Dado un árbol de búsqueda binario y una subsecuencia ordenada. la tarea es verificar si la subsecuencia ordenada dada existe en el árbol de búsqueda binaria o no.
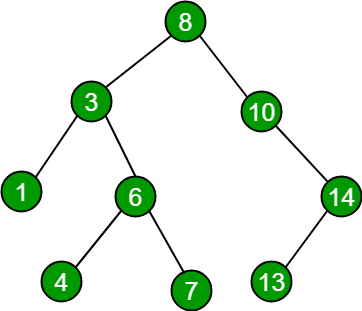
Ejemplos:
// For above binary search tree
Input : seq[] = {4, 6, 8, 14}
Output: "Yes"
Input : seq[] = {4, 6, 8, 12, 13}
Output: "No"
Una solución simple es almacenar el recorrido en orden en una array auxiliar y luego, al hacer coincidir los elementos de la subsecuencia ordenada uno por uno con el recorrido en orden del árbol, podemos saber si la subsecuencia existe en BST o no. La complejidad del tiempo para este enfoque será O(n), pero requiere espacio adicional O(n) para almacenar el recorrido en una array.
Una solución eficiente es hacer coincidir los elementos de la subsecuencia mientras atravesamos BST en orden . Tomamos el índice como un iterador para la subsecuencia ordenada dada y comenzamos el recorrido en orden de bst dado, si el Node actual coincide con seq [índice] , luego movemos el índiceen dirección hacia adelante incrementando 1 y después de atravesar completamente BST si index==n eso significa que todos los elementos de la subsecuencia dada han sido emparejados y existen como una subsecuencia ordenada en BST dada.
C++
// C++ program to find if given array exists as a
// subsequence in BST
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// A binary Tree node
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
// A utility function to create a new BST node
// with key as given num
struct Node* newNode(int num)
{
struct Node* temp = new Node;
temp->data = num;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to insert a given key to BST
struct Node* insert(struct Node* root, int key)
{
if (root == NULL)
return newNode(key);
if (root->data > key)
root->left = insert(root->left, key);
else
root->right = insert(root->right, key);
return root;
}
// function to check if given sorted sub-sequence exist in BST
// index --> iterator for given sorted sub-sequence
// seq[] --> given sorted sub-sequence
void seqExistUtil(struct Node *ptr, int seq[], int &index)
{
if (ptr == NULL)
return;
// We traverse left subtree first in Inorder
seqExistUtil(ptr->left, seq, index);
// If current node matches with se[index] then move
// forward in sub-sequence
if (ptr->data == seq[index])
index++;
// We traverse left subtree in the end in Inorder
seqExistUtil(ptr->right, seq, index);
}
// A wrapper over seqExistUtil. It returns true
// if seq[0..n-1] exists in tree.
bool seqExist(struct Node *root, int seq[], int n)
{
// Initialize index in seq[]
int index = 0;
// Do an inorder traversal and find if all
// elements of seq[] were present
seqExistUtil(root, seq, index);
// index would become n if all elements of
// seq[] were present
return (index == n);
}
// driver program to run the case
int main()
{
struct Node* root = NULL;
root = insert(root, 8);
root = insert(root, 10);
root = insert(root, 3);
root = insert(root, 6);
root = insert(root, 1);
root = insert(root, 4);
root = insert(root, 7);
root = insert(root, 14);
root = insert(root, 13);
int seq[] = {4, 6, 8, 14};
int n = sizeof(seq)/sizeof(seq[0]);
seqExist(root, seq, n)? cout << "Yes" :
cout << "No";
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to find if given array
// exists as a subsequence in BST
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// A binary Tree node
static class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
};
//structure of int class
static class INT
{
int a;
}
// A utility function to create a new BST node
// with key as given num
static Node newNode(int num)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = num;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to insert a given key to BST
static Node insert( Node root, int key)
{
if (root == null)
return newNode(key);
if (root.data > key)
root.left = insert(root.left, key);
else
root.right = insert(root.right, key);
return root;
}
// function to check if given sorted
// sub-sequence exist in BST index -.
// iterator for given sorted sub-sequence
// seq[] -. given sorted sub-sequence
static void seqExistUtil( Node ptr, int seq[], INT index)
{
if (ptr == null)
return;
// We traverse left subtree
// first in Inorder
seqExistUtil(ptr.left, seq, index);
// If current node matches
// with se[index] then move
// forward in sub-sequence
if (ptr.data == seq[index.a])
index.a++;
// We traverse left subtree
// in the end in Inorder
seqExistUtil(ptr.right, seq, index);
}
// A wrapper over seqExistUtil.
// It returns true if seq[0..n-1]
// exists in tree.
static boolean seqExist( Node root, int seq[], int n)
{
// Initialize index in seq[]
INT index = new INT();
index.a = 0;
// Do an inorder traversal and find if all
// elements of seq[] were present
seqExistUtil(root, seq, index);
// index would become n if all
// elements of seq[] were present
return (index.a == n);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node root = null;
root = insert(root, 8);
root = insert(root, 10);
root = insert(root, 3);
root = insert(root, 6);
root = insert(root, 1);
root = insert(root, 4);
root = insert(root, 7);
root = insert(root, 14);
root = insert(root, 13);
int seq[] = {4, 6, 8, 14};
int n = seq.length;
if(seqExist(root, seq, n))
System.out.println("Yes");
else
System.out.println("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu
Python3
# Python3 program to find if given array
# exists as a subsequence in BST
class Node:
# Constructor to create a new node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
# A utility function to insert a
# given key to BST
def insert(root, key):
if root == None:
return Node(key)
if root.data > key:
root.left = insert(root.left, key)
else:
root.right = insert(root.right, key)
return root
# function to check if given sorted
# sub-sequence exist in BST index .
# iterator for given sorted sub-sequence
# seq[] . given sorted sub-sequence
def seqExistUtil(ptr, seq, index):
if ptr == None:
return
# We traverse left subtree
# first in Inorder
seqExistUtil(ptr.left, seq, index)
# If current node matches with se[index[0]]
# then move forward in sub-sequence
if ptr.data == seq[index[0]]:
index[0] += 1
# We traverse left subtree in
# the end in Inorder
seqExistUtil(ptr.right, seq, index)
# A wrapper over seqExistUtil. It returns
# true if seq[0..n-1] exists in tree.
def seqExist(root, seq, n):
# Initialize index in seq[]
index = [0]
# Do an inorder traversal and find if
# all elements of seq[] were present
seqExistUtil(root, seq, index)
# index would become n if all elements
# of seq[] were present
if index[0] == n:
return True
else:
return False
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = None
root = insert(root, 8)
root = insert(root, 10)
root = insert(root, 3)
root = insert(root, 6)
root = insert(root, 1)
root = insert(root, 4)
root = insert(root, 7)
root = insert(root, 14)
root = insert(root, 13)
seq = [4, 6, 8, 14]
n = len(seq)
if seqExist(root, seq, n):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
# This code is contributed by PranchalK
C#
// C# program to find if given array
// exists as a subsequence in BST
using System;
class GFG
{
// A binary Tree node
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
};
// structure of int class
public class INT
{
public int a;
}
// A utility function to create a new BST node
// with key as given num
static Node newNode(int num)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = num;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to insert a given key to BST
static Node insert( Node root, int key)
{
if (root == null)
return newNode(key);
if (root.data > key)
root.left = insert(root.left, key);
else
root.right = insert(root.right, key);
return root;
}
// function to check if given sorted
// sub-sequence exist in BST index -.
// iterator for given sorted sub-sequence
// seq[] -. given sorted sub-sequence
static void seqExistUtil( Node ptr, int []seq, INT index)
{
if (ptr == null)
return;
// We traverse left subtree
// first in Inorder
seqExistUtil(ptr.left, seq, index);
// If current node matches
// with se[index] then move
// forward in sub-sequence
if (ptr.data == seq[index.a])
index.a++;
// We traverse left subtree
// in the end in Inorder
seqExistUtil(ptr.right, seq, index);
}
// A wrapper over seqExistUtil.
// It returns true if seq[0..n-1]
// exists in tree.
static bool seqExist( Node root, int []seq, int n)
{
// Initialize index in seq[]
INT index = new INT();
index.a = 0;
// Do an inorder traversal and find if all
// elements of seq[] were present
seqExistUtil(root, seq, index);
// index would become n if all
// elements of seq[] were present
return (index.a == n);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
Node root = null;
root = insert(root, 8);
root = insert(root, 10);
root = insert(root, 3);
root = insert(root, 6);
root = insert(root, 1);
root = insert(root, 4);
root = insert(root, 7);
root = insert(root, 14);
root = insert(root, 13);
int []seq = {4, 6, 8, 14};
int n = seq.Length;
if(seqExist(root, seq, n))
Console.WriteLine("Yes");
else
Console.WriteLine("No");
}
}
/* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program to find if given array
// exists as a subsequence in BST
// A binary Tree node
class Node
{
constructor()
{
this.data = 0;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
};
// structure of int class
class INT
{
constructor()
{
this.a = 0;
}
}
// A utility function to create a new BST node
// with key as given num
function newNode(num)
{
var temp = new Node();
temp.data = num;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to insert a given key to BST
function insert( root, key)
{
if (root == null)
return newNode(key);
if (root.data > key)
root.left = insert(root.left, key);
else
root.right = insert(root.right, key);
return root;
}
// function to check if given sorted
// sub-sequence exist in BST index -.
// iterator for given sorted sub-sequence
// seq[] -. given sorted sub-sequence
function seqExistUtil( ptr, seq, index)
{
if (ptr == null)
return;
// We traverse left subtree
// first in Inorder
seqExistUtil(ptr.left, seq, index);
// If current node matches
// with se[index] then move
// forward in sub-sequence
if (ptr.data == seq[index.a])
index.a++;
// We traverse left subtree
// in the end in Inorder
seqExistUtil(ptr.right, seq, index);
}
// A wrapper over seqExistUtil.
// It returns true if seq[0..n-1]
// exists in tree.
function seqExist( root, seq, n)
{
// Initialize index in seq[]
var index = new INT();
index.a = 0;
// Do an inorder traversal and find if all
// elements of seq[] were present
seqExistUtil(root, seq, index);
// index would become n if all
// elements of seq[] were present
return (index.a == n);
}
// Driver code
var root = null;
root = insert(root, 8);
root = insert(root, 10);
root = insert(root, 3);
root = insert(root, 6);
root = insert(root, 1);
root = insert(root, 4);
root = insert(root, 7);
root = insert(root, 14);
root = insert(root, 13);
var seq = [4, 6, 8, 14];
var n = seq.length;
if(seqExist(root, seq, n))
document.write("Yes");
else
document.write("No");
</script>
Producción:
Yes
Complejidad temporal: O(n)
Espacio auxiliar : O (n) para la pila de llamadas desde que se usa la recursividad, donde n es el número total de Nodes en BST
Este artículo es una contribución de Shashank Mishra (Gullu) . Si te gusta GeeksforGeeks y te gustaría contribuir, también puedes escribir un artículo usando write.geeksforgeeks.org o enviar tu artículo por correo a review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA