Construya un árbol binario a partir de una string que consta de paréntesis y números enteros. Toda la entrada representa un árbol binario. Contiene un número entero seguido de cero, uno o dos pares de paréntesis. El entero representa el valor de la raíz y un par de paréntesis contiene un árbol binario hijo con la misma estructura. Siempre comience a construir primero el Node secundario izquierdo del padre, si existe.
Ejemplos:
Input : "1(2)(3)"
Output : 1 2 3
Explanation :
1
/ \
2 3
Explanation: first pair of parenthesis contains
left subtree and second one contains the right
subtree. Preorder of above tree is "1 2 3".
Input : "4(2(3)(1))(6(5))"
Output : 4 2 3 1 6 5
Explanation :
4
/ \
2 6
/ \ /
3 1 5
Sabemos que el primer carácter de la string es root. La substring dentro del primer par de paréntesis adyacentes es para el subárbol izquierdo y la substring dentro del segundo par de paréntesis es para el subárbol derecho, como se muestra en el siguiente diagrama.
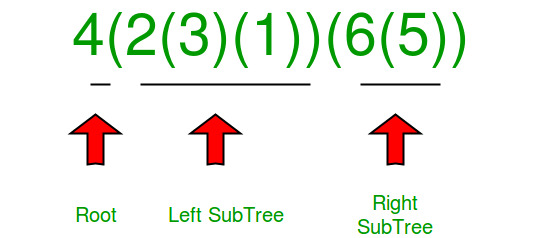
Necesitamos encontrar la substring correspondiente al subárbol izquierdo y la substring correspondiente al subárbol derecho y luego llamar recursivamente a ambas substrings.
Para esto, primero encuentre el índice de inicio y el índice final de cada substring.
Para encontrar el índice del paréntesis de cierre de la substring del subárbol izquierdo, use una pila. Deje que el índice encontrado se almacene en la variable de índice.
C++
/* C++ program to construct a binary tree from
the given string */
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left
child and a pointer to right child */
struct Node {
int data;
Node *left, *right;
};
/* Helper function that allocates a new node */
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
/* This function is here just to test */
void preOrder(Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
printf("%d ", node->data);
preOrder(node->left);
preOrder(node->right);
}
// function to return the index of close parenthesis
int findIndex(string str, int si, int ei)
{
if (si > ei)
return -1;
// Inbuilt stack
stack<char> s;
for (int i = si; i <= ei; i++) {
// if open parenthesis, push it
if (str[i] == '(')
s.push(str[i]);
// if close parenthesis
else if (str[i] == ')') {
if (s.top() == '(') {
s.pop();
// if stack is empty, this is
// the required index
if (s.empty())
return i;
}
}
}
// if not found return -1
return -1;
}
// function to construct tree from string
Node* treeFromString(string str, int si, int ei)
{
// Base case
if (si > ei)
return NULL;
// new root
Node* root = newNode(str[si] - '0');
int index = -1;
// if next char is '(' find the index of
// its complement ')'
if (si + 1 <= ei && str[si + 1] == '(')
index = findIndex(str, si + 1, ei);
// if index found
if (index != -1) {
// call for left subtree
root->left = treeFromString(str, si + 2, index - 1);
// call for right subtree
root->right
= treeFromString(str, index + 2, ei - 1);
}
return root;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
string str = "4(2(3)(1))(6(5))";
Node* root = treeFromString(str, 0, str.length() - 1);
preOrder(root);
}
Java
/* Java program to construct a binary tree from
the given String */
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left
child and a pointer to right child */
static class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
};
/* Helper function that allocates a new node */
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node node = new Node();
node.data = data;
node.left = node.right = null;
return (node);
}
/* This function is here just to test */
static void preOrder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
System.out.printf("%d ", node.data);
preOrder(node.left);
preOrder(node.right);
}
// function to return the index of close parenthesis
static int findIndex(String str, int si, int ei)
{
if (si > ei)
return -1;
// Inbuilt stack
Stack<Character> s = new Stack<>();
for (int i = si; i <= ei; i++)
{
// if open parenthesis, push it
if (str.charAt(i) == '(')
s.add(str.charAt(i));
// if close parenthesis
else if (str.charAt(i) == ')')
{
if (s.peek() == '(')
{
s.pop();
// if stack is empty, this is
// the required index
if (s.isEmpty())
return i;
}
}
}
// if not found return -1
return -1;
}
// function to construct tree from String
static Node treeFromString(String str, int si, int ei)
{
// Base case
if (si > ei)
return null;
// new root
Node root = newNode(str.charAt(si) - '0');
int index = -1;
// if next char is '(' find the index of
// its complement ')'
if (si + 1 <= ei && str.charAt(si+1) == '(')
index = findIndex(str, si + 1, ei);
// if index found
if (index != -1)
{
// call for left subtree
root.left = treeFromString(str, si + 2, index - 1);
// call for right subtree
root.right
= treeFromString(str, index + 2, ei - 1);
}
return root;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str = "4(2(3)(1))(6(5))";
Node root = treeFromString(str, 0, str.length() - 1);
preOrder(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
Python
# Python3 program to conStruct a
# binary tree from the given String
# Helper class that allocates a new node
class newNode:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = self.right = None
# This function is here just to test
def preOrder(node):
if (node == None):
return
print(node.data, end=" ")
preOrder(node.left)
preOrder(node.right)
# function to return the index of
# close parenthesis
def findIndex(Str, si, ei):
if (si > ei):
return -1
# Inbuilt stack
s = []
for i in range(si, ei + 1):
# if open parenthesis, push it
if (Str[i] == '('):
s.append(Str[i])
# if close parenthesis
elif (Str[i] == ')'):
if (s[-1] == '('):
s.pop(-1)
# if stack is empty, this is
# the required index
if len(s) == 0:
return i
# if not found return -1
return -1
# function to conStruct tree from String
def treeFromString(Str, si, ei):
# Base case
if (si > ei):
return None
# new root
root = newNode(ord(Str[si]) - ord('0'))
index = -1
# if next char is '(' find the
# index of its complement ')'
if (si + 1 <= ei and Str[si + 1] == '('):
index = findIndex(Str, si + 1, ei)
# if index found
if (index != -1):
# call for left subtree
root.left = treeFromString(Str, si + 2,
index - 1)
# call for right subtree
root.right = treeFromString(Str, index + 2,
ei - 1)
return root
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
Str = "4(2(3)(1))(6(5))"
root = treeFromString(Str, 0, len(Str) - 1)
preOrder(root)
# This code is contributed by pranchalK
C#
/* C# program to construct a binary tree from
the given String */
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG
{
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left
child and a pointer to right child */
public
class Node
{
public
int data;
public
Node left, right;
};
/* Helper function that allocates a new node */
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node node = new Node();
node.data = data;
node.left = node.right = null;
return (node);
}
/* This function is here just to test */
static void preOrder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
Console.Write("{0} ", node.data);
preOrder(node.left);
preOrder(node.right);
}
// function to return the index of close parenthesis
static int findIndex(String str, int si, int ei)
{
if (si > ei)
return -1;
// Inbuilt stack
Stack<char> s = new Stack<char>();
for (int i = si; i <= ei; i++)
{
// if open parenthesis, push it
if (str[i] == '(')
s.Push(str[i]);
// if close parenthesis
else if (str[i] == ')')
{
if (s.Peek() == '(')
{
s.Pop();
// if stack is empty, this is
// the required index
if (s.Count==0)
return i;
}
}
}
// if not found return -1
return -1;
}
// function to construct tree from String
static Node treeFromString(String str, int si, int ei)
{
// Base case
if (si > ei)
return null;
// new root
Node root = newNode(str[si] - '0');
int index = -1;
// if next char is '(' find the index of
// its complement ')'
if (si + 1 <= ei && str[si+1] == '(')
index = findIndex(str, si + 1, ei);
// if index found
if (index != -1)
{
// call for left subtree
root.left = treeFromString(str, si + 2, index - 1);
// call for right subtree
root.right
= treeFromString(str, index + 2, ei - 1);
}
return root;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
String str = "4(2(3)(1))(6(5))";
Node root = treeFromString(str, 0, str.Length - 1);
preOrder(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
Javascript
<script>
/* Javascript program to construct a binary tree from
the given String */
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left
child and a pointer to right child */
class Node
{
constructor()
{
this.data = 0;
this.left = this.right = null;
}
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node */
function newNode(data)
{
let node = new Node();
node.data = data;
node.left = node.right = null;
return (node);
}
/* This function is here just to test */
function preOrder(node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
document.write(node.data + " ");
preOrder(node.left);
preOrder(node.right);
}
// function to return the index of close parenthesis
function findIndex(str, si, ei)
{
if (si > ei)
return -1;
// Inbuilt stack
let s = [];
for (let i = si; i <= ei; i++)
{
// if open parenthesis, push it
if (str[i] == '(')
s.push(str[i]);
// if close parenthesis
else if (str[i] == ')')
{
if (s[s.length-1] == '(')
{
s.pop();
// if stack is empty, this is
// the required index
if (s.length == 0)
return i;
}
}
}
// if not found return -1
return -1;
}
// function to construct tree from String
function treeFromString(str,si,ei)
{
// Base case
if (si > ei)
return null;
// new root
let root = newNode(str[si].charCodeAt(0) - '0'.charCodeAt(0));
let index = -1;
// if next char is '(' find the index of
// its complement ')'
if (si + 1 <= ei && str[si + 1] == '(')
index = findIndex(str, si + 1, ei);
// if index found
if (index != -1)
{
// call for left subtree
root.left = treeFromString(str, si + 2, index - 1);
// call for right subtree
root.right
= treeFromString(str, index + 2, ei - 1);
}
return root;
}
// Driver Code
let str = "4(2(3)(1))(6(5))";
let root = treeFromString(str, 0, str.length - 1);
preOrder(root);
// This code is contributed by patel2127
</script>
4 2 3 1 6 5
Tiempo Complejidad: O(N 2 )
Espacio Auxiliar: O(N)
Otro enfoque recursivo:
Algoritmo:
- El primer elemento de la string es la raíz.
- Si los siguientes dos elementos consecutivos son «(» y «)», esto significa que no hay un elemento secundario izquierdo; de lo contrario, crearemos y agregaremos el elemento secundario izquierdo al Node principal de forma recursiva.
- Una vez que el hijo izquierdo se agrega recursivamente, buscaremos «(» consecutivos y agregaremos el hijo derecho al Node principal.
- Encontrar «)» significa el final del Node izquierdo o derecho e incrementaremos el índice de inicio
- La recursión termina cuando el índice de inicio es mayor que igual al índice final
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// custom data type for tree building
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* left;
struct Node* right;
Node(int val)
{
data = val;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
// Below function accepts string and a pointer variable as
// an argument
// and draw the tree. Returns the root of the tree
Node* constructtree(string s, int* start)
{
// Assuming there is/are no negative
// character/characters in the string
if (s.size() == 0 || *start >= s.size())
return NULL;
// constructing a number from the continuous digits
int num = 0;
while (*start < s.size() && s[*start] != '('
&& s[*start] != ')') {
int num_here = (int)(s[*start] - '0');
num = num * 10 + num_here;
*start = *start + 1;
}
// creating a node from the constructed number from
// above loop
struct Node* root = NULL;
if(num > 0)
root = new Node(num);
// As soon as we see first right parenthesis from the
// current node we start to construct the tree in the
// left
if (*start < s.size() && s[*start] == '(') {
*start = *start + 1;
root->left = constructtree(s, start);
}
if (*start < s.size() && s[*start] == ')')
{
*start = *start + 1;
return root;
}
// As soon as we see second right parenthesis from the
// current node we start to construct the tree in the
// right
if (*start < s.size() && s[*start] == '(') {
*start = *start + 1;
root->right = constructtree(s, start);
}
if (*start < s.size() && s[*start] == ')')
*start = *start + 1;
return root;
}
void preorder(Node* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
cout << root->data << " ";
preorder(root->left);
preorder(root->right);
}
int main()
{
string s = "4(2(3)(1))(6(5))";
// cin>>s;
int start = 0;
Node* root = constructtree(s, &start);
preorder(root);
return 0;
}
//This code is contributed by Chaitanya Sharma.
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Node class for the Tree
static class Node
{
int data;
Node left,right;
Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
this.left = this.right = null;
}
}
// static variable to point to the
// starting index of the string.
static int start = 0;
// Construct Tree Function which accepts
// a string and return root of the tree;
static Node constructTree(String s)
{
// Check for null or empty string
// and return null;
if (s.length() == 0 || s == null)
{
return null;
}
if (start >= s.length())
return null;
// Boolean variable to check
// for negative numbers
boolean neg = false;
// Condition to check for negative number
if (s.charAt(start) == '-')
{
neg = true;
start++;
}
// This loop basically construct the
// number from the continuous digits
int num = 0;
while (start < s.length() &&
Character.isDigit(s.charAt(start)))
{
int digit = Character.getNumericValue(
s.charAt(start));
num = num * 10 + digit;
start++;
}
// If string contains - minus sign
// then append - to the number;
if (neg)
num = -num;
// Create the node object i.e. root of
// the tree with data = num;
Node node = new Node(num);
if (start >= s.length())
{
return node;
}
// Check for open bracket and add the
// data to the left subtree recursively
if (start < s.length() && s.charAt(start) == '(' )
{
start++;
node.left = constructTree(s);
}
if (start < s.length() && s.charAt(start) == ')')
{
start++;
return node;
}
// Check for open bracket and add the data
// to the right subtree recursively
if (start < s.length() && s.charAt(start) == '(')
{
start++;
node.right = constructTree(s);
}
if (start < s.length() && s.charAt(start) == ')')
{
start++;
return node;
}
return node;
}
// Print tree function
public static void printTree(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
System.out.println(node.data + " ");
printTree(node.left);
printTree(node.right);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Input
String s = "4(2(3)(1))(6(5))";
// Call the function construct tree
// to create the tree pass the string;
Node root = constructTree(s);
// Function to print preorder of the tree
printTree(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by yash181999
Python3
class newNode:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = self.right = None
def preOrder(node):
if (node == None):
return
print(node.data, end=" ")
preOrder(node.left)
preOrder(node.right)
def treeFromStringHelper(si, ei, arr, root):
if si[0] >= ei:
return None
if arr[si[0]] == "(":
if arr[si[0]+1] != ")":
if root.left is None:
if si[0] >= ei:
return
new_root = newNode(arr[si[0]+1])
root.left = new_root
si[0] += 2
treeFromStringHelper(si, ei, arr, new_root)
else:
si[0] += 2
if root.right is None:
if si[0] >= ei:
return
if arr[si[0]] != "(":
si[0] += 1
return
new_root = newNode(arr[si[0]+1])
root.right = new_root
si[0] += 2
treeFromStringHelper(si, ei, arr, new_root)
else:
return
if arr[si[0]] == ")":
if si[0] >= ei:
return
si[0] += 1
return
return
def treeFromString(string):
root = newNode(string[0])
if len(string) > 1:
si = [1]
ei = len(string)-1
treeFromStringHelper(si, ei, string, root)
return root
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
Str = "4(2(3)(1))(6(5))"
root = treeFromString(Str)
preOrder(root)
# This code is contributed by dheerajalimchandani
C#
using System;
class GFG {
// Class containing left and
// right child of current
// node and key value
class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
// static variable to point to the
// starting index of the string.
static int start = 0;
// Construct Tree Function which accepts
// a string and return root of the tree;
static Node constructTree(string s)
{
// Check for null or empty string
// and return null;
if (s.Length == 0 || s == null)
{
return null;
}
if (start >= s.Length)
return null;
// Boolean variable to check
// for negative numbers
bool neg = false;
// Condition to check for negative number
if (s[start] == '-')
{
neg = true;
start++;
}
// This loop basically construct the
// number from the continuous digits
int num = 0;
while (start < s.Length &&
Char.IsDigit(s[start]))
{
int digit = (int)Char.GetNumericValue(
s[start]);
num = num * 10 + digit;
start++;
}
// If string contains - minus sign
// then append - to the number;
if (neg)
num = -num;
// Create the node object i.e. root of
// the tree with data = num;
Node node = new Node(num);
if (start >= s.Length)
{
return node;
}
// Check for open bracket and add the
// data to the left subtree recursively
if (start < s.Length && s[start] == '(' )
{
start++;
node.left = constructTree(s);
}
if (start < s.Length && s[start] == ')')
{
start++;
return node;
}
// Check for open bracket and add the data
// to the right subtree recursively
if (start < s.Length && s[start] == '(')
{
start++;
node.right = constructTree(s);
}
if (start < s.Length && s[start] == ')')
{
start++;
return node;
}
return node;
}
// Print tree function
static void printTree(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
printTree(node.left);
printTree(node.right);
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
// Input
string s = "4(2(3)(1))(6(5))";
// Call the function construct tree
// to create the tree pass the string;
Node root = constructTree(s);
// Function to print preorder of the tree
printTree(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by decode2207.
Javascript
<script>
// Node class for the Tree
class Node
{
constructor(data)
{
this.data=data;
this.left = this.right = null;
}
}
// static variable to point to the
// starting index of the string.
let start = 0;
// Construct Tree Function which accepts
// a string and return root of the tree;
function constructTree(s)
{
// Check for null or empty string
// and return null;
if (s.length == 0 || s == null)
{
return null;
}
if (start >= s.length)
return null;
// Boolean variable to check
// for negative numbers
let neg = false;
// Condition to check for negative number
if (s[start] == '-')
{
neg = true;
start++;
}
// This loop basically construct the
// number from the continuous digits
let num = 0;
while (start < s.length && !isNaN(s[start] -
parseInt(s[start])))
{
let digit = parseInt(
s[start]);
num = num * 10 + digit;
start++;
}
// If string contains - minus sign
// then append - to the number;
if (neg)
num = -num;
// Create the node object i.e. root of
// the tree with data = num;
let node = new Node(num);
if (start >= s.length)
{
return node;
}
// Check for open bracket and add the
// data to the left subtree recursively
if (start < s.length && s[start] == '(' )
{
start++;
node.left = constructTree(s);
}
if (start < s.length && s[start] == ')')
{
start++;
return node;
}
// Check for open bracket and add the data
// to the right subtree recursively
if (start < s.length && s[start] == '(')
{
start++;
node.right = constructTree(s);
}
if (start < s.length && s[start] == ')')
{
start++;
return node;
}
return node;
}
// Print tree function
function printTree(node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
document.write(node.data + " ");
printTree(node.left);
printTree(node.right);
}
// Driver Code
// Input
let s = "4(2(3)(1))(6(5))";
// Call the function construct tree
// to create the tree pass the string;
let root = constructTree(s);
// Function to print preorder of the tree
printTree(root);
// This code is contributed by unknown2108
</script>
4 2 3 1 6 5
Este artículo es una contribución de Chhavi . Si le gusta GeeksforGeeks y le gustaría contribuir, también puede escribir un artículo usando contribuya.geeksforgeeks.org o envíe su artículo por correo a review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA