el subarreglo izquierdo del recorrido de Inorder. Para calcular la altura del subárbol izquierdo de la raíz, recurrimos a los elementos extraídos del recorrido de orden de nivel y el subarreglo izquierdo del recorrido de orden. En el ejemplo anterior, recurrimos a las siguientes dos arrays.
// Recur for following arrays to
// calculate the height of the left subtree
In[] = {4, 8, 10, 12, 14}
level[] = {8, 4, 12, 10, 14}
De manera similar, recurrimos a las siguientes dos arrays y calculamos la altura del subárbol derecho.
// Recur for following arrays to calculate
// height of the right subtree
In[] = {22}
level[] = {22}
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program to caulate height of Binary Tree
// from InOrder and LevelOrder Traversals
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/* Function to find index of value
in the InOrder Traversal array */
int search(int arr[], int strt, int end, int value)
{
for (int i = strt; i <= end; i++)
if (arr[i] == value)
return i;
return -1;
}
// Function to calculate the height
// of the Binary Tree
int getHeight(int in[], int level[], int start,
int end, int& height, int n)
{
// Base Case
if (start > end)
return 0;
// Get index of current root in InOrder Traversal
int getIndex = search(in, start, end, level[0]);
if (getIndex == -1)
return 0;
// Count elements in Left Subtree
int leftCount = getIndex - start;
// Count elements in right Subtree
int rightCount = end - getIndex;
// Declare two arrays for left and
// right subtrees
int* newLeftLevel = new int[leftCount];
int* newRightLevel = new int[rightCount];
int lheight = 0, rheight = 0;
int k = 0;
// Extract values from level order traversal array
// for current left subtree
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = start; j < getIndex; j++) {
if (level[i] == in[j]) {
newLeftLevel[k] = level[i];
k++;
break;
}
}
}
k = 0;
// Extract values from level order traversal array
// for current right subtree
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = getIndex + 1; j <= end; j++) {
if (level[i] == in[j]) {
newRightLevel[k] = level[i];
k++;
break;
}
}
}
// Recursively call to calculate height of left Subtree
if (leftCount > 0)
lheight = getHeight(in, newLeftLevel, start,
getIndex - 1, height, leftCount);
// Recursively call to calculate height of right Subtree
if (rightCount > 0)
rheight = getHeight(in, newRightLevel,
getIndex + 1, end, height, rightCount);
// Current height
height = max(lheight + 1, rheight + 1);
// Delete Auxiliary arrays
delete[] newRightLevel;
delete[] newLeftLevel;
// return height
return height;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
int in[] = { 4, 8, 10, 12, 14, 20, 22 };
int level[] = { 20, 8, 22, 4, 12, 10, 14 };
int n = sizeof(in) / sizeof(in[0]);
int h = 0;
cout << getHeight(in, level, 0, n - 1, h, n);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to caulate height of Binary Tree
// from InOrder and LevelOrder Traversals
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static int height;
/* Function to find index of value
in the InOrder Traversal array */
static int search(int arr[], int strt,
int end, int value)
{
for (int i = strt; i <= end; i++)
if (arr[i] == value)
return i;
return -1;
}
// Function to calculate the height
// of the Binary Tree
static int getHeight(int in[], int level[],
int start, int end, int n)
{
// Base Case
if (start > end)
return 0;
// Get index of current root in InOrder Traversal
int getIndex = search(in, start, end, level[0]);
if (getIndex == -1)
return 0;
// Count elements in Left Subtree
int leftCount = getIndex - start;
// Count elements in right Subtree
int rightCount = end - getIndex;
// Declare two arrays for left and
// right subtrees
int []newLeftLevel = new int[leftCount];
int []newRightLevel = new int[rightCount];
int lheight = 0, rheight = 0;
int k = 0;
// Extract values from level order traversal array
// for current left subtree
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = start; j < getIndex; j++)
{
if (level[i] == in[j])
{
newLeftLevel[k] = level[i];
k++;
break;
}
}
}
k = 0;
// Extract values from level order traversal array
// for current right subtree
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = getIndex + 1; j <= end; j++)
{
if (level[i] == in[j])
{
newRightLevel[k] = level[i];
k++;
break;
}
}
}
// Recursively call to calculate
// height of left Subtree
if (leftCount > 0)
lheight = getHeight(in, newLeftLevel, start,
getIndex - 1, leftCount);
// Recursively call to calculate
// height of right Subtree
if (rightCount > 0)
rheight = getHeight(in, newRightLevel,
getIndex + 1, end, rightCount);
// Current height
height = Math.max(lheight + 1, rheight + 1);
// Delete Auxiliary arrays
newRightLevel=null;
newLeftLevel=null;
// return height
return height;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int in[] = {4, 8, 10, 12, 14, 20, 22};
int level[] = {20, 8, 22, 4, 12, 10, 14};
int n = in.length;
height = 0;
System.out.println(getHeight(in, level, 0, n - 1, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Python3
# Python3 program to calculate height of Binary Tree from # InOrder and LevelOrder Traversals ''' Function to find the index of value in the InOrder Traversal list ''' def search(arr, start, end, value): for i in range(start, end + 1): if arr[i] == value: return i return -1 ''' Function to calculate the height of the Binary Tree ''' def getHeight(inOrder, levelOrder, start, end, height, n): # Base Case if start > end: return 0 # Get Index of current root in InOrder Traversal getIndex = search(inOrder, start, end, levelOrder[0]) if getIndex == -1: return 0 # Count elements in Left Subtree leftCount = getIndex - start # Count elements in Right Subtree rightCount = end - getIndex # Declare two lists for left and right subtrees newLeftLevel = [None for _ in range(leftCount)] newRightLevel = [None for _ in range(rightCount)] lheight, rheight, k = 0, 0, 0 # Extract values from level order traversal list # for current left subtree for i in range(n): for j in range(start, getIndex): if levelOrder[i] == inOrder[j]: newLeftLevel[k] = levelOrder[i] k += 1 break k = 0 # Extract values from level order traversal list # for current right subtree for i in range(n): for j in range(getIndex + 1, end + 1): if levelOrder[i] == inOrder[j]: newRightLevel[k] = levelOrder[i] k += 1 break # Recursively call to calculate height # of left subtree if leftCount > 0: lheight = getHeight(inOrder, newLeftLevel, start, getIndex - 1, height, leftCount) # Recursively call to calculate height # of right subtree if rightCount > 0: rheight = getHeight(inOrder, newRightLevel, getIndex + 1, end, height, rightCount) # current height height = max(lheight + 1, rheight + 1) # return height return height # Driver Code if __name__=='__main__': inOrder = [4, 8, 10, 12, 14, 20, 22] levelOrder = [20, 8, 22, 4, 12, 10, 14] n, h = len(inOrder), 0 print(getHeight(inOrder, levelOrder, 0, n - 1, h, n)) # This code is contributed by harshraj22
C#
// C# program to caulate height of Binary Tree
// from InOrder and LevelOrder Traversals
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
static int height;
/* Function to find index of value
in the InOrder Traversal array */
static int search(int []arr, int strt,
int end, int value)
{
for (int i = strt; i <= end; i++)
if (arr[i] == value)
return i;
return -1;
}
// Function to calculate the height
// of the Binary Tree
static int getHeight(int []In, int []level,
int start, int end, int n)
{
// Base Case
if (start > end)
return 0;
// Get index of current root in
// InOrder Traversal
int getIndex = search(In, start, end, level[0]);
if (getIndex == -1)
return 0;
// Count elements in Left Subtree
int leftCount = getIndex - start;
// Count elements in right Subtree
int rightCount = end - getIndex;
// Declare two arrays for left and
// right subtrees
int []newLeftLevel = new int[leftCount];
int []newRightLevel = new int[rightCount];
int lheight = 0, rheight = 0;
int k = 0;
// Extract values from level order traversal array
// for current left subtree
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = start; j < getIndex; j++)
{
if (level[i] == In[j])
{
newLeftLevel[k] = level[i];
k++;
break;
}
}
}
k = 0;
// Extract values from level order traversal array
// for current right subtree
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = getIndex + 1; j <= end; j++)
{
if (level[i] == In[j])
{
newRightLevel[k] = level[i];
k++;
break;
}
}
}
// Recursively call to calculate
// height of left Subtree
if (leftCount > 0)
lheight = getHeight(In, newLeftLevel, start,
getIndex - 1, leftCount);
// Recursively call to calculate
// height of right Subtree
if (rightCount > 0)
rheight = getHeight(In, newRightLevel,
getIndex + 1, end, rightCount);
// Current height
height = Math.Max(lheight + 1, rheight + 1);
// Delete Auxiliary arrays
newRightLevel = null;
newLeftLevel = null;
// return height
return height;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int []In = {4, 8, 10, 12, 14, 20, 22};
int []level = {20, 8, 22, 4, 12, 10, 14};
int n = In.Length;
height = 0;
Console.WriteLine(getHeight(In, level, 0, n - 1, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh
Javascript
<script>
//Javascript program to caulate height of Binary Tree
// from InOrder and LevelOrder Traversals
var height = 0;
/* Function to find index of value
in the InOrder Traversal array */
function search(arr, strt, end, value)
{
for (var i = strt; i <= end; i++)
if (arr[i] == value)
return i;
return -1;
}
// Function to calculate the height
// of the Binary Tree
function getHeight(In, level, start, end, n)
{
// Base Case
if (start > end)
return 0;
// Get index of current root in
// InOrder Traversal
var getIndex = search(In, start, end, level[0]);
if (getIndex == -1)
return 0;
// Count elements in Left Subtree
var leftCount = getIndex - start;
// Count elements in right Subtree
var rightCount = end - getIndex;
// Declare two arrays for left and
// right subtrees
var newLeftLevel = Array(leftCount);
var newRightLevel = Array(rightCount);
var lheight = 0, rheight = 0;
var k = 0;
// Extract values from level order traversal array
// for current left subtree
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (var j = start; j < getIndex; j++)
{
if (level[i] == In[j])
{
newLeftLevel[k] = level[i];
k++;
break;
}
}
}
k = 0;
// Extract values from level order traversal array
// for current right subtree
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (var j = getIndex + 1; j <= end; j++)
{
if (level[i] == In[j])
{
newRightLevel[k] = level[i];
k++;
break;
}
}
}
// Recursively call to calculate
// height of left Subtree
if (leftCount > 0)
lheight = getHeight(In, newLeftLevel, start,
getIndex - 1, leftCount);
// Recursively call to calculate
// height of right Subtree
if (rightCount > 0)
rheight = getHeight(In, newRightLevel,
getIndex + 1, end, rightCount);
// Current height
height = Math.max(lheight + 1, rheight + 1);
// Delete Auxiliary arrays
newRightLevel = null;
newLeftLevel = null;
// return height
return height;
}
// Driver Code
var In = [4, 8, 10, 12, 14, 20, 22];
var level = [20, 8, 22, 4, 12, 10, 14];
var n = In.length;
height = 0;
document.write(getHeight(In, level, 0, n - 1, n));
</script>
Salida :
4
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por harshitasinghal1803 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA