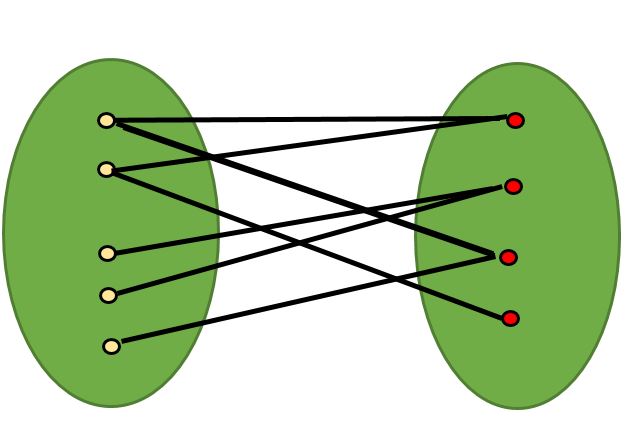
Un gráfico bipartito es un gráfico cuyos vértices se pueden dividir en dos conjuntos independientes, U y V, de modo que cada arista (u, v) conecta un vértice de U a V o un vértice de V a U. En otras palabras, para cada arista (u, v), u pertenece a U y v a V, o u pertenece a V y v a U. También podemos decir que no hay arista que conecte vértices del mismo conjunto.
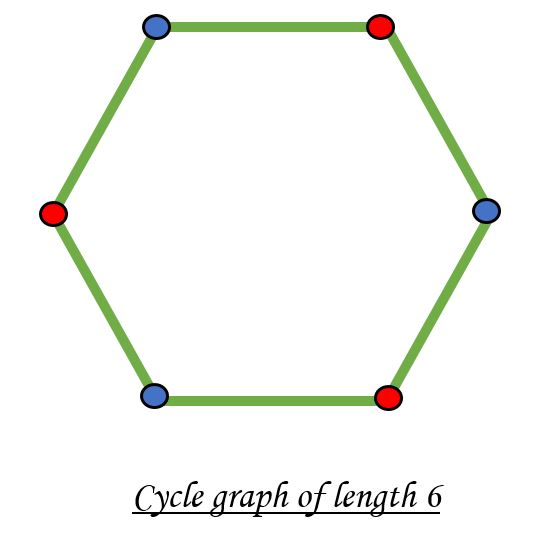
Un gráfico bipartito es posible si la coloración del gráfico es posible utilizando dos colores, de modo que los vértices de un conjunto estén coloreados con el mismo color. Tenga en cuenta que es posible colorear un gráfico de ciclo con un ciclo par usando dos colores. Por ejemplo, vea el siguiente gráfico.
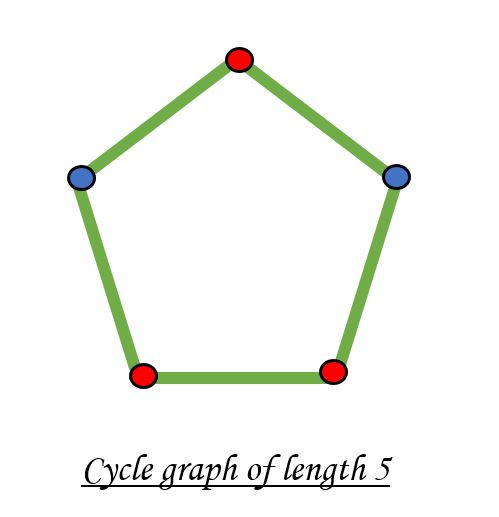
No es posible colorear un gráfico de ciclo con ciclo impar utilizando dos colores.
Algoritmo para verificar si un gráfico es bipartito:
un enfoque es verificar si el gráfico es de 2 colores o no utilizando el algoritmo de retroceso en el problema de coloración .
A continuación, se muestra un algoritmo simple para averiguar si un gráfico dado es bipartito o no mediante Breadth First Search (BFS).
1. Asigne el color ROJO al vértice de origen (colocándolo en el conjunto U).
2. Colorea a todos los vecinos de color AZUL (poniéndolos en el conjunto V).
3. Colorea a todos los vecinos de los vecinos con el color ROJO (colocándolos en el conjunto U).
4. De esta manera, asigne color a todos los vértices de manera que satisfaga todas las restricciones del problema de coloración de m vías donde m = 2.
5. Al asignar colores, si encontramos un vecino que tiene el mismo color que el vértice actual, entonces el gráfico no se puede colorear con 2 vértices (o el gráfico no es bipartito)
C++
// C++ program to find out whether a
// given graph is Bipartite or not
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#define V 4
using namespace std;
// This function returns true if graph
// G[V][V] is Bipartite, else false
bool isBipartite(int G[][V], int src)
{
// Create a color array to store colors
// assigned to all vertices. Vertex
// number is used as index in this array.
// The value '-1' of colorArr[i]
// is used to indicate that no color
// is assigned to vertex 'i'. The value 1
// is used to indicate first color
// is assigned and value 0 indicates
// second color is assigned.
int colorArr[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
colorArr[i] = -1;
// Assign first color to source
colorArr[src] = 1;
// Create a queue (FIFO) of vertex
// numbers and enqueue source vertex
// for BFS traversal
queue <int> q;
q.push(src);
// Run while there are vertices
// in queue (Similar to BFS)
while (!q.empty())
{
// Dequeue a vertex from queue ( Refer http://goo.gl/35oz8 )
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
// Return false if there is a self-loop
if (G[u][u] == 1)
return false;
// Find all non-colored adjacent vertices
for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v)
{
// An edge from u to v exists and
// destination v is not colored
if (G[u][v] && colorArr[v] == -1)
{
// Assign alternate color to this adjacent v of u
colorArr[v] = 1 - colorArr[u];
q.push(v);
}
// An edge from u to v exists and destination
// v is colored with same color as u
else if (G[u][v] && colorArr[v] == colorArr[u])
return false;
}
}
// If we reach here, then all adjacent
// vertices can be colored with alternate color
return true;
}
// Driver program to test above function
int main()
{
int G[][V] = {{0, 1, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 0}
};
isBipartite(G, 0) ? cout << "Yes" : cout << "No";
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to find out whether
// a given graph is Bipartite or not
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class Bipartite
{
final static int V = 4; // No. of Vertices
// This function returns true if
// graph G[V][V] is Bipartite, else false
boolean isBipartite(int G[][],int src)
{
// Create a color array to store
// colors assigned to all vertices.
// Vertex number is used as index
// in this array. The value '-1'
// of colorArr[i] is used to indicate
// that no color is assigned
// to vertex 'i'. The value 1 is
// used to indicate first color
// is assigned and value 0 indicates
// second color is assigned.
int colorArr[] = new int[V];
for (int i=0; i<V; ++i)
colorArr[i] = -1;
// Assign first color to source
colorArr[src] = 1;
// Create a queue (FIFO) of vertex numbers
// and enqueue source vertex for BFS traversal
LinkedList<Integer>q = new LinkedList<Integer>();
q.add(src);
// Run while there are vertices in queue (Similar to BFS)
while (q.size() != 0)
{
// Dequeue a vertex from queue
int u = q.poll();
// Return false if there is a self-loop
if (G[u][u] == 1)
return false;
// Find all non-colored adjacent vertices
for (int v=0; v<V; ++v)
{
// An edge from u to v exists
// and destination v is not colored
if (G[u][v]==1 && colorArr[v]==-1)
{
// Assign alternate color to this adjacent v of u
colorArr[v] = 1-colorArr[u];
q.add(v);
}
// An edge from u to v exists and destination
// v is colored with same color as u
else if (G[u][v]==1 && colorArr[v]==colorArr[u])
return false;
}
}
// If we reach here, then all adjacent vertices can
// be colored with alternate color
return true;
}
// Driver program to test above function
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int G[][] = {{0, 1, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 0}
};
Bipartite b = new Bipartite();
if (b.isBipartite(G, 0))
System.out.println("Yes");
else
System.out.println("No");
}
}
// Contributed by Aakash Hasija
Python3
# Python program to find out whether a
# given graph is Bipartite or not
class Graph():
def __init__(self, V):
self.V = V
self.graph = [[0 for column in range(V)] \
for row in range(V)]
# This function returns true if graph G[V][V]
# is Bipartite, else false
def isBipartite(self, src):
# Create a color array to store colors
# assigned to all vertices. Vertex
# number is used as index in this array.
# The value '-1' of colorArr[i] is used to
# indicate that no color is assigned to
# vertex 'i'. The value 1 is used to indicate
# first color is assigned and value 0
# indicates second color is assigned.
colorArr = [-1] * self.V
# Assign first color to source
colorArr[src] = 1
# Create a queue (FIFO) of vertex numbers and
# enqueue source vertex for BFS traversal
queue = []
queue.append(src)
# Run while there are vertices in queue
# (Similar to BFS)
while queue:
u = queue.pop()
# Return false if there is a self-loop
if self.graph[u][u] == 1:
return False;
for v in range(self.V):
# An edge from u to v exists and destination
# v is not colored
if self.graph[u][v] == 1 and colorArr[v] == -1:
# Assign alternate color to this
# adjacent v of u
colorArr[v] = 1 - colorArr[u]
queue.append(v)
# An edge from u to v exists and destination
# v is colored with same color as u
elif self.graph[u][v] == 1 and colorArr[v] == colorArr[u]:
return False
# If we reach here, then all adjacent
# vertices can be colored with alternate
# color
return True
# Driver program to test above function
g = Graph(4)
g.graph = [[0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0]
]
print ("Yes" if g.isBipartite(0) else "No")
# This code is contributed by Divyanshu Mehta
C#
// C# program to find out whether
// a given graph is Bipartite or not
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
readonly static int V = 4; // No. of Vertices
// This function returns true if
// graph G[V,V] is Bipartite, else false
bool isBipartite(int [,]G, int src)
{
// Create a color array to store
// colors assigned to all vertices.
// Vertex number is used as index
// in this array. The value '-1'
// of colorArr[i] is used to indicate
// that no color is assigned
// to vertex 'i'. The value 1 is
// used to indicate first color
// is assigned and value 0 indicates
// second color is assigned.
int []colorArr = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
colorArr[i] = -1;
// Assign first color to source
colorArr[src] = 1;
// Create a queue (FIFO) of vertex numbers
// and enqueue source vertex for BFS traversal
List<int>q = new List<int>();
q.Add(src);
// Run while there are vertices
// in queue (Similar to BFS)
while (q.Count != 0)
{
// Dequeue a vertex from queue
int u = q[0];
q.RemoveAt(0);
// Return false if there is a self-loop
if (G[u, u] == 1)
return false;
// Find all non-colored adjacent vertices
for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v)
{
// An edge from u to v exists
// and destination v is not colored
if (G[u, v] == 1 && colorArr[v] == -1)
{
// Assign alternate color
// to this adjacent v of u
colorArr[v] = 1 - colorArr[u];
q.Add(v);
}
// An edge from u to v exists and
// destination v is colored with
// same color as u
else if (G[u, v] == 1 &&
colorArr[v] == colorArr[u])
return false;
}
}
// If we reach here, then all adjacent vertices
// can be colored with alternate color
return true;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int [,]G = {{0, 1, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 0}};
GFG b = new GFG();
if (b.isBipartite(G, 0))
Console.WriteLine("Yes");
else
Console.WriteLine("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program to find out whether
// a given graph is Bipartite or not
let V = 4; // No. of Vertices
// This function returns true if
// graph G[V][V] is Bipartite, else false
function isBipartite(G,src)
{
// Create a color array to store
// colors assigned to all vertices.
// Vertex number is used as index
// in this array. The value '-1'
// of colorArr[i] is used to indicate
// that no color is assigned
// to vertex 'i'. The value 1 is
// used to indicate first color
// is assigned and value 0 indicates
// second color is assigned.
let colorArr = new Array(V);
for (let i=0; i<V; ++i)
colorArr[i] = -1;
// Assign first color to source
colorArr[src] = 1;
// Create a queue (FIFO) of vertex numbers
// and enqueue source vertex for BFS traversal
let q = [];
q.push(src);
// Run while there are vertices in queue (Similar to BFS)
while (q.length != 0)
{
// Dequeue a vertex from queue
let u = q.shift();
// Return false if there is a self-loop
if (G[u][u] == 1)
return false;
// Find all non-colored adjacent vertices
for (let v=0; v<V; ++v)
{
// An edge from u to v exists
// and destination v is not colored
if (G[u][v]==1 && colorArr[v]==-1)
{
// Assign alternate color to this adjacent v of u
colorArr[v] = 1-colorArr[u];
q.push(v);
}
// An edge from u to v exists and destination
// v is colored with same color as u
else if (G[u][v]==1 && colorArr[v]==colorArr[u])
return false;
}
}
// If we reach here, then all adjacent vertices can
// be colored with alternate color
return true;
}
// Driver program to test above function
let G=[[0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0]];
if (isBipartite(G, 0))
document.write("Yes");
else
document.write("No");
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
</script>
Producción:
Yes
Complejidad de tiempo: O (V * V) como array de adyacencia se usa para el gráfico, pero se puede hacer O (V + E) usando la lista de adyacencia
Complejidad espacial: O(V) debido a la cola y al vector de color.
El algoritmo anterior funciona solo si el gráfico está conectado . En el código anterior, siempre comenzamos con la fuente 0 y asumimos que se visitan los vértices desde ella. Una observación importante es que un gráfico sin bordes también es bipartito. Tenga en cuenta que la condición bipartita dice que todos los bordes deben ser de un conjunto a otro.
Podemos extender el código anterior para manejar casos cuando un gráfico no está conectado. La idea se llama repetidamente método anterior para todos los vértices aún no visitados.
C++
// C++ program to find out whether
// a given graph is Bipartite or not.
// It works for disconnected graph also.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int V = 4;
// This function returns true if
// graph G[V][V] is Bipartite, else false
bool isBipartiteUtil(int G[][V], int src, int colorArr[])
{
colorArr[src] = 1;
// Create a queue (FIFO) of vertex numbers a
// nd enqueue source vertex for BFS traversal
queue<int> q;
q.push(src);
// Run while there are vertices in queue (Similar to
// BFS)
while (!q.empty()) {
// Dequeue a vertex from queue ( Refer
// http://goo.gl/35oz8 )
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
// Return false if there is a self-loop
if (G[u][u] == 1)
return false;
// Find all non-colored adjacent vertices
for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v) {
// An edge from u to v exists and
// destination v is not colored
if (G[u][v] && colorArr[v] == -1) {
// Assign alternate color to this
// adjacent v of u
colorArr[v] = 1 - colorArr[u];
q.push(v);
}
// An edge from u to v exists and destination
// v is colored with same color as u
else if (G[u][v] && colorArr[v] == colorArr[u])
return false;
}
}
// If we reach here, then all adjacent vertices can
// be colored with alternate color
return true;
}
// Returns true if G[][] is Bipartite, else false
bool isBipartite(int G[][V])
{
// Create a color array to store colors assigned to all
// vertices. Vertex/ number is used as index in this
// array. The value '-1' of colorArr[i] is used to
// indicate that no color is assigned to vertex 'i'.
// The value 1 is used to indicate first color is
// assigned and value 0 indicates second color is
// assigned.
int colorArr[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
colorArr[i] = -1;
// This code is to handle disconnected graph
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (colorArr[i] == -1)
if (isBipartiteUtil(G, i, colorArr) == false)
return false;
return true;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int G[][V] = { { 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 } };
isBipartite(G) ? cout << "Yes" : cout << "No";
return 0;
}
Java
// JAVA Code to check whether a given
// graph is Bipartite or not
import java.util.*;
class Bipartite {
public static int V = 4;
// This function returns true if graph
// G[V][V] is Bipartite, else false
public static boolean
isBipartiteUtil(int G[][], int src, int colorArr[])
{
colorArr[src] = 1;
// Create a queue (FIFO) of vertex numbers and
// enqueue source vertex for BFS traversal
LinkedList<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer>();
q.add(src);
// Run while there are vertices in queue
// (Similar to BFS)
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
// Dequeue a vertex from queue
// ( Refer http://goo.gl/35oz8 )
int u = q.getFirst();
q.pop();
// Return false if there is a self-loop
if (G[u][u] == 1)
return false;
// Find all non-colored adjacent vertices
for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v) {
// An edge from u to v exists and
// destination v is not colored
if (G[u][v] == 1 && colorArr[v] == -1) {
// Assign alternate color to this
// adjacent v of u
colorArr[v] = 1 - colorArr[u];
q.push(v);
}
// An edge from u to v exists and
// destination v is colored with same
// color as u
else if (G[u][v] == 1
&& colorArr[v] == colorArr[u])
return false;
}
}
// If we reach here, then all adjacent vertices
// can be colored with alternate color
return true;
}
// Returns true if G[][] is Bipartite, else false
public static boolean isBipartite(int G[][])
{
// Create a color array to store colors assigned
// to all vertices. Vertex/ number is used as
// index in this array. The value '-1' of
// colorArr[i] is used to indicate that no color
// is assigned to vertex 'i'. The value 1 is used
// to indicate first color is assigned and value
// 0 indicates second color is assigned.
int colorArr[] = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
colorArr[i] = -1;
// This code is to handle disconnected graph
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (colorArr[i] == -1)
if (isBipartiteUtil(G, i, colorArr)
== false)
return false;
return true;
}
/* Driver code*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int G[][] = { { 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 } };
if (isBipartite(G))
System.out.println("Yes");
else
System.out.println("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnav Kr. Mandal.
Python3
# Python3 program to find out whether a
# given graph is Bipartite or not
class Graph():
def __init__(self, V):
self.V = V
self.graph = [[0 for column in range(V)]
for row in range(V)]
self.colorArr = [-1 for i in range(self.V)]
# This function returns true if graph G[V][V]
# is Bipartite, else false
def isBipartiteUtil(self, src):
# Create a color array to store colors
# assigned to all vertices. Vertex
# number is used as index in this array.
# The value '-1' of self.colorArr[i] is used
# to indicate that no color is assigned to
# vertex 'i'. The value 1 is used to indicate
# first color is assigned and value 0
# indicates second color is assigned.
# Assign first color to source
# Create a queue (FIFO) of vertex numbers and
# enqueue source vertex for BFS traversal
queue = []
queue.append(src)
# Run while there are vertices in queue
# (Similar to BFS)
while queue:
u = queue.pop()
# Return false if there is a self-loop
if self.graph[u][u] == 1:
return False
for v in range(self.V):
# An edge from u to v exists and
# destination v is not colored
if (self.graph[u][v] == 1 and
self.colorArr[v] == -1):
# Assign alternate color to
# this adjacent v of u
self.colorArr[v] = 1 - self.colorArr[u]
queue.append(v)
# An edge from u to v exists and destination
# v is colored with same color as u
elif (self.graph[u][v] == 1 and
self.colorArr[v] == self.colorArr[u]):
return False
# If we reach here, then all adjacent
# vertices can be colored with alternate
# color
return True
def isBipartite(self):
self.colorArr = [-1 for i in range(self.V)]
for i in range(self.V):
if self.colorArr[i] == -1:
if not self.isBipartiteUtil(i):
return False
return True
# Driver Code
g = Graph(4)
g.graph = [[0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0]]
print ("Yes" if g.isBipartite() else "No")
# This code is contributed by Anshuman Sharma
C#
// C# Code to check whether a given
// graph is Bipartite or not
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
public static int V = 4;
// This function returns true if graph
// G[V,V] is Bipartite, else false
public static bool isBipartiteUtil(int[, ] G, int src,
int[] colorArr)
{
colorArr[src] = 1;
// Create a queue (FIFO) of vertex numbers and
// enqueue source vertex for BFS traversal
Queue<int> q = new Queue<int>();
q.Enqueue(src);
// Run while there are vertices in queue
// (Similar to BFS)
while (q.Count != 0) {
// Dequeue a vertex from queue
// ( Refer http://goo.gl/35oz8 )
int u = q.Peek();
q.Dequeue();
// Return false if there is a self-loop
if (G[u, u] == 1)
return false;
// Find all non-colored adjacent vertices
for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v) {
// An edge from u to v exists and
// destination v is not colored
if (G[u, v] == 1 && colorArr[v] == -1) {
// Assign alternate color to this
// adjacent v of u
colorArr[v] = 1 - colorArr[u];
q.Enqueue(v);
}
// An edge from u to v exists and
// destination v is colored with same
// color as u
else if (G[u, v] == 1
&& colorArr[v] == colorArr[u])
return false;
}
}
// If we reach here, then all
// adjacent vertices can be colored
// with alternate color
return true;
}
// Returns true if G[,] is Bipartite,
// else false
public static bool isBipartite(int[, ] G)
{
// Create a color array to store
// colors assigned to all vertices.
// Vertex/ number is used as
// index in this array. The value '-1'
// of colorArr[i] is used to indicate
// that no color is assigned to vertex 'i'.
// The value 1 is used to indicate
// first color is assigned and value
// 0 indicates second color is assigned.
int[] colorArr = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
colorArr[i] = -1;
// This code is to handle disconnected graph
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (colorArr[i] == -1)
if (isBipartiteUtil(G, i, colorArr)
== false)
return false;
return true;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int[, ] G = { { 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 } };
if (isBipartite(G))
Console.WriteLine("Yes");
else
Console.WriteLine("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript Code to check whether a given
// graph is Bipartite or not
var V = 4;
// This function returns true if graph
// G[V,V] is Bipartite, else false
function isBipartiteUtil(G, src, colorArr)
{
colorArr[src] = 1;
// Create a queue (FIFO) of vertex numbers and
// enqueue source vertex for BFS traversal
var q = [];
q.push(src);
// Run while there are vertices in queue
// (Similar to BFS)
while (q.length != 0)
{
// Dequeue a vertex from queue
// ( Refer http://goo.gl/35oz8 )
var u = q[0];
q.shift();
// Return false if there is a self-loop
if (G[u, u] == 1)
return false;
// Find all non-colored adjacent vertices
for (var v = 0; v < V; ++v)
{
// An edge from u to v exists and
// destination v is not colored
if (G[u][v] == 1 && colorArr[v] == -1)
{
// Assign alternate color to this
// adjacent v of u
colorArr[v] = 1 - colorArr[u];
q.push(v);
}
// An edge from u to v exists and
// destination v is colored with same
// color as u
else if (G[u, v] == 1
&& colorArr[v] == colorArr[u])
return false;
}
}
// If we reach here, then all
// adjacent vertices can be colored
// with alternate color
return true;
}
// Returns true if G[,] is Bipartite,
// else false
function isBipartite(G)
{
// Create a color array to store
// colors assigned to all vertices.
// Vertex/ number is used as
// index in this array. The value '-1'
// of colorArr[i] is used to indicate
// that no color is assigned to vertex 'i'.
// The value 1 is used to indicate
// first color is assigned and value
// 0 indicates second color is assigned.
var colorArr = Array(V);
for (var i = 0; i < V; ++i)
colorArr[i] = -1;
// This code is to handle disconnected graph
for (var i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (colorArr[i] == -1)
if (isBipartiteUtil(G, i, colorArr)
== false)
return false;
return true;
}
// Driver Code
var G = [ [ 0, 1, 0, 1 ],
[ 1, 0, 1, 0 ],
[ 0, 1, 0, 1 ],
[ 1, 0, 1, 0 ] ];
if (isBipartite(G))
document.write("Yes");
else
document.write("No");
// This code is contributed by rrrtnx.
</script>
Producción:
Yes
La complejidad temporal del enfoque anterior es la misma que la búsqueda primero en amplitud. En la implementación anterior es O(V^2) donde V es el número de vértices. Si el gráfico se representa usando una lista de adyacencia, entonces la complejidad se convierte en O(V+E).
Si el gráfico se representa usando la lista de adyacencia , la complejidad del tiempo será O (V + E).
Funciona tanto para gráficos conectados como desconectados.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool isBipartite(int V, vector<int> adj[])
{
// vector to store colour of vertex
// assigning all to -1 i.e. uncoloured
// colours are either 0 or 1
// for understanding take 0 as red and 1 as blue
vector<int> col(V, -1);
// queue for BFS storing {vertex , colour}
queue<pair<int, int> > q;
//loop incase graph is not connected
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
//if not coloured
if (col[i] == -1) {
//colouring with 0 i.e. red
q.push({ i, 0 });
col[i] = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
pair<int, int> p = q.front();
q.pop();
//current vertex
int v = p.first;
//colour of current vertex
int c = p.second;
//traversing vertexes connected to current vertex
for (int j : adj[v]) {
//if already coloured with parent vertex color
//then bipartite graph is not possible
if (col[j] == c)
return 0;
//if uncoloured
if (col[j] == -1) {
//colouring with opposite color to that of parent
col[j] = (c) ? 0 : 1;
q.push({ j, col[j] });
}
}
}
}
}
//if all vertexes are coloured such that
//no two connected vertex have same colours
return 1;
}
// { Driver Code Starts.
int main()
{
int V, E;
V = 4 , E = 8;
//adjacency list for storing graph
vector<int> adj[V];
adj[0] = {1,3};
adj[1] = {0,2};
adj[2] = {1,3};
adj[3] = {0,2};
bool ans = isBipartite(V, adj);
//returns 1 if bipartite graph is possible
if (ans)
cout << "Yes\n";
//returns 0 if bipartite graph is not possible
else
cout << "No\n";
return 0;
}
// code Contributed By Devendra Kolhe
Java
import java.util.*;
public class GFG{
static class Pair{
int first, second;
Pair(int f, int s){
first = f;
second = s;
}
}
static boolean isBipartite(int V, ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj)
{
// vector to store colour of vertex
// assigning all to -1 i.e. uncoloured
// colours are either 0 or 1
// for understanding take 0 as red and 1 as blue
int col[] = new int[V];
Arrays.fill(col, -1);
// queue for BFS storing {vertex , colour}
Queue<Pair> q = new LinkedList<Pair>();
//loop incase graph is not connected
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
// if not coloured
if (col[i] == -1) {
// colouring with 0 i.e. red
q.add(new Pair(i, 0));
col[i] = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Pair p = q.peek();
q.poll();
//current vertex
int v = p.first;
// colour of current vertex
int c = p.second;
// traversing vertexes connected to current vertex
for (int j : adj.get(v))
{
// if already coloured with parent vertex color
// then bipartite graph is not possible
if (col[j] == c)
return false;
// if uncoloured
if (col[j] == -1)
{
// colouring with opposite color to that of parent
col[j] = (c==1) ? 0 : 1;
q.add(new Pair(j, col[j]));
}
}
}
}
}
// if all vertexes are coloured such that
// no two connected vertex have same colours
return true;
}
// Driver Code Starts.
public static void main(String args[])
{
int V, E;
V = 4 ;
E = 8;
// adjacency list for storing graph
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++){
adj.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
adj.get(0).add(1);
adj.get(0).add(3);
adj.get(1).add(0);
adj.get(1).add(2);
adj.get(2).add(1);
adj.get(2).add(3);
adj.get(3).add(0);
adj.get(3).add(2);
boolean ans = isBipartite(V, adj);
// returns 1 if bipartite graph is possible
if (ans)
System.out.println("Yes");
// returns 0 if bipartite graph is not possible
else
System.out.println("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by adityapande88.
Python3
def isBipartite(V, adj):
# vector to store colour of vertex
# assigning all to -1 i.e. uncoloured
# colours are either 0 or 1
# for understanding take 0 as red and 1 as blue
col = [-1]*(V)
# queue for BFS storing {vertex , colour}
q = []
#loop incase graph is not connected
for i in range(V):
# if not coloured
if (col[i] == -1):
# colouring with 0 i.e. red
q.append([i, 0])
col[i] = 0
while len(q) != 0:
p = q[0]
q.pop(0)
# current vertex
v = p[0]
# colour of current vertex
c = p[1]
# traversing vertexes connected to current vertex
for j in adj[v]:
# if already coloured with parent vertex color
# then bipartite graph is not possible
if (col[j] == c):
return False
# if uncoloured
if (col[j] == -1):
# colouring with opposite color to that of parent
if c == 1:
col[j] = 0
else:
col[j] = 1
q.append([j, col[j]])
# if all vertexes are coloured such that
# no two connected vertex have same colours
return True
V, E = 4, 8
# adjacency list for storing graph
adj = []
adj.append([1,3])
adj.append([0,2])
adj.append([1,3])
adj.append([0,2])
ans = isBipartite(V, adj)
# returns 1 if bipartite graph is possible
if (ans):
print("Yes")
# returns 0 if bipartite graph is not possible
else:
print("No")
# This code is contributed by divyesh072019.
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
static bool isBipartite(int V, List<List<int>> adj)
{
// vector to store colour of vertex
// assigning all to -1 i.e. uncoloured
// colours are either 0 or 1
// for understanding take 0 as red and 1 as blue
int[] col = new int[V];
Array.Fill(col, -1);
// queue for BFS storing {vertex , colour}
List<Tuple<int,int>> q = new List<Tuple<int,int>>();
//loop incase graph is not connected
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
// if not coloured
if (col[i] == -1) {
// colouring with 0 i.e. red
q.Add(new Tuple<int,int>(i, 0));
col[i] = 0;
while (q.Count > 0) {
Tuple<int,int> p = q[0];
q.RemoveAt(0);
//current vertex
int v = p.Item1;
// colour of current vertex
int c = p.Item2;
// traversing vertexes connected to current vertex
foreach(int j in adj[v])
{
// if already coloured with parent vertex color
// then bipartite graph is not possible
if (col[j] == c)
return false;
// if uncoloured
if (col[j] == -1)
{
// colouring with opposite color to that of parent
col[j] = (c==1) ? 0 : 1;
q.Add(new Tuple<int,int>(j, col[j]));
}
}
}
}
}
// if all vertexes are coloured such that
// no two connected vertex have same colours
return true;
}
static void Main() {
int V;
V = 4 ;
// adjacency list for storing graph
List<List<int>> adj = new List<List<int>>();
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++){
adj.Add(new List<int>());
}
adj[0].Add(1);
adj[0].Add(3);
adj[1].Add(0);
adj[1].Add(2);
adj[2].Add(1);
adj[2].Add(3);
adj[3].Add(0);
adj[3].Add(2);
bool ans = isBipartite(V, adj);
// returns 1 if bipartite graph is possible
if (ans)
Console.WriteLine("Yes");
// returns 0 if bipartite graph is not possible
else
Console.WriteLine("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by decode2207.
Javascript
<script>
class Pair
{
constructor(f,s)
{
this.first = f;
this.second = s;
}
}
function isBipartite(V, adj)
{
// vector to store colour of vertex
// assigning all to -1 i.e. uncoloured
// colours are either 0 or 1
// for understanding take 0 as red and 1 as blue
let col = new Array(V);
for(let i = 0; i < V; i++)
col[i] = -1;
// queue for BFS storing {vertex , colour}
let q = [];
//loop incase graph is not connected
for (let i = 0; i < V; i++) {
// if not coloured
if (col[i] == -1) {
// colouring with 0 i.e. red
q.push(new Pair(i, 0));
col[i] = 0;
while (q.length!=0) {
let p = q[0];
q.shift();
//current vertex
let v = p.first;
// colour of current vertex
let c = p.second;
// traversing vertexes connected to current vertex
for (let j of adj[v])
{
// if already coloured with parent vertex color
// then bipartite graph is not possible
if (col[j] == c)
return false;
// if uncoloured
if (col[j] == -1)
{
// colouring with opposite color to that of parent
col[j] = (c==1) ? 0 : 1;
q.push(new Pair(j, col[j]));
}
}
}
}
}
// if all vertexes are coloured such that
// no two connected vertex have same colours
return true;
}
// Driver Code Starts.
let V, E;
V = 4 ;
E = 8;
// adjacency list for storing graph
let adj = [];
for(let i = 0; i < V; i++){
adj.push([]);
}
adj[0].push(1);
adj[0].push(3);
adj[1].push(0);
adj[1].push(2);
adj[2].push(1);
adj[2].push(3);
adj[3].push(0);
adj[3].push(2);
let ans = isBipartite(V, adj);
// returns 1 if bipartite graph is possible
if (ans)
document.write("Yes");
// returns 0 if bipartite graph is not possible
else
document.write("No");
// This code is contributed by patel2127
</script>
Yes
Complejidad temporal: O(V+E)
Espacio Auxiliar: O(V)
Ejercicio:
1. ¿Se puede usar el algoritmo DFS para verificar la bipartición de un gráfico? Si es así, ¿cómo?
Solución :
C++
// C++ program to find out whether a given graph is Bipartite or not.
// Using recursion.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define V 4
bool colorGraph(int G[][V],int color[],int pos, int c){
if(color[pos] != -1 && color[pos] !=c)
return false;
// color this pos as c and all its neighbours and 1-c
color[pos] = c;
bool ans = true;
for(int i=0;i<V;i++){
if(G[pos][i]){
if(color[i] == -1)
ans &= colorGraph(G,color,i,1-c);
if(color[i] !=-1 && color[i] != 1-c)
return false;
}
if (!ans)
return false;
}
return true;
}
bool isBipartite(int G[][V]){
int color[V];
for(int i=0;i<V;i++)
color[i] = -1;
//start is vertex 0;
int pos = 0;
// two colors 1 and 0
return colorGraph(G,color,pos,1);
}
int main()
{
int G[][V] = {{0, 1, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 0}
};
isBipartite(G) ? cout<< "Yes" : cout << "No";
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed By Mudit Verma
Java
// Java program to find out whether
// a given graph is Bipartite or not.
// Using recursion.
class GFG
{
static final int V = 4;
static boolean colorGraph(int G[][],
int color[],
int pos, int c)
{
if (color[pos] != -1 &&
color[pos] != c)
return false;
// color this pos as c and
// all its neighbours as 1-c
color[pos] = c;
boolean ans = true;
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
if (G[pos][i] == 1)
{
if (color[i] == -1)
ans &= colorGraph(G, color, i, 1 - c);
if (color[i] != -1 && color[i] != 1 - c)
return false;
}
if (!ans)
return false;
}
return true;
}
static boolean isBipartite(int G[][])
{
int[] color = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
color[i] = -1;
// start is vertex 0;
int pos = 0;
// two colors 1 and 0
return colorGraph(G, color, pos, 1);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int G[][] = { { 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 } };
if (isBipartite(G))
System.out.print("Yes");
else
System.out.print("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Python3
# Python3 program to find out whether a given
# graph is Bipartite or not using recursion.
V = 4
def colorGraph(G, color, pos, c):
if color[pos] != -1 and color[pos] != c:
return False
# color this pos as c and all its neighbours and 1-c
color[pos] = c
ans = True
for i in range(0, V):
if G[pos][i]:
if color[i] == -1:
ans &= colorGraph(G, color, i, 1-c)
if color[i] !=-1 and color[i] != 1-c:
return False
if not ans:
return False
return True
def isBipartite(G):
color = [-1] * V
#start is vertex 0
pos = 0
# two colors 1 and 0
return colorGraph(G, color, pos, 1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
G = [[0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0]]
if isBipartite(G): print("Yes")
else: print("No")
# This code is contributed by Rituraj Jain
C#
// C# program to find out whether
// a given graph is Bipartite or not.
// Using recursion.
using System;
class GFG
{
static readonly int V = 4;
static bool colorGraph(int [,]G,
int []color,
int pos, int c)
{
if (color[pos] != -1 &&
color[pos] != c)
return false;
// color this pos as c and
// all its neighbours as 1-c
color[pos] = c;
bool ans = true;
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
if (G[pos, i] == 1)
{
if (color[i] == -1)
ans &= colorGraph(G, color, i, 1 - c);
if (color[i] != -1 && color[i] != 1 - c)
return false;
}
if (!ans)
return false;
}
return true;
}
static bool isBipartite(int [,]G)
{
int[] color = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
color[i] = -1;
// start is vertex 0;
int pos = 0;
// two colors 1 and 0
return colorGraph(G, color, pos, 1);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int [,]G = {{ 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0 }};
if (isBipartite(G))
Console.Write("Yes");
else
Console.Write("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program to find out whether
// a given graph is Bipartite or not.
// Using recursion.
var V = 4;
function colorGraph(G, color, pos, c) {
if (color[pos] != -1 && color[pos] != c) return false;
// color this pos as c and
// all its neighbours as 1-c
color[pos] = c;
var ans = true;
for (var i = 0; i < V; i++) {
if (G[pos][i] == 1) {
if (color[i] == -1) ans &= colorGraph(G, color, i, 1 - c);
if (color[i] != -1 && color[i] != 1 - c) return false;
}
if (!ans) return false;
}
return true;
}
function isBipartite(G) {
var color = new Array(V).fill(0);
for (var i = 0; i < V; i++) color[i] = -1;
// start is vertex 0;
var pos = 0;
// two colors 1 and 0
return colorGraph(G, color, pos, 1);
}
// Driver Code
var G = [
[0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0],
];
if (isBipartite(G)) document.write("Yes");
else document.write("No");
// This code is contributed by rdtank.
</script>
Yes
Complejidad temporal: O(V+E)
Espacio Auxiliar: O(V)
Referencias:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graph_coloring
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bipartite_graph
Este artículo fue compilado por Aashish Barnwal . Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA