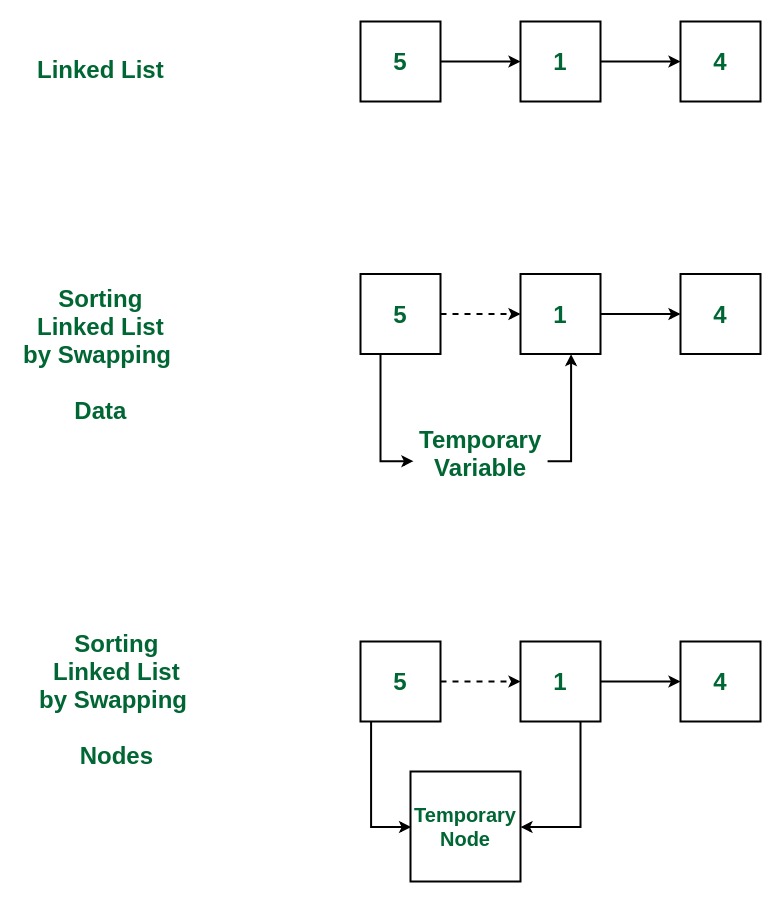
Dada una lista enlazada individualmente, ordénela usando la ordenación de burbujas intercambiando Nodes.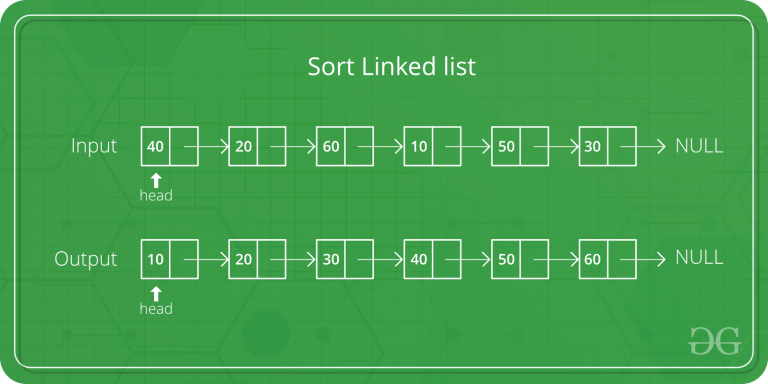
Ejemplo:
Input: 10->30->20->5 Output: 5->10->20->30 Input: 20->4->3 Output: 3->4->20
Acercarse:
- Obtener la Lista Vinculada para ser ordenada
- Aplique Bubble Sort a esta lista vinculada , en la que, al comparar los dos Nodes adyacentes, los Nodes reales se intercambian en lugar de solo intercambiar los datos.
- Imprimir la lista ordenada
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program to sort Linked List
// using Bubble Sort
// by swapping nodes
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/* structure for a node */
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* next;
} Node;
/*Function to swap the nodes */
struct Node* swap(struct Node* ptr1, struct Node* ptr2)
{
struct Node* tmp = ptr2->next;
ptr2->next = ptr1;
ptr1->next = tmp;
return ptr2;
}
/* Function to sort the list */
int bubbleSort(struct Node** head, int count)
{
struct Node** h;
int i, j, swapped;
for (i = 0; i <= count; i++)
{
h = head;
swapped = 0;
for (j = 0; j < count - i - 1; j++)
{
struct Node* p1 = *h;
struct Node* p2 = p1->next;
if (p1->data > p2->data)
{
/* update the link after swapping */
*h = swap(p1, p2);
swapped = 1;
}
h = &(*h)->next;
}
/* break if the loop ended without any swap */
if (swapped == 0)
break;
}
}
/* Function to print the list */
void printList(struct Node* n)
{
while (n != NULL)
{
cout << n->data << " -> ";
n = n->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
/* Function to insert a struct Node
at the beginning of a linked list */
void insertAtTheBegin(struct Node** start_ref, int data)
{
struct Node* ptr1
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
ptr1->data = data;
ptr1->next = *start_ref;
*start_ref = ptr1;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 78, 20, 10, 32, 1, 5 };
int list_size, i;
/* start with empty linked list */
struct Node* start = NULL;
list_size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
/* Create linked list from the array arr[] */
for (i = 0; i < list_size; i++)
insertAtTheBegin(&start, arr[i]);
/* print list before sorting */
cout <<"Linked list before sorting\n";
printList(start);
/* sort the linked list */
bubbleSort(&start, list_size);
/* print list after sorting */
cout <<"Linked list after sorting\n";
printList(start);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by
// shubhamsingh10
C
// C program to sort Linked List
// using Bubble Sort
// by swapping nodes
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/* structure for a node */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
} Node;
/*Function to swap the nodes */
struct Node* swap(struct Node* ptr1, struct Node* ptr2)
{
struct Node* tmp = ptr2->next;
ptr2->next = ptr1;
ptr1->next = tmp;
return ptr2;
}
/* Function to sort the list */
int bubbleSort(struct Node** head, int count)
{
struct Node** h;
int i, j, swapped;
for (i = 0; i <= count; i++) {
h = head;
swapped = 0;
for (j = 0; j < count - i - 1; j++) {
struct Node* p1 = *h;
struct Node* p2 = p1->next;
if (p1->data > p2->data) {
/* update the link after swapping */
*h = swap(p1, p2);
swapped = 1;
}
h = &(*h)->next;
}
/* break if the loop ended without any swap */
if (swapped == 0)
break;
}
}
/* Function to print the list */
void printList(struct Node* n)
{
while (n != NULL) {
printf("%d -> ", n->data);
n = n->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
/* Function to insert a struct Node
at the beginning of a linked list */
void insertAtTheBegin(struct Node** start_ref, int data)
{
struct Node* ptr1
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
ptr1->data = data;
ptr1->next = *start_ref;
*start_ref = ptr1;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 78, 20, 10, 32, 1, 5 };
int list_size, i;
/* start with empty linked list */
struct Node* start = NULL;
list_size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
/* Create linked list from the array arr[] */
for (i = 0; i < list_size; i++)
insertAtTheBegin(&start, arr[i]);
/* print list before sorting */
printf("Linked list before sorting\n");
printList(start);
/* sort the linked list */
bubbleSort(&start, list_size);
/* print list after sorting */
printf("Linked list after sorting\n");
printList(start);
return 0;
}
Producción:
Linked list before sorting 5 -> 1 -> 32 -> 10 -> 20 -> 78 -> Linked list after sorting 1 -> 5 -> 10 -> 20 -> 32 -> 78 ->
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por kalaikarthick y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA