La lista enlazada es parte de la colección en el paquete java.util . La clase LinkedList es una implementación de la estructura de datos LinkedList , es una estructura de datos lineal. En LinkedList, debido a la asignación dinámica de memoria, las inserciones y eliminaciones son procesos sencillos. Para eliminar duplicados de
Ejemplo:
Initial composition : 7 2 3 3 2 7 6 2 After removing duplicates : 7 2 3 6
Representación pictórica : (un Node en una LinkedList tiene dos partes: datos y enlace al siguiente Node (nulo en el caso del último elemento)
Algoritmo:
- Inicialmente, se crea un nuevo Node que apunta a la cabeza.
- Un Node temporal apuntará a actual y el Node de índice apuntará a actual.siguiente.
- Si los datos del Node índice y el Node actual son los mismos, es decir, si se encuentra un elemento duplicado, temp.next apunta a index.next, es decir, omite el elemento duplicado.
- Si no se cumple la condición anterior, se hace que la temperatura apunte al Node anterior de un índice.
- El Node de índice itera hasta el final y se repiten los pasos 3 y 4.
- Los pasos 2 a 5 se ejecutan hasta que el Node actual apunta al final, es decir, llega a su final.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
Java
// Java Program to Remove Duplicate Elements From LinkedList
import java.io.*;
// Creating the node class for a singly linkedlist
class Node {
Node next;
int data;
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
public class singlyLinkedList {
// Defining the head and tail of a singly linkedlist
public Node head = null;
public Node tail = null;
// creating add() that enables addition
// of a new node to the list
public void add(int data)
{
// Creating a new node
Node newNode = new Node(data);
// Checking whether the list is empty or not
if (head == null) {
// If the list is found to be empty, both head
// and tail are made to point to the new node
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
}
else {
// newNode is added after tail in such a way
// that next node of the tail points to newNode
tail.next = newNode;
// newNode becomes the new tail of the list
tail = newNode;
}
}
// Creating removeDuplicates() to remove
// duplicates from the linkedlist
public void removeDuplicates()
{
// current node points to the head element
Node current = head, index = null, temp = null;
if (head == null) {
return;
}
else {
while (current != null) {
// temp node points to the previous node
temp = current;
// index node points to node next to current
index = current.next;
while (index != null) {
// checking if node of current data is
// equal to index node data
if (current.data == index.data) {
// duplicate node is skipped
temp.next = index.next;
}
else {
// temp node points to the previous
// node of index node
temp = index;
}
index = index.next;
}
current = current.next;
}
}
}
// creating print() to print all the data
// of nodes present in the list
public void print()
{
// Node current will point to head
Node current = head;
if (head == null) {
System.out.println(
"Empty list please insert some elements first");
return;
}
while (current != null) {
System.out.print(current.data + " ");
// incrementing pointer
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
singlyLinkedList List = new singlyLinkedList();
// Adding data to the list
List.add(9);
List.add(1);
List.add(1);
List.add(3);
List.add(4);
List.add(8);
List.add(2);
List.add(1);
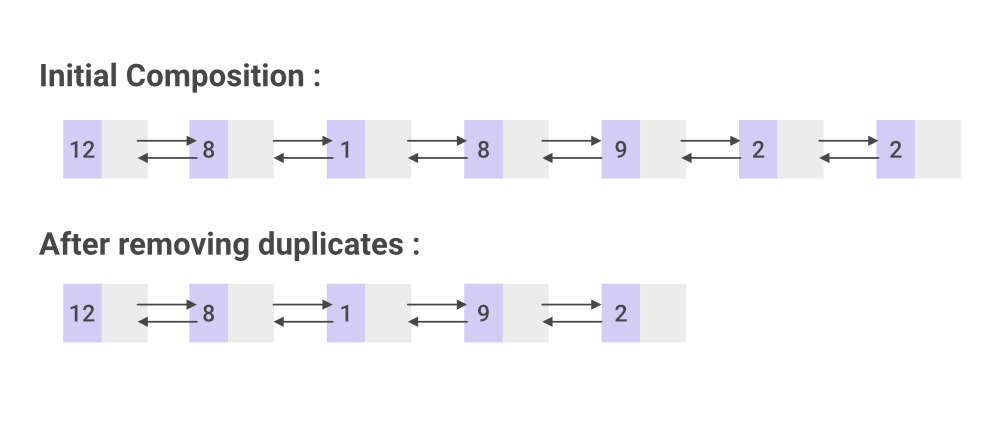
System.out.println("Initial composition : ");
List.print();
// removing duplicate nodes
List.removeDuplicates();
System.out.println("After removing duplicates : ");
List.print();
}
}
Producción
Initial composition : 9 1 1 3 4 8 2 1 After removing duplicates : 9 1 3 4 8 2
Complejidad del tiempo: O(N 2 )
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por dikshapatro y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA