Dado un grafo no dirigido y una arista, la tarea es encontrar si la arista dada es un puente en el gráfico, es decir, quitar la arista desconecta el gráfico.
A continuación se muestran algunos gráficos de ejemplo con puentes resaltados en color rojo.

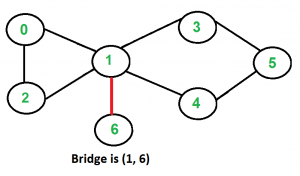
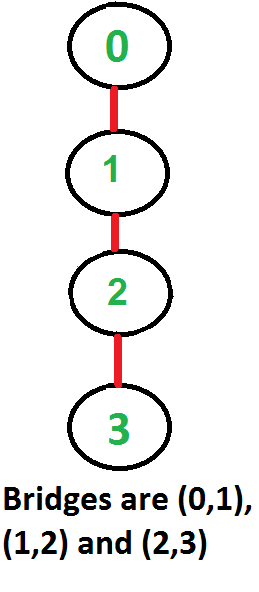
Una solución es encontrar todos los puentes en el gráfico dado y luego verificar si el borde dado es un puente o no.
Una solución más simple es eliminar el borde, verificar si el gráfico permanece conectado después de la eliminación o no, finalmente agregar el borde nuevamente. Siempre podemos encontrar si un no dirigido está conectado o no encontrando todos los vértices alcanzables desde cualquier vértice. Si el número de vértices alcanzables es igual al número de vértices en el gráfico, entonces el gráfico no está conectado. Podemos encontrar todos los vértices alcanzables usando BFS o DFS. A continuación se muestran los pasos completos.
- Eliminar el borde dado
- Encuentra todos los vértices alcanzables desde cualquier vértice. Hemos elegido el primer vértice en la siguiente implementación.
- Si el recuento de Nodes accesibles es V, devuelve falso [dado que no es Bridge]. De lo contrario volver sí.
Implementación:
C++
// C++ program to check if removing an
// edge disconnects a graph or not.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Graph class represents a directed graph
// using adjacency list representation
class Graph
{
int V; // No. of vertices
list<int> *adj;
void DFS(int v, bool visited[]);
public:
Graph(int V); // Constructor
// function to add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int v, int w);
// Returns true if graph is connected
bool isConnected();
bool isBridge(int u, int v);
};
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list<int>[V];
}
void Graph::addEdge(int u, int v)
{
adj[u].push_back(v); // Add w to v’s list.
adj[v].push_back(u); // Add w to v’s list.
}
void Graph::DFS(int v, bool visited[])
{
// Mark the current node as visited and print it
visited[v] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to
// this vertex
list<int>::iterator i;
for (i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i)
if (!visited[*i])
DFS(*i, visited);
}
// Returns true if given graph is connected, else false
bool Graph::isConnected()
{
bool visited[V];
memset(visited, false, sizeof(visited));
// Find all reachable vertices from first vertex
DFS(0, visited);
// If set of reachable vertices includes all,
// return true.
for (int i=1; i<V; i++)
if (visited[i] == false)
return false;
return true;
}
// This function assumes that edge (u, v)
// exists in graph or not,
bool Graph::isBridge(int u, int v)
{
// Remove edge from undirected graph
adj[u].remove(v);
adj[v].remove(u);
bool res = isConnected();
// Adding the edge back
addEdge(u, v);
// Return true if graph becomes disconnected
// after removing the edge.
return (res == false);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Create a graph given in the above diagram
Graph g(4);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.isBridge(1, 2)? cout << "Yes" : cout << "No";
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to check if removing an
// edge disconnects a graph or not.
import java.util.*;
// Graph class represents a directed graph
// using adjacency list representation
class Graph {
int V; // No. of vertices
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > adj;
private void DFS(int v, boolean[] visited)
{
// Mark the current node as visited and print it
visited[v] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to
// this vertex
for (Integer i : adj.get(v)) {
if (!visited[i]) {
DFS(i, visited);
}
}
}
public Graph(int V)
{
this.V = V;
adj = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
}
public void addEdge(int u, int v)
{
adj.get(u).add(v); // Add v to u’s list.
adj.get(v).add(u); // Add u to v’s list.
}
// Returns true if given graph is connected, else false
public boolean isConnected()
{
boolean[] visited = new boolean[V];
// Find all reachable vertices from first vertex
DFS(0, visited);
// If set of reachable vertices includes all,
// return true.
for (int i = 1; i < V; i++)
if (visited[i] == false)
return false;
return true;
}
// This function assumes that edge (u, v)
// exists in graph or not,
public boolean isBridge(int u, int v)
{
// Remove edge from undirected graph
adj.get(u).remove(Integer.valueOf(v));
adj.get(v).remove(Integer.valueOf(u));
boolean res = isConnected();
// Adding the edge back
addEdge(u, v);
// Return true if graph becomes disconnected
// after removing the edge.
return (res == false);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Graph g = new Graph(4);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
if (g.isBridge(1, 2)) {
System.out.println("Yes");
}
else {
System.out.println("No");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Karandeep Singh
Python3
# Python3 program to check if removing
# an edge disconnects a graph or not.
# Graph class represents a directed graph
# using adjacency list representation
class Graph:
def __init__(self, V):
self.V = V
self.adj = [[] for i in range(V)]
def addEdge(self, u, v):
self.adj[u].append(v) # Add w to v’s list.
self.adj[v].append(u) # Add w to v’s list.
def DFS(self, v, visited):
# Mark the current node as
# visited and print it
visited[v] = True
# Recur for all the vertices
# adjacent to this vertex
i = 0
while i != len(self.adj[v]):
if (not visited[self.adj[v][i]]):
self.DFS(self.adj[v][i], visited)
i += 1
# Returns true if given graph is
# connected, else false
def isConnected(self):
visited = [False] * self.V
# Find all reachable vertices
# from first vertex
self.DFS(0, visited)
# If set of reachable vertices
# includes all, return true.
for i in range(1, self.V):
if (visited[i] == False):
return False
return True
# This function assumes that edge
# (u, v) exists in graph or not,
def isBridge(self, u, v):
# Remove edge from undirected graph
indU = self.adj[v].index(u)
indV = self.adj[u].index(v)
del self.adj[u][indV]
del self.adj[v][indU]
res = self.isConnected()
# Adding the edge back
self.addEdge(u, v)
# Return true if graph becomes
# disconnected after removing
# the edge.
return (res == False)
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Create a graph given in the
# above diagram
g = Graph(4)
g.addEdge(0, 1)
g.addEdge(1, 2)
g.addEdge(2, 3)
if g.isBridge(1, 2):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
# This code is contributed by PranchalK
Yes
Tiempo Complejidad : O(V + E)
Este artículo es una contribución de Pankaj Sharma . Si le gusta GeeksforGeeks y le gustaría contribuir, también puede escribir un artículo y enviarlo por correo a review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA