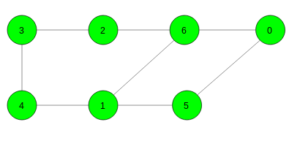
Dado un gráfico no ponderado no dirigido. La tarea es encontrar la duración del ciclo más corto en el gráfico dado. Si no existe ningún ciclo, imprima -1.
Ejemplos:
Aporte:
Salida: 4
Ciclo 6 -> 1 -> 5 -> 0 -> 6Aporte:
Salida: 3
Ciclo 6 -> 1 -> 2 -> 6
Requisitos previos: Dijkstra
Enfoque: para cada vértice, verificamos si es posible obtener el ciclo más corto que involucre a este vértice. Para cada vértice primero, inserte el vértice actual en la cola y luego sus vecinos y si el vértice que ya se visitó vuelve, entonces el ciclo está presente.
Aplique el proceso anterior para cada vértice y obtenga la duración del ciclo más corto.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 100200
vector<int> gr[N];
// Function to add edge
void Add_edge(int x, int y)
{
gr[x].push_back(y);
gr[y].push_back(x);
}
// Function to find the length of
// the shortest cycle in the graph
int shortest_cycle(int n)
{
// To store length of the shortest cycle
int ans = INT_MAX;
// For all vertices
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Make distance maximum
vector<int> dist(n, (int)(1e9));
// Take a imaginary parent
vector<int> par(n, -1);
// Distance of source to source is 0
dist[i] = 0;
queue<int> q;
// Push the source element
q.push(i);
// Continue until queue is not empty
while (!q.empty()) {
// Take the first element
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
// Traverse for all it's childs
for (int child : gr[x]) {
// If it is not visited yet
if (dist[child] == (int)(1e9)) {
// Increase distance by 1
dist[child] = 1 + dist[x];
// Change parent
par[child] = x;
// Push into the queue
q.push(child);
}
// If it is already visited
else if (par[x] != child and par[child] != x)
ans = min(ans, dist[x] + dist[child] + 1);
}
}
}
// If graph contains no cycle
if (ans == INT_MAX)
return -1;
// If graph contains cycle
else
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Number of vertices
int n = 7;
// Add edges
Add_edge(0, 6);
Add_edge(0, 5);
Add_edge(5, 1);
Add_edge(1, 6);
Add_edge(2, 6);
Add_edge(2, 3);
Add_edge(3, 4);
Add_edge(4, 1);
// Function call
cout << shortest_cycle(n);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static final int N = 100200;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static Vector<Integer>[] gr = new Vector[N];
// Function to add edge
static void Add_edge(int x, int y)
{
gr[x].add(y);
gr[y].add(x);
}
// Function to find the length of
// the shortest cycle in the graph
static int shortest_cycle(int n)
{
// To store length of the shortest cycle
int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// For all vertices
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Make distance maximum
int[] dist = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(dist, (int) 1e9);
// Take a imaginary parent
int[] par = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(par, -1);
// Distance of source to source is 0
dist[i] = 0;
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
// Push the source element
q.add(i);
// Continue until queue is not empty
while (!q.isEmpty())
{
// Take the first element
int x = q.poll();
// Traverse for all it's childs
for (int child : gr[x])
{
// If it is not visited yet
if (dist[child] == (int) (1e9))
{
// Increase distance by 1
dist[child] = 1 + dist[x];
// Change parent
par[child] = x;
// Push into the queue
q.add(child);
} else if (par[x] != child && par[child] != x)
ans = Math.min(ans, dist[x] + dist[child] + 1);
}
}
}
// If graph contains no cycle
if (ans == Integer.MAX_VALUE)
return -1;
// If graph contains cycle
else
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
gr[i] = new Vector<>();
// Number of vertices
int n = 7;
// Add edges
Add_edge(0, 6);
Add_edge(0, 5);
Add_edge(5, 1);
Add_edge(1, 6);
Add_edge(2, 6);
Add_edge(2, 3);
Add_edge(3, 4);
Add_edge(4, 1);
// Function call
System.out.println(shortest_cycle(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by
// sanjeev2552
Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach from sys import maxsize as INT_MAX from collections import deque N = 100200 gr = [0] * N for i in range(N): gr[i] = [] # Function to add edge def add_edge(x: int, y: int) -> None: global gr gr[x].append(y) gr[y].append(x) # Function to find the length of # the shortest cycle in the graph def shortest_cycle(n: int) -> int: # To store length of the shortest cycle ans = INT_MAX # For all vertices for i in range(n): # Make distance maximum dist = [int(1e9)] * n # Take a imaginary parent par = [-1] * n # Distance of source to source is 0 dist[i] = 0 q = deque() # Push the source element q.append(i) # Continue until queue is not empty while q: # Take the first element x = q[0] q.popleft() # Traverse for all it's childs for child in gr[x]: # If it is not visited yet if dist[child] == int(1e9): # Increase distance by 1 dist[child] = 1 + dist[x] # Change parent par[child] = x # Push into the queue q.append(child) # If it is already visited elif par[x] != child and par[child] != x: ans = min(ans, dist[x] + dist[child] + 1) # If graph contains no cycle if ans == INT_MAX: return -1 # If graph contains cycle else: return ans # Driver Code if __name__ == "__main__": # Number of vertices n = 7 # Add edges add_edge(0, 6) add_edge(0, 5) add_edge(5, 1) add_edge(1, 6) add_edge(2, 6) add_edge(2, 3) add_edge(3, 4) add_edge(4, 1) # Function call print(shortest_cycle(n)) # This code is contributed by # sanjeev2552
C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
static readonly int N = 100200;
static List<int>[] gr = new List<int>[N];
// Function to add edge
static void Add_edge(int x, int y)
{
gr[x].Add(y);
gr[y].Add(x);
}
// Function to find the length of
// the shortest cycle in the graph
static int shortest_cycle(int n)
{
// To store length of the shortest cycle
int ans = int.MaxValue;
// For all vertices
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Make distance maximum
int[] dist = new int[n];
fill(dist, (int) 1e9);
// Take a imaginary parent
int[] par = new int[n];
fill(par, -1);
// Distance of source to source is 0
dist[i] = 0;
List<int> q = new List<int>();
// Push the source element
q.Add(i);
// Continue until queue is not empty
while (q.Count!=0)
{
// Take the first element
int x = q[0];
q.RemoveAt(0);
// Traverse for all it's childs
foreach (int child in gr[x])
{
// If it is not visited yet
if (dist[child] == (int) (1e9))
{
// Increase distance by 1
dist[child] = 1 + dist[x];
// Change parent
par[child] = x;
// Push into the queue
q.Add(child);
} else if (par[x] != child && par[child] != x)
ans = Math.Min(ans, dist[x] + dist[child] + 1);
}
}
}
// If graph contains no cycle
if (ans == int.MaxValue)
return -1;
// If graph contains cycle
else
return ans;
}
static int[] fill(int []arr, int val)
{
for(int i = 0;i<arr.GetLength(0);i++)
arr[i] = val;
return arr;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
gr[i] = new List<int>();
// Number of vertices
int n = 7;
// Add edges
Add_edge(0, 6);
Add_edge(0, 5);
Add_edge(5, 1);
Add_edge(1, 6);
Add_edge(2, 6);
Add_edge(2, 3);
Add_edge(3, 4);
Add_edge(4, 1);
// Function call
Console.WriteLine(shortest_cycle(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript implementation of the approach
var N = 100200;
var gr = Array.from(Array(N),()=>Array());
// Function to add edge
function Add_edge(x, y)
{
gr[x].push(y);
gr[y].push(x);
}
// Function to find the length of
// the shortest cycle in the graph
function shortest_cycle(n)
{
// To store length of the shortest cycle
var ans = 1000000000;
// For all vertices
for(var i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Make distance maximum
var dist = Array(n).fill(1000000000);
// Take a imaginary parent
var par = Array(n).fill(-1);
// Distance of source to source is 0
dist[i] = 0;
var q = [];
// Push the source element
q.push(i);
// Continue until queue is not empty
while (q.length!=0)
{
// Take the first element
var x = q[0];
q.shift();
// Traverse for all it's childs
for(var child of gr[x])
{
// If it is not visited yet
if (dist[child] == 1000000000)
{
// Increase distance by 1
dist[child] = 1 + dist[x];
// Change parent
par[child] = x;
// Push into the queue
q.push(child);
} else if (par[x] != child && par[child] != x)
ans = Math.min(ans, dist[x] + dist[child] + 1);
}
}
}
// If graph contains no cycle
if (ans == 1000000000)
return -1;
// If graph contains cycle
else
return ans;
}
function fill(arr, val)
{
for(var i = 0;i<arr.length;i++)
arr[i] = val;
return arr;
}
// Driver Code
// Number of vertices
var n = 7;
// push edges
Add_edge(0, 6);
Add_edge(0, 5);
Add_edge(5, 1);
Add_edge(1, 6);
Add_edge(2, 6);
Add_edge(2, 3);
Add_edge(3, 4);
Add_edge(4, 1);
// Function call
document.write(shortest_cycle(n));
</script>
4
Complejidad de tiempo : O( |V| * (|V|+|E|)) para un gráfico G=(V, E)
Complejidad de la memoria : O(V^2) para un gráfico G=(V, E)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por pawan_asipu y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA