Dado un árbol de búsqueda binario y una SUMA. La tarea es verificar si existe algún triplete (grupo de 3 elementos) en el BST dado con la SUMA dada.
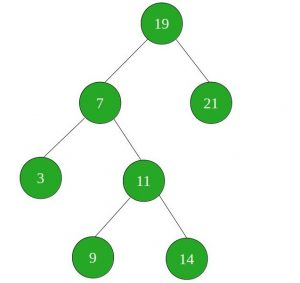
Ejemplos:
Input : SUM = 21 Output : YES There exists a triplet (7, 3, 11) in the above given BST with sum 21. Input : SUM = 101 Output : NO
Se sabe que los elementos en el recorrido en orden de BST se clasifican en orden creciente. Entonces, la idea es hacer un recorrido en orden en el BST dado y almacenar los elementos en un vector o array. Ahora la tarea se reduce a buscar un triplete con la suma dada en una array ordenada .
Ahora, para hacer esto, comience a recorrer la array y, para cada elemento A[i], busque un par con una suma (SUM – A[i]) en la array ordenada restante.
To do this:
1) Initialize two index variables to find the candidate
elements in the sorted array.
(a) Initialize first to the leftmost index: l = 0
(b) Initialize second the rightmost index: r = ar_size-1
2) Loop while l < r.
(a) If (A[l] + A[r] == sum) then return 1
(b) Else if( A[l] + A[r] < sum ) then l++
(c) Else r--
3) If no such candidates are found in the whole array,
return 0
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program to check if a triplet with
// given SUM exists in the BST or not
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
// A utility function to create a new BST node
struct Node* newNode(int item)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = item;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to do inorder traversal
// of the BST and store values in a vector
void inorder(Node* root, vector<int>& vec)
{
if (root != NULL) {
inorder(root->left, vec);
vec.push_back(root->key);
inorder(root->right, vec);
}
}
// A utility function to insert a new node
// with given key in BST
struct Node* insert(Node* node, int key)
{
/* If the tree is empty, return a new node */
if (node == NULL)
return newNode(key);
/* Otherwise, recur down the tree */
if (key < node->key)
node->left = insert(node->left, key);
else if (key > node->key)
node->right = insert(node->right, key);
/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */
return node;
}
// Function to check if a triplet with given SUM
// exists in the BST or not
bool checkForTriplet(Node* root, int sum)
{
// Vector to store the inorder traversal
// of the BST
vector<int> vec;
// Call inorder() to do the inorder
// on the BST and store it in vec
inorder(root, vec);
// Now, check if any triplet with given sum
// exists in the BST or not
int l, r;
// Now fix the first element one by one and find the
// other two elements
for (int i = 0; i < vec.size() - 2; i++) {
// To find the other two elements, start two index
// variables from two corners of the array and move
// them toward each other
l = i + 1; // index of the first element in the
// remaining elements
// index of the last element
r = vec.size() - 1;
while (l < r) {
if (vec[i] + vec[l] + vec[r] == sum) {
return true;
}
else if (vec[i] + vec[l] + vec[r] < sum)
l++;
else // vec[i] + vec[l] + vec[r] > sum
r--;
}
}
// If we reach here, then no triplet was found
return false;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
/* Let us create following BST
50
/ \
30 70
/ \ / \
20 40 60 80 */
struct Node* root = NULL;
root = insert(root, 50);
insert(root, 30);
insert(root, 20);
insert(root, 40);
insert(root, 70);
insert(root, 60);
insert(root, 80);
int sum = 120;
if (checkForTriplet(root, sum))
cout << "YES";
else
cout << "NO";
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to check if a triplet with
// given SUM exists in the BST or not
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static class Node
{
int key;
Node left, right;
};
// A utility function to
// create a new BST node
static Node newNode(int item)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = item;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to do inorder traversal
// of the BST and store values in a vector
static void inorder(Node root,
Vector<Integer> vec)
{
if (root != null)
{
inorder(root.left, vec);
vec.add(root.key);
inorder(root.right, vec);
}
}
// A utility function to insert a new node
// with given key in BST
static Node insert(Node node, int key)
{
/* If the tree is empty,
return a new node */
if (node == null)
return newNode(key);
/* Otherwise, recur down the tree */
if (key < node.key)
node.left = insert(node.left, key);
else if (key > node.key)
node.right = insert(node.right, key);
/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */
return node;
}
// Function to check if a triplet with
// given SUM exists in the BST or not
static boolean checkForTriplet(Node root, int sum)
{
// Vector to store the inorder traversal
// of the BST
Vector<Integer> vec = new Vector<Integer>();
// Call inorder() to do the inorder
// on the BST and store it in vec
inorder(root, vec);
// Now, check if any triplet with given sum
// exists in the BST or not
int l, r;
// Now fix the first element one by one
// and find the other two elements
for (int i = 0; i < vec.size() - 2; i++)
{
// To find the other two elements,
// start two index variables from two corners
// of the array and move them toward each other
l = i + 1; // index of the first element in the
// remaining elements
// index of the last element
r = vec.size() - 1;
while (l < r)
{
if (vec.get(i) +
vec.get(l) + vec.get(r) == sum)
{
return true;
}
else if (vec.get(i) +
vec.get(l) + vec.get(r) < sum)
l++;
else // vec[i] + vec[l] + vec[r] > sum
r--;
}
}
// If we reach here,
// then no triplet was found
return false;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* Let us create following BST
50
/ \
30 70
/ \ / \
20 40 60 80 */
Node root = null;
root = insert(root, 50);
insert(root, 30);
insert(root, 20);
insert(root, 40);
insert(root, 70);
insert(root, 60);
insert(root, 80);
int sum = 120;
if (checkForTriplet(root, sum))
System.out.print("YES");
else
System.out.print("NO");
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Python3
# Python3 program to check if a triplet with
# given SUM exists in the BST or not
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.right = self.left = None
# A utility function to insert a
# new node with given key in BST
def insert(root, x):
if root is None:
root = Node(x)
else:
if root.data < x:
if root.right is None:
root.right = Node(x)
else:
insert(root.right, x)
else:
if root.left is None:
root.left = Node(x)
else:
insert(root.left, x)
# A utility function to do inorder
# traversal of the BST and store
# values in an array
def inorder(root, ior):
if root is None:
return
inorder(root.left, ior)
ior.append(root.data)
inorder(root.right, ior)
# Function to check if a triplet with
# given SUM exists in the BST or not
def checkForTriplet(root, sum):
# Initialize an empty array
vec = [0]
# Call to function inorder to
# store values in array
inorder(root, vec)
# Traverse the array and find
# triplet with sum
for i in range(0, len(vec) - 2, 1):
l = i + 1
# Index of the last element
r = len(vec) - 1
while(l < r):
if vec[i] + vec[l] + vec[r] == sum:
return True
elif vec[i] + vec[l] + vec[r] < sum:
l += 1
else: # vec[i] + vec[l] + vec[r] > sum
r -= 1
# If we reach here, then
# no triplet was found
return False
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
""" Let us create following BST
50
/ \
30 70
/ \ / \
20 40 60 80
"""
root = Node(50)
insert(root, 30)
insert(root, 20)
insert(root, 40)
insert(root, 70)
insert(root, 60)
insert(root, 80)
sum = 120
if (checkForTriplet(root, sum)):
print("YES")
else:
print("NO")
# This code is contributed by MRINALWALIA
C#
// C# program to check if a triplet with
// given SUM exists in the BST or not
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
class Node
{
public int key;
public Node left, right;
};
// A utility function to
// create a new BST node
static Node newNode(int item)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = item;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to do inorder traversal
// of the BST and store values in a vector
static void inorder(Node root,
List<int> vec)
{
if (root != null)
{
inorder(root.left, vec);
vec.Add(root.key);
inorder(root.right, vec);
}
}
// A utility function to insert a new node
// with given key in BST
static Node insert(Node node, int key)
{
/* If the tree is empty,
return a new node */
if (node == null)
return newNode(key);
/* Otherwise, recur down the tree */
if (key < node.key)
node.left = insert(node.left, key);
else if (key > node.key)
node.right = insert(node.right, key);
/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */
return node;
}
// Function to check if a triplet with
// given SUM exists in the BST or not
static bool checkForTriplet(Node root, int sum)
{
// List to store the inorder traversal
// of the BST
List<int> vec = new List<int>();
// Call inorder() to do the inorder
// on the BST and store it in vec
inorder(root, vec);
// Now, check if any triplet with given sum
// exists in the BST or not
int l, r;
// Now fix the first element one by one
// and find the other two elements
for (int i = 0; i < vec.Count - 2; i++)
{
// To find the other two elements,
// start two index variables from two corners
// of the array and move them toward each other
l = i + 1; // index of the first element in the
// remaining elements
// index of the last element
r = vec.Count - 1;
while (l < r)
{
if (vec[i] +
vec[l] + vec[r] == sum)
{
return true;
}
else if (vec[i] +
vec[l] + vec[r] < sum)
l++;
else // vec[i] + vec[l] + vec[r] > sum
r--;
}
}
// If we reach here,
// then no triplet was found
return false;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
/* Let us create following BST
50
/ \
30 70
/ \ / \
20 40 60 80 */
Node root = null;
root = insert(root, 50);
insert(root, 30);
insert(root, 20);
insert(root, 40);
insert(root, 70);
insert(root, 60);
insert(root, 80);
int sum = 120;
if (checkForTriplet(root, sum))
Console.Write("YES");
else
Console.Write("NO");
}
}
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program to check if a triplet with
// given SUM exists in the BST or not
class Node
{
constructor()
{
this.key = 0;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
};
// A utility function to
// create a new BST node
function newNode(item)
{
var temp = new Node();
temp.key = item;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to do inorder traversal
// of the BST and store values in a vector
function inorder(root, vec)
{
if (root != null)
{
inorder(root.left, vec);
vec.push(root.key);
inorder(root.right, vec);
}
}
// A utility function to insert a new node
// with given key in BST
function insert(node, key)
{
/* If the tree is empty,
return a new node */
if (node == null)
return newNode(key);
/* Otherwise, recur down the tree */
if (key < node.key)
node.left = insert(node.left, key);
else if (key > node.key)
node.right = insert(node.right, key);
/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */
return node;
}
// Function to check if a triplet with
// given SUM exists in the BST or not
function checkForTriplet(root, sum)
{
// List to store the inorder traversal
// of the BST
var vec = [];
// Call inorder() to do the inorder
// on the BST and store it in vec
inorder(root, vec);
// Now, check if any triplet with given sum
// exists in the BST or not
var l, r;
// Now fix the first element one by one
// and find the other two elements
for (var i = 0; i < vec.length - 2; i++)
{
// To find the other two elements,
// start two index variables from two corners
// of the array and move them toward each other
l = i + 1; // index of the first element in the
// remaining elements
// index of the last element
r = vec.length - 1;
while (l < r)
{
if (vec[i] +
vec[l] + vec[r] == sum)
{
return true;
}
else if (vec[i] +
vec[l] + vec[r] < sum)
l++;
else // vec[i] + vec[l] + vec[r] > sum
r--;
}
}
// If we reach here,
// then no triplet was found
return false;
}
// Driver Code
/* Let us create following BST
50
/ \
30 70
/ \ / \
20 40 60 80 */
var root = null;
root = insert(root, 50);
insert(root, 30);
insert(root, 20);
insert(root, 40);
insert(root, 70);
insert(root, 60);
insert(root, 80);
var sum = 120;
if (checkForTriplet(root, sum))
document.write("YES");
else
document.write("NO");
// This code is contributed by itsok.
</script>
YES
Complejidad de tiempo : O(N 2 ), ya que estamos usando bucles anidados, el bucle exterior atraviesa N veces y el bucle interior atraviesa N veces en el peor de los casos.
Espacio auxiliar : O(N), donde N es el número de Nodes en el BST dado. (ya que estamos usando espacio extra para el árbol)