A veces queremos subir un archivo a través de la ruta del archivo, pero pocas veces el archivo no existe. En ese caso, tenemos que responder a los usuarios que la ruta dada no encuentra ningún archivo o no existe en el archivo mencionado.
Enfoque 1: use el método ajax() de jQuery para verificar si un archivo existe en una URL determinada o no. El método ajax() se utiliza para activar la solicitud HTTP asíncrona. Si el archivo existe, el método ajax() a su vez llamará al método ajaxSuccess(), de lo contrario llamará a la función Error .
- Ejemplo: Este ejemplo ilustra el enfoque anterior.
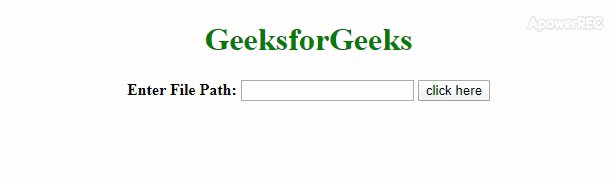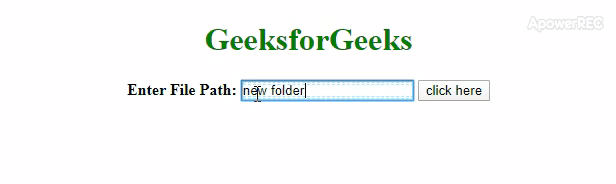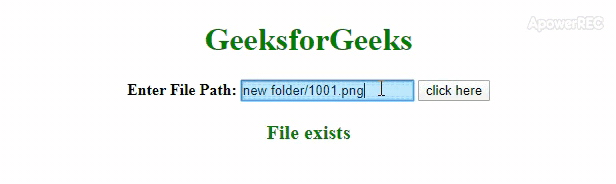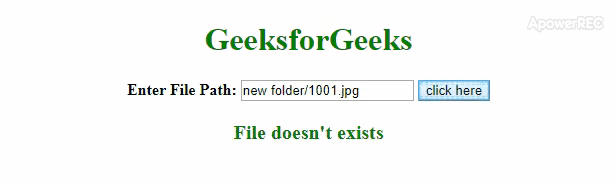
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><title>How to check if file exist using jquery</title><scriptsrc=</script><style>body {text-align: center;}h1 {color: green;}#output {color: green;font-size: 20px;font-weight: bold;}</style></head><body><h1>GeeksforGeeks</h1><labelid="File_Path"><b>Enter File Path:</b></label><inputtype="text"id="File_URL"><buttonid="Check_File">click here</button><pid="output"></p><script>$(document).ready(function() {$("#Check_File").click(function() {var url = $("#File_URL").val();if (url != "") {$.ajax({url: url,type: 'HEAD',error: function(){$("#output").text("File doesn't exists");},success: function(){$("#output").text('File exists');}});} else {$("#Output").text("Please enter File URL");}});});</script></body></html> - Producción:
Enfoque 2: utilice el método XMLHttpRequest() para activar la solicitud ajax. Si el estado HTTP es 200, el archivo existe; de lo contrario, el archivo no está presente.
- Ejemplo: Este ejemplo ilustra el enfoque anterior.
<!DOCTYPE HTML><html><head><title>How to check if file exist ornot on HTTP status is 200</title><style>body {text-align: center;}h1 {color: green;}#output {color: green;font-size: 20px;font-weight: bold;}</style></head><body><h1>GeeksforGeeks</h1><labelid="File_Path"><b>Enter File Path: </b></label><inputtype="text"id="File_URL"><buttonid="Check_File"onclick="checkFileExist()">click here</button><pid="output"></p><script>var url = document.getElementById("File_URL");var output = document.getElementById("output");var http = new XMLHttpRequest();function checkFileExist() {if (url.length === 0) {output.innerHTML = "Please enter File URL";} else {http.open('HEAD', url, false);http.send();if (http.status === 200) {output.innerHTML = "File exists";} else {output.innerHTML = "File doesn't exists";}}}</script></body></html> - Salida: el estado HTTP no es 200, por lo que si el archivo existe, mostrará que no existe hasta que el estado sea 200.

jQuery es una biblioteca JavaScript de código abierto que simplifica las interacciones entre un documento HTML/CSS. Es muy famosa por su filosofía de «Escribir menos, hacer más» .
Puede aprender jQuery desde cero siguiendo este tutorial de jQuery y ejemplos de jQuery .
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por priyankahiranandani y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA