Tenemos una array arr[]. Necesitamos encontrar la suma de todos los elementos en el rango L y R donde 0 <= L <= R <= n-1. Considere una situación en la que hay muchas consultas de rango.
Ejemplos:
Input : 3 7 2 5 8 9
query(0, 5)
query(3, 5)
query(2, 4)
Output : 34
22
15
Note : array is 0 based indexed
and queries too.
Dado que no hay actualizaciones/modificaciones, usamos la tabla Sparse para responder consultas de manera eficiente. En una tabla dispersa, dividimos las consultas en potencias de 2.
Suppose we are asked to compute sum of
elements from arr[i] to arr[i+12].
We do the following:
// Use sum of 8 (or 23) elements
table[i][3] = sum(arr[i], arr[i + 1], ...
arr[i + 7]).
// Use sum of 4 elements
table[i+8][2] = sum(arr[i+8], arr[i+9], ..
arr[i+11]).
// Use sum of single element
table[i + 12][0] = sum(arr[i + 12]).
Our result is sum of above values.
Observe que se necesitaron solo 4 acciones para calcular el resultado sobre un subarreglo de tamaño 13.
Diagrama de flujo:
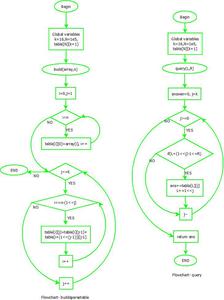
diagrama de flujo
C++
// CPP program to find the sum in a given
// range in an array using sparse table.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Because 2^17 is larger than 10^5
const int k = 16;
// Maximum value of array
const int N = 1e5;
// k + 1 because we need to access
// table[r][k]
long long table[N][k + 1];
// it builds sparse table.
void buildSparseTable(int arr[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
table[i][0] = arr[i];
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++)
for (int i = 0; i <= n - (1 << j); i++)
table[i][j] = table[i][j - 1] +
table[i + (1 << (j - 1))][j - 1];
}
// Returns the sum of the elements in the range
// L and R.
long long query(int L, int R)
{
// boundaries of next query, 0-indexed
long long answer = 0;
for (int j = k; j >= 0; j--) {
if (L + (1 << j) - 1 <= R) {
answer = answer + table[L][j];
// instead of having L', we
// increment L directly
L += 1 << j;
}
}
return answer;
}
// Driver program.
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 3, 7, 2, 5, 8, 9 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
buildSparseTable(arr, n);
cout << query(0, 5) << endl;
cout << query(3, 5) << endl;
cout << query(2, 4) << endl;
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to find the sum
// in a given range in an array
// using sparse table.
class GFG
{
// Because 2^17 is larger than 10^5
static int k = 16;
// Maximum value of array
static int N = 100000;
// k + 1 because we need
// to access table[r][k]
static long table[][] = new long[N][k + 1];
// it builds sparse table.
static void buildSparseTable(int arr[],
int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
table[i][0] = arr[i];
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++)
for (int i = 0; i <= n - (1 << j); i++)
table[i][j] = table[i][j - 1] +
table[i + (1 << (j - 1))][j - 1];
}
// Returns the sum of the
// elements in the range L and R.
static long query(int L, int R)
{
// boundaries of next query,
// 0-indexed
long answer = 0;
for (int j = k; j >= 0; j--)
{
if (L + (1 << j) - 1 <= R)
{
answer = answer + table[L][j];
// instead of having L', we
// increment L directly
L += 1 << j;
}
}
return answer;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = { 3, 7, 2, 5, 8, 9 };
int n = arr.length;
buildSparseTable(arr, n);
System.out.println(query(0, 5));
System.out.println(query(3, 5));
System.out.println(query(2, 4));
}
}
// This code is contributed
// by Kirti_Mangal
C#
// C# program to find the
// sum in a given range
// in an array using
// sparse table.
using System;
class GFG
{
// Because 2^17 is
// larger than 10^5
static int k = 16;
// Maximum value
// of array
static int N = 100000;
// k + 1 because we
// need to access table[r,k]
static long [,]table =
new long[N, k + 1];
// it builds sparse table.
static void buildSparseTable(int []arr,
int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
table[i, 0] = arr[i];
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++)
for (int i = 0;
i <= n - (1 << j); i++)
table[i, j] = table[i, j - 1] +
table[i + (1 << (j - 1)), j - 1];
}
// Returns the sum of the
// elements in the range
// L and R.
static long query(int L, int R)
{
// boundaries of next
// query, 0-indexed
long answer = 0;
for (int j = k; j >= 0; j--)
{
if (L + (1 << j) - 1 <= R)
{
answer = answer +
table[L, j];
// instead of having
// L', we increment
// L directly
L += 1 << j;
}
}
return answer;
}
// Driver Code
static void Main()
{
int []arr = new int[]{3, 7, 2,
5, 8, 9};
int n = arr.Length;
buildSparseTable(arr, n);
Console.WriteLine(query(0, 5));
Console.WriteLine(query(3, 5));
Console.WriteLine(query(2, 4));
}
}
// This code is contributed by
// Manish Shaw(manishshaw1)
Python3
# Python3 program to find the sum in a given # range in an array using sparse table. # Because 2^17 is larger than 10^5 k = 16 # Maximum value of array n = 100000 # k + 1 because we need to access # table[r][k] table = [[0 for j in range(k+1)] for i in range(n)] # it builds sparse table def buildSparseTable(arr, n): global table, k for i in range(n): table[i][0] = arr[i] for j in range(1,k+1): for i in range(0,n-(1<<j)+1): table[i][j] = table[i][j-1] + \ table[i + (1 << (j - 1))][j - 1] # Returns the sum of the elements in the range # L and R. def query(L, R): global table, k # boundaries of next query, 0 - indexed answer = 0 for j in range(k,-1,-1): if (L + (1 << j) - 1 <= R): answer = answer + table[L][j] # instead of having L ', we # increment L directly L+=1<<j return answer # Driver program if __name__ == '__main__': arr = [3, 7, 2, 5, 8, 9] n = len(arr) buildSparseTable(arr, n) print(query(0,5)) print(query(3,5)) print(query(2,4)) # This code is contributed by # chaudhary_19 (Mayank Chaudhary)
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program to find the sum in a given
// range in an array using sparse table.
// Because 2^17 is larger than 10^5
const k = 16;
// Maximum value of array
const N = 1e5;
// k + 1 because we need to access
// table[r][k]
const table = new Array(N).fill(0).map(() => new Array(k + 1).fill(0));
// it builds sparse table.
function buildSparseTable(arr, n)
{
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
table[i][0] = arr[i];
for (let j = 1; j <= k; j++)
for (let i = 0; i <= n - (1 << j); i++)
table[i][j] = table[i][j - 1] +
table[i + (1 << (j - 1))][j - 1];
}
// Returns the sum of the elements in the range
// L and R.
function query(L, R)
{
// boundaries of next query, 0-indexed
let answer = 0;
for (let j = k; j >= 0; j--)
{
if (L + (1 << j) - 1 <= R)
{
answer = answer + table[L][j];
// instead of having L', we
// increment L directly
L += 1 << j;
}
}
return answer;
}
// Driver program.
let arr = [ 3, 7, 2, 5, 8, 9 ];
let n = arr.length;
buildSparseTable(arr, n);
document.write(query(0, 5) + "<br>");
document.write(query(3, 5) + "<br>");
document.write(query(2, 4) + "<br>");
// This code is contributed by Manoj.
</script>
Producción:
34 22 15
Este algoritmo para responder consultas con Sparse Table funciona en O(k), que es O(log(n)) porque elegimos k mínimo tal que 2^k+1 > n.
Complejidad temporal de la construcción de tablas dispersas: el bucle externo se ejecuta en O(k), el bucle interno se ejecuta en O(n). Así, en total obtenemos O(n * k) = O(n * log(n))
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por pawan_asipu y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA