Una array es una colección de elementos almacenados en ubicaciones de memoria contiguas. En este artículo, veremos cómo insertar un elemento en una array en Java .
Dada una array arr de tamaño n , este artículo explica cómo insertar un elemento x en esta array arr en una posición específica pos .
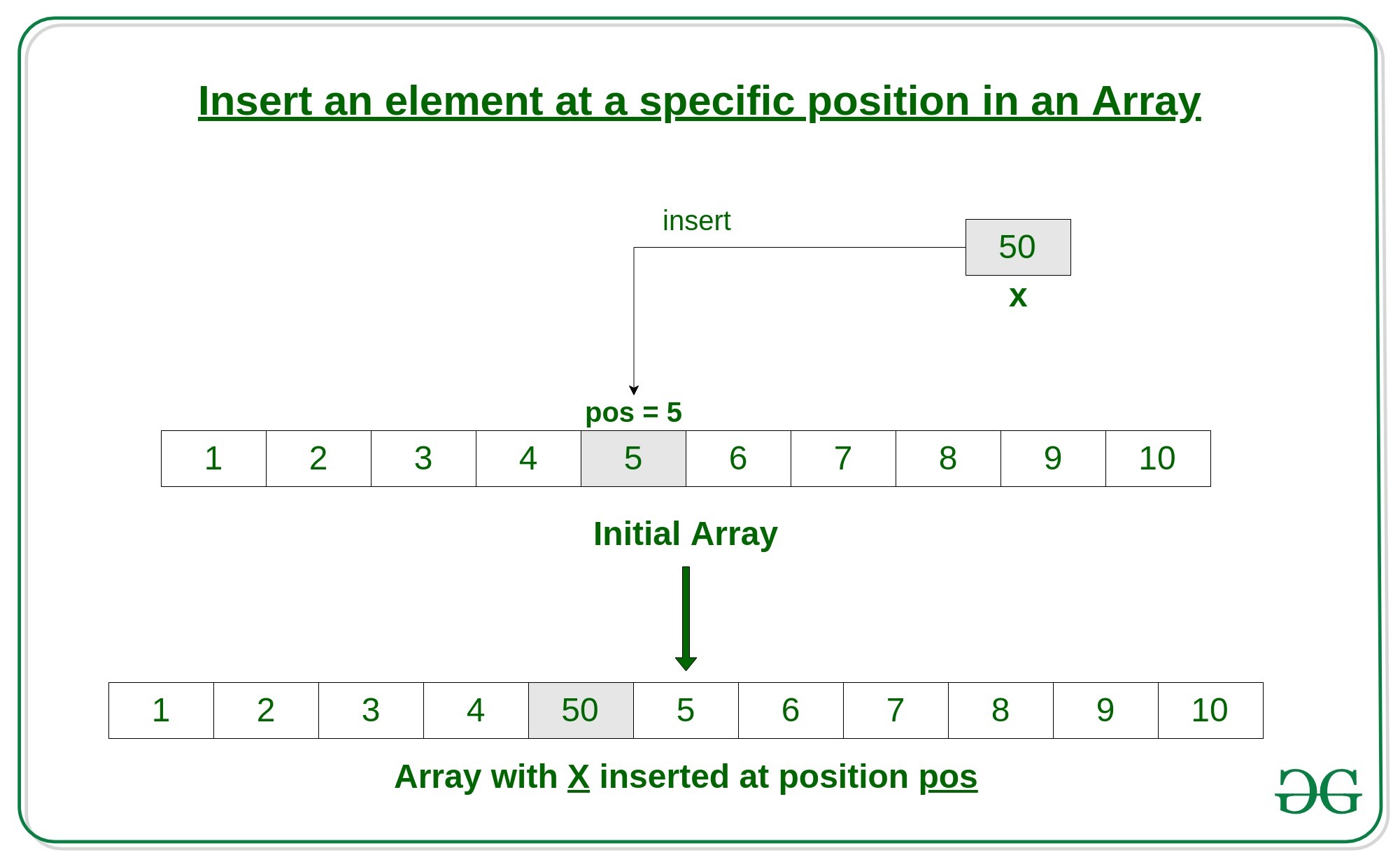
Enfoque 1:
aquí se explica cómo hacerlo.
- Primero obtenga el elemento que se insertará, digamos x
- Luego obtenga la posición en la que se insertará este elemento, digamos pos
- Cree una nueva array con un tamaño mayor que el tamaño anterior
- Copie todos los elementos de la array anterior en la nueva array hasta la posición pos.
- Inserte el elemento x en la posición pos
- Inserte el resto de los elementos de la array anterior en la nueva array después de la posición
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
Java
// Java Program to Insert an element
// at a specific position in an Array
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Function to insert x in arr at position pos
public static int[] insertX(int n, int arr[],
int x, int pos)
{
int i;
// create a new array of size n+1
int newarr[] = new int[n + 1];
// insert the elements from
// the old array into the new array
// insert all elements till pos
// then insert x at pos
// then insert rest of the elements
for (i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) {
if (i < pos - 1)
newarr[i] = arr[i];
else if (i == pos - 1)
newarr[i] = x;
else
newarr[i] = arr[i - 1];
}
return newarr;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 10;
int i;
// initial array of size 10
int arr[]
= { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
// print the original array
System.out.println("Initial Array:\n"
+ Arrays.toString(arr));
// element to be inserted
int x = 50;
// position at which element
// is to be inserted
int pos = 5;
// call the method to insert x
// in arr at position pos
arr = insertX(n, arr, x, pos);
// print the updated array
System.out.println("\nArray with " + x
+ " inserted at position "
+ pos + ":\n"
+ Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
Producción:
Initial Array: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] Array with 50 inserted at position 5: [1, 2, 3, 4, 50, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
Enfoque 2:
aquí se explica cómo hacerlo.
- Primero obtenga el elemento que se insertará, digamos elemento
- Luego obtenga la posición en la que se insertará este elemento, digamos position
- Convertir array a ArrayList
- Agregue el elemento en la posición usando list.add (posición, elemento)
- Convierta ArrayList de nuevo a array e imprima
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
Java
// Java Program to Insert an element
// at a specific position in an Array
// using ArrayList
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class AddElementAtPositionInArray {
// Method to add element at position
private static void addElement(
Integer[] arr, int element,
int position)
{
// Converting array to ArrayList
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(
Arrays.asList(arr));
// Adding the element at position
list.add(position - 1, element);
// Converting the list back to array
arr = list.toArray(arr);
// Printing the original array
System.out.println("Initial Array:\n"
+ Arrays.toString(arr));
// Printing the updated array
System.out.println("\nArray with " + element
+ " inserted at position "
+ position + ":\n"
+ Arrays.toString(arr));
}
// Drivers Method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Sample array
Integer[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,
6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
// Element to be inserted
int element = 50;
// Position to insert
int position = 5;
// Calling the function to insert
addElement(arr, element, position);
}
}
Producción:
Initial Array: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] Array with 50 inserted at position 5: [1, 2, 3, 4, 50, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]