Las clases de almacenamiento se utilizan para describir las características de una variable/función. Estas características incluyen básicamente el alcance, la visibilidad y el tiempo de vida que nos ayudan a rastrear la existencia de una variable en particular durante el tiempo de ejecución de un programa.
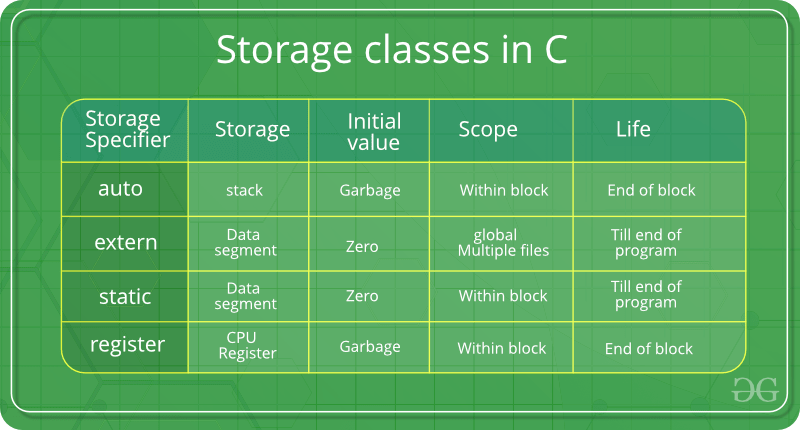
El lenguaje C utiliza 4 clases de almacenamiento , a saber:
C
// A C program to demonstrate different storage
// classes
#include <stdio.h>
// declaring the variable which is to be made extern
// an initial value can also be initialized to x
int x;
void autoStorageClass()
{
printf("\nDemonstrating auto class\n\n");
// declaring an auto variable (simply
// writing "int a=32;" works as well)
auto int a = 32;
// printing the auto variable 'a'
printf("Value of the variable 'a'"
" declared as auto: %d\n",
a);
printf("--------------------------------");
}
void registerStorageClass()
{
printf("\nDemonstrating register class\n\n");
// declaring a register variable
register char b = 'G';
// printing the register variable 'b'
printf("Value of the variable 'b'"
" declared as register: %d\n",
b);
printf("--------------------------------");
}
void externStorageClass()
{
printf("\nDemonstrating extern class\n\n");
// telling the compiler that the variable
// x is an extern variable and has been
// defined elsewhere (above the main
// function)
extern int x;
// printing the extern variables 'x'
printf("Value of the variable 'x'"
" declared as extern: %d\n",
x);
// value of extern variable x modified
x = 2;
// printing the modified values of
// extern variables 'x'
printf("Modified value of the variable 'x'"
" declared as extern: %d\n",
x);
printf("--------------------------------");
}
void staticStorageClass()
{
int i = 0;
printf("\nDemonstrating static class\n\n");
// using a static variable 'y'
printf("Declaring 'y' as static inside the loop.\n"
"But this declaration will occur only"
" once as 'y' is static.\n"
"If not, then every time the value of 'y' "
"will be the declared value 5"
" as in the case of variable 'p'\n");
printf("\nLoop started:\n");
for (i = 1; i < 5; i++) {
// Declaring the static variable 'y'
static int y = 5;
// Declare a non-static variable 'p'
int p = 10;
// Incrementing the value of y and p by 1
y++;
p++;
// printing value of y at each iteration
printf("\nThe value of 'y', "
"declared as static, in %d "
"iteration is %d\n",
i, y);
// printing value of p at each iteration
printf("The value of non-static variable 'p', "
"in %d iteration is %d\n",
i, p);
}
printf("\nLoop ended:\n");
printf("--------------------------------");
}
int main()
{
printf("A program to demonstrate"
" Storage Classes in C\n\n");
// To demonstrate auto Storage Class
autoStorageClass();
// To demonstrate register Storage Class
registerStorageClass();
// To demonstrate extern Storage Class
externStorageClass();
// To demonstrate static Storage Class
staticStorageClass();
// exiting
printf("\n\nStorage Classes demonstrated");
return 0;
}
// This code is improved by RishabhPrabhu
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA