Dada una array arr[] de N enteros y consultas Q . Las consultas son de dos tipos:
- Actualice un índice dado por X .
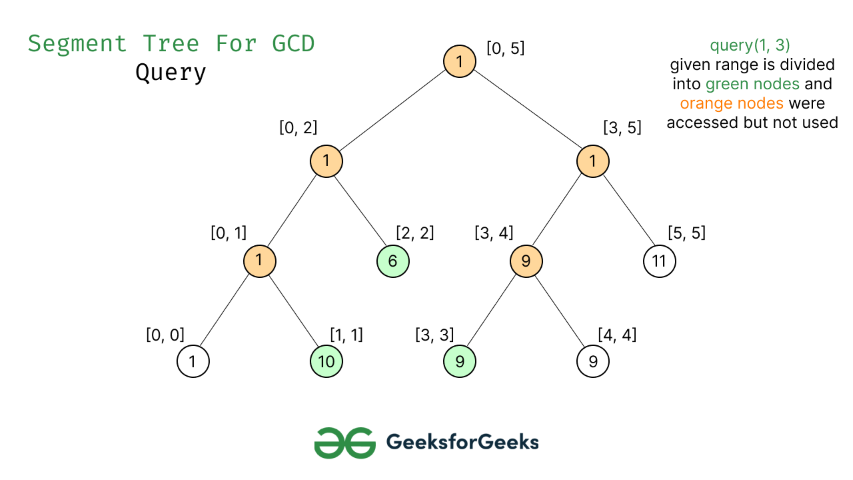
- Encuentre el gcd de los elementos en el rango de índice [L, R] .
Ejemplos:
Entrada: arr[] = {1, 3, 6, 9, 9, 11}
Consulta de tipo 2: L = 1, R = 3 Consulta de
tipo 1: ind = 1, X = 10 Consulta de
tipo 2: L = 1, R = 3
Salida:
3
1Entrada: arr[] = {1, 2, 4, 9, 3}
Consulta de tipo 2: L = 1, R = 2 Consulta de
tipo 1: ind = 2, X = 7 Consulta de
tipo 2: L = 1, R = 2
Consulta tipo 2: L = 3, R = 4
Salida:
2
1
3
Enfoque: El siguiente problema se puede resolver usando el Árbol de Segmentos .
Se puede usar un árbol de segmentos para realizar preprocesamiento y consultas en un tiempo moderado. Con el árbol de segmentos, el tiempo de preprocesamiento es O(n) y el tiempo para la consulta GCD es O(Logn). El espacio adicional requerido es O(n) para almacenar el árbol de segmentos.
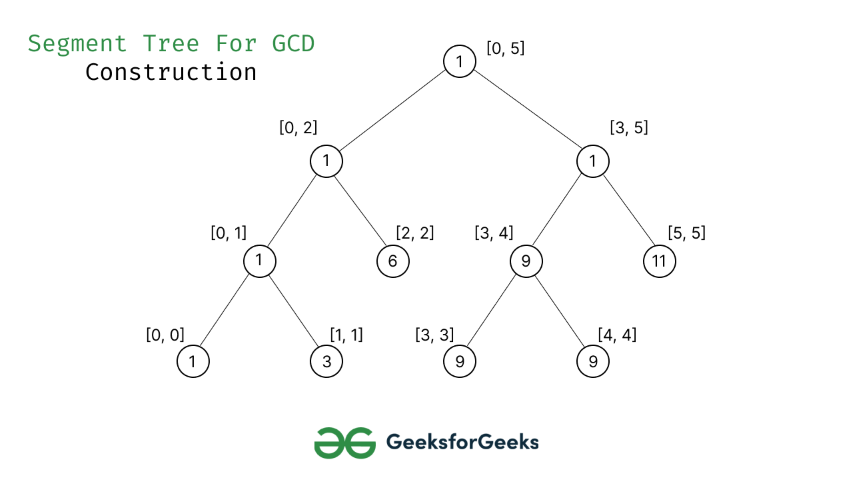
Representación de árboles de segmentos
- Los Nodes hoja son los elementos de la array de entrada.
- Cada Node interno representa el GCD de todas las hojas debajo de él.
La representación de array del árbol se utiliza para representar árboles de segmentos, es decir, para cada Node en el índice i
- El hijo izquierdo está en el índice 2*i+1
- Hijo derecho en 2*i+2 y el padre está en el piso ((i-1)/2).
Construcción del árbol de segmentos a partir de la array dada
- Comience con un segmento arr[0 . . . n-1] y seguir dividiendo en dos mitades. Cada vez que dividimos el segmento actual en dos mitades (si aún no se ha convertido en un segmento de longitud 1), llamamos al mismo procedimiento en ambas mitades y, para cada segmento, almacenamos el valor GCD en un Node de árbol de segmento.
- Todos los niveles del árbol de segmentos construido se llenarán por completo excepto el último nivel. Además, el árbol será un árbol binario completo (cada Node tiene 0 o dos hijos) porque siempre dividimos los segmentos en dos mitades en cada nivel.
- Dado que el árbol construido siempre es un árbol binario completo con n hojas, habrá n-1 Nodes internos. Entonces, el número total de Nodes será 2*n – 1.
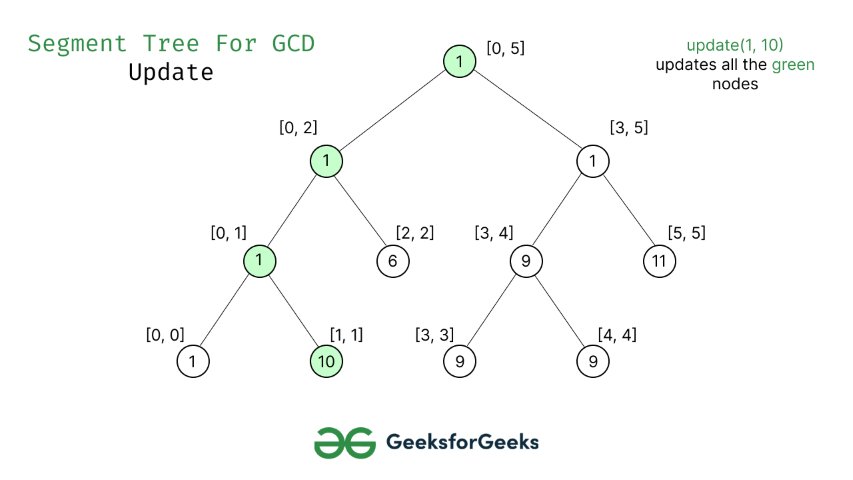
- Al igual que la construcción de árboles y las operaciones de consulta, la actualización también se puede realizar de forma recursiva.
- Nos dan un índice que necesita ser actualizado. Sea diff el valor a sumar. Comenzamos desde la raíz del árbol de segmentos y agregamos diferencias a todos los Nodes que han dado un índice en su rango. Si un Node no tiene un índice determinado en su rango, no hacemos ningún cambio en ese Node.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// A utility function to get the
// middle index from corner indexes
int getMid(int s, int e)
{
return (s + (e - s) / 2);
}
// A recursive function to get the gcd of values in given range
// of the array. The following are parameters for this function
// st --> Pointer to segment tree
// si --> Index of current node in the segment tree. Initially
// 0 is passed as root is always at index 0
// ss & se --> Starting and ending indexes of the segment represented
// by current node, i.e., st[si]
// qs & qe --> Starting and ending indexes of query range
int getGcdUtil(int* st, int ss, int se, int qs, int qe, int si)
{
// If segment of this node is a part of given range
// then return the gcd of the segment
if (qs <= ss && qe >= se)
return st[si];
// If segment of this node is outside the given range
if (se < qs || ss > qe)
return 0;
// If a part of this segment overlaps with the given range
int mid = getMid(ss, se);
return __gcd(getGcdUtil(st, ss, mid, qs, qe, 2 * si + 1),
getGcdUtil(st, mid + 1, se, qs, qe, 2 * si + 2));
}
// A recursive function to update the nodes which have the given
// index in their range. The following are parameters
// st, si, ss and se are same as getSumUtil()
// i --> index of the element to be updated. This index is
// in the input array.
// diff --> Value to be added to all nodes which have i in range
void updateValueUtil(int* st, int ss, int se, int i, int new_val, int si)
{
// Base Case: If the input index lies outside the range of
// this segment
if (i < ss || i > se)
return;
// If only single element is left in the range
if(ss == se)
{
st[si] = new_val;
return;
}
int mid = getMid(ss, se);
updateValueUtil(st, ss, mid, i, new_val, 2 * si + 1);
updateValueUtil(st, mid + 1, se, i, new_val, 2 * si + 2);
st[si] = __gcd(st[2*si + 1], st[2*si + 2]);
}
// The function to update a value in input array and segment tree.
// It uses updateValueUtil() to update the value in segment tree
void updateValue(int arr[], int* st, int n, int i, int new_val)
{
// Check for erroneous input index
if (i < 0 || i > n - 1) {
cout << "Invalid Input";
return;
}
// Update the values of nodes in segment tree
updateValueUtil(st, 0, n - 1, i, new_val, 0);
}
// Function to return the sum of elements in range
// from index qs (query start) to qe (query end)
// It mainly uses getSumUtil()
int getGcd(int* st, int n, int qs, int qe)
{
// Check for erroneous input values
if (qs < 0 || qe > n - 1 || qs > qe) {
cout << "Invalid Input";
return -1;
}
return getGcdUtil(st, 0, n - 1, qs, qe, 0);
}
// A recursive function that constructs Segment Tree for array[ss..se].
// si is index of current node in segment tree st
int constructGcdUtil(int arr[], int ss, int se, int* st, int si)
{
// If there is one element in array, store it in current node of
// segment tree and return
if (ss == se) {
st[si] = arr[ss];
return arr[ss];
}
// If there are more than one element then recur for left and
// right subtrees and store the sum of values in this node
int mid = getMid(ss, se);
st[si] = __gcd(constructGcdUtil(arr, ss, mid, st, si * 2 + 1),
constructGcdUtil(arr, mid + 1, se, st, si * 2 + 2));
return st[si];
}
// Function to construct segment tree from given array. This function
// allocates memory for segment tree and calls constructSTUtil() to
// fill the allocated memory
int* constructGcd(int arr[], int n)
{
// Allocate memory for the segment tree
// Height of segment tree
int x = (int)(ceil(log2(n)));
// Maximum size of segment tree
int max_size = 2 * (int)pow(2, x) - 1;
// Allocate memory
int* st = new int[max_size];
// Fill the allocated memory st
constructGcdUtil(arr, 0, n - 1, st, 0);
// Return the constructed segment tree
return st;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 3, 6, 9, 9, 11 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Build segment tree from given array
int* st = constructGcd(arr, n);
// Print GCD of values in array from index 1 to 3
cout << getGcd(st, n, 1, 3) << endl;
// Update: set arr[1] = 10 and update corresponding
// segment tree nodes
updateValue(arr, st, n, 1, 10);
// Find GCD after the value is updated
cout << getGcd(st, n, 1, 3) << endl;
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation of the approach
class GFG
{
// segment tree
static int st[];
// Recursive function to return gcd of a and b
static int __gcd(int a, int b)
{
if (b == 0)
return a;
return __gcd(b, a % b);
}
// A utility function to get the
// middle index from corner indexes
static int getMid(int s, int e)
{
return (s + (e - s) / 2);
}
// A recursive function to get the gcd of values in given range
// of the array. The following are parameters for this function
// st --> Pointer to segment tree
// si --> Index of current node in the segment tree. Initially
// 0 is passed as root is always at index 0
// ss & se --> Starting and ending indexes of the segment represented
// by current node, i.e., st[si]
// qs & qe --> Starting and ending indexes of query range
static int getGcdUtil( int ss, int se, int qs, int qe, int si)
{
// If segment of this node is a part of given range
// then return the gcd of the segment
if (qs <= ss && qe >= se)
return st[si];
// If segment of this node is outside the given range
if (se < qs || ss > qe)
return 0;
// If a part of this segment overlaps with the given range
int mid = getMid(ss, se);
return __gcd(getGcdUtil( ss, mid, qs, qe, 2 * si + 1),
getGcdUtil( mid + 1, se, qs, qe, 2 * si + 2));
}
// A recursive function to update the nodes which have the given
// index in their range. The following are parameters
// si, ss and se are same as getSumUtil()
// i --> index of the element to be updated. This index is
// in the input array.
// diff --> Value to be added to all nodes which have i in range
static void updateValueUtil( int ss, int se, int i, int new_val, int si)
{
// Base Case: If the input index lies outside the range of
// this segment
if (i < ss || i > se)
return;
// If only single element is left in the range
if(ss == se)
{
st[si] = new_val;
return;
}
int mid = getMid(ss, se);
updateValueUtil(ss, mid, i, new_val, 2 * si + 1);
updateValueUtil(mid + 1, se, i, new_val, 2 * si + 2);
st[si] = __gcd(st[2*si + 1], st[2*si + 2]);
}
// The function to update a value in input array and segment tree.
// It uses updateValueUtil() to update the value in segment tree
static void updateValue(int arr[], int n, int i, int new_val)
{
// Check for erroneous input index
if (i < 0 || i > n - 1)
{
System.out.println("Invalid Input");
return;
}
// Update the values of nodes in segment tree
updateValueUtil( 0, n - 1, i, new_val, 0);
}
// Function to return the sum of elements in range
// from index qs (query start) to qe (query end)
// It mainly uses getSumUtil()
static int getGcd( int n, int qs, int qe)
{
// Check for erroneous input values
if (qs < 0 || qe > n - 1 || qs > qe)
{
System.out.println( "Invalid Input");
return -1;
}
return getGcdUtil( 0, n - 1, qs, qe, 0);
}
// A recursive function that constructs Segment Tree for array[ss..se].
// si is index of current node in segment tree st
static int constructGcdUtil(int arr[], int ss, int se, int si)
{
// If there is one element in array, store it in current node of
// segment tree and return
if (ss == se)
{
st[si] = arr[ss];
return arr[ss];
}
// If there are more than one element then recur for left and
// right subtrees and store the sum of values in this node
int mid = getMid(ss, se);
st[si] = __gcd(constructGcdUtil(arr, ss, mid, si * 2 + 1),
constructGcdUtil(arr, mid + 1, se, si * 2 + 2));
return st[si];
}
// Function to construct segment tree from given array. This function
// allocates memory for segment tree and calls constructSTUtil() to
// fill the allocated memory
static void constructGcd(int arr[], int n)
{
// Allocate memory for the segment tree
// Height of segment tree
int x = (int)(Math.ceil(Math.log(n)/Math.log(2)));
// Maximum size of segment tree
int max_size = 2 * (int)Math.pow(2, x) - 1;
// Allocate memory
st = new int[max_size];
// Fill the allocated memory st
constructGcdUtil(arr, 0, n - 1, 0);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = { 1, 3, 6, 9, 9, 11 };
int n = arr.length;
// Build segment tree from given array
constructGcd(arr, n);
// Print GCD of values in array from index 1 to 3
System.out.println( getGcd( n, 1, 3) );
// Update: set arr[1] = 10 and update corresponding
// segment tree nodes
updateValue(arr, n, 1, 10);
// Find GCD after the value is updated
System.out.println( getGcd( n, 1, 3) );
}
}
// This code is constructed by Arnab Kundu
Python3
# Python 3 implementation of the approach
from math import gcd,ceil,log2,pow
# A utility function to get the
# middle index from corner indexes
def getMid(s, e):
return (s + int((e - s) / 2))
# A recursive function to get the gcd of values in given range
# of the array. The following are parameters for this function
# st --> Pointer to segment tree
# si --> Index of current node in the segment tree. Initially
# 0 is passed as root is always at index 0
# ss & se --> Starting and ending indexes of the segment represented
# by current node, i.e., st[si]
# qs & qe --> Starting and ending indexes of query range
def getGcdUtil(st,ss,se,qs,qe,si):
# If segment of this node is a part of given range
# then return the gcd of the segment
if (qs <= ss and qe >= se):
return st[si]
# If segment of this node is outside the given range
if (se < qs or ss > qe):
return 0
# If a part of this segment overlaps with the given range
mid = getMid(ss, se)
return gcd(getGcdUtil(st, ss, mid, qs, qe, 2 * si + 1),
getGcdUtil(st, mid + 1, se, qs, qe, 2 * si + 2))
# A recursive function to update the nodes which have the given
# index in their range. The following are parameters
# st, si, ss and se are same as getSumUtil()
# i --> index of the element to be updated. This index is
# in the input array.
# diff --> Value to be added to all nodes which have i in range
def updateValueUtil(st,ss,se,i,new_val,si):
# Base Case: If the input index lies outside the range of
# this segment
if (i < ss or i > se):
return
if(ss == se):
st[si] = new_val
return
# If the input index is in range of this node, then update
# the value of the node and its children
mid = getMid(ss, se)
updateValueUtil(st, ss, mid, i, new_val, 2 * si + 1)
updateValueUtil(st, mid + 1, se, i, new_val, 2 * si + 2)
st[si] = gcd(st[2*si + 1], st[2*si + 2])
# The function to update a value in input array and segment tree.
# It uses updateValueUtil() to update the value in segment tree
def updateValue(arr, st, n, i, new_val):
# Check for erroneous input index
if (i < 0 or i > n - 1):
print("Invalid Input")
return
# Update the values of nodes in segment tree
updateValueUtil(st, 0, n - 1, i, new_val, 0)
# Function to return the sum of elements in range
# from index qs (query start) to qe (query end)
# It mainly uses getSumUtil()
def getGcd(st,n,qs,qe):
# Check for erroneous input values
if (qs < 0 or qe > n - 1 or qs > qe):
cout << "Invalid Input"
return -1
return getGcdUtil(st, 0, n - 1, qs, qe, 0)
# A recursive function that constructs Segment Tree for array[ss..se].
# si is index of current node in segment tree st
def constructGcdUtil(arr, ss,se, st, si):
# If there is one element in array, store it in current node of
# segment tree and return
if (ss == se):
st[si] = arr[ss]
return arr[ss]
# If there are more than one element then recur for left and
# right subtrees and store the sum of values in this node
mid = getMid(ss, se)
st[si] = gcd(constructGcdUtil(arr, ss, mid, st, si * 2 + 1),
constructGcdUtil(arr, mid + 1, se, st, si * 2 + 2))
return st[si]
# Function to construct segment tree from given array. This function
# allocates memory for segment tree and calls constructSTUtil() to
# fill the allocated memory
def constructGcd(arr, n):
# Allocate memory for the segment tree
# Height of segment tree
x = int(ceil(log2(n)))
# Maximum size of segment tree
max_size = 2 * int(pow(2, x) - 1)
# Allocate memory
st = [0 for i in range(max_size)]
# Fill the allocated memory st
constructGcdUtil(arr, 0, n - 1, st, 0)
# Return the constructed segment tree
return st
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [1, 3, 6, 9, 9, 11]
n = len(arr)
# Build segment tree from given array
st = constructGcd(arr, n)
# Print GCD of values in array from index 1 to 3
print(getGcd(st, n, 1, 3))
# Update: set arr[1] = 10 and update corresponding
# segment tree nodes
updateValue(arr, st, n, 1, 10)
# Find GCD after the value is updated
print(getGcd(st, n, 1, 3))
# This code is contributed by
# SURENDRA_GANGWAR
C#
// C# implementation of the approach.
using System;
class GFG
{
// segment tree
static int []st;
// Recursive function to return gcd of a and b
static int __gcd(int a, int b)
{
if (b == 0)
return a;
return __gcd(b, a % b);
}
// A utility function to get the
// middle index from corner indexes
static int getMid(int s, int e)
{
return (s + (e - s) / 2);
}
// A recursive function to get the gcd of values in given range
// of the array. The following are parameters for this function
// st --> Pointer to segment tree
// si --> Index of current node in the segment tree. Initially
// 0 is passed as root is always at index 0
// ss & se --> Starting and ending indexes of the segment represented
// by current node, i.e., st[si]
// qs & qe --> Starting and ending indexes of query range
static int getGcdUtil( int ss, int se, int qs, int qe, int si)
{
// If segment of this node is a part of given range
// then return the gcd of the segment
if (qs <= ss && qe >= se)
return st[si];
// If segment of this node is outside the given range
if (se < qs || ss > qe)
return 0;
// If a part of this segment overlaps with the given range
int mid = getMid(ss, se);
return __gcd(getGcdUtil( ss, mid, qs, qe, 2 * si + 1),
getGcdUtil( mid + 1, se, qs, qe, 2 * si + 2));
}
// A recursive function to update the nodes which have the given
// index in their range. The following are parameters
// si, ss and se are same as getSumUtil()
// i --> index of the element to be updated. This index is
// in the input array.
// diff --> Value to be added to all nodes which have i in range
static void updateValueUtil( int ss, int se, int i, int new_val, int si)
{
// Base Case: If the input index lies outside the range of
// this segment
if (i < ss || i > se)
return;
// If only single element is left in the range
if(ss == se)
{
st[si] = new_val;
return;
}
int mid = getMid(ss, se);
updateValueUtil(ss, mid, i, new_val, 2 * si + 1);
updateValueUtil(mid + 1, se, i, new_val, 2 * si + 2);
st[si] = __gcd(st[2*si + 1], st[2*si + 2]);
}
// The function to update a value in input array and segment tree.
// It uses updateValueUtil() to update the value in segment tree
static void updateValue(int []arr, int n, int i, int new_val)
{
// Check for erroneous input index
if (i < 0 || i > n - 1)
{
Console.WriteLine("Invalid Input");
return;
}
// Update the values of nodes in segment tree
updateValueUtil( 0, n - 1, i, new_val, 0);
}
// Function to return the sum of elements in range
// from index qs (query start) to qe (query end)
// It mainly uses getSumUtil()
static int getGcd( int n, int qs, int qe)
{
// Check for erroneous input values
if (qs < 0 || qe > n - 1 || qs > qe)
{
Console.WriteLine( "Invalid Input");
return -1;
}
return getGcdUtil( 0, n - 1, qs, qe, 0);
}
// A recursive function that constructs Segment Tree for array[ss..se].
// si is index of current node in segment tree st
static int constructGcdUtil(int []arr, int ss, int se, int si)
{
// If there is one element in array, store it in current node of
// segment tree and return
if (ss == se)
{
st[si] = arr[ss];
return arr[ss];
}
// If there are more than one element then recur for left and
// right subtrees and store the sum of values in this node
int mid = getMid(ss, se);
st[si] = __gcd(constructGcdUtil(arr, ss, mid, si * 2 + 1),
constructGcdUtil(arr, mid + 1, se, si * 2 + 2));
return st[si];
}
// Function to construct segment tree from given array. This function
// allocates memory for segment tree and calls constructSTUtil() to
// fill the allocated memory
static void constructGcd(int []arr, int n)
{
// Allocate memory for the segment tree
// Height of segment tree
int x = (int)(Math.Ceiling(Math.Log(n)/Math.Log(2)));
// Maximum size of segment tree
int max_size = 2 * (int)Math.Pow(2, x) - 1;
// Allocate memory
st = new int[max_size];
// Fill the allocated memory st
constructGcdUtil(arr, 0, n - 1, 0);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
int []arr = { 1, 3, 6, 9, 9, 11 };
int n = arr.Length;
// Build segment tree from given array
constructGcd(arr, n);
// Print GCD of values in array from index 1 to 3
Console.WriteLine( getGcd( n, 1, 3) );
// Update: set arr[1] = 10 and update corresponding
// segment tree nodes
updateValue(arr, n, 1, 10);
// Find GCD after the value is updated
Console.WriteLine( getGcd( n, 1, 3) );
}
}
// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji
Javascript
<script>
// javascript implementation of the approach // segment tree
var st;
// Recursive function to return gcd of a and b
function __gcd(a , b) {
if (b == 0)
return a;
return __gcd(b, a % b);
}
// A utility function to get the
// middle index from corner indexes
function getMid(s , e) {
return (s + parseInt((e - s) / 2));
}
// A recursive function to get the gcd of values in given range
// of the array. The following are parameters for this function
// st --> Pointer to segment tree
// si --> Index of current node in the segment tree. Initially
// 0 is passed as root is always at index 0
// ss & se --> Starting and ending indexes of the segment represented
// by current node, i.e., st[si]
// qs & qe --> Starting and ending indexes of query range
function getGcdUtil(ss , se , qs , qe , si) {
// If segment of this node is a part of given range
// then return the gcd of the segment
if (qs <= ss && qe >= se)
return st[si];
// If segment of this node is outside the given range
if (se < qs || ss > qe)
return 0;
// If a part of this segment overlaps with the given range
var mid = getMid(ss, se);
return __gcd(getGcdUtil(ss, mid, qs, qe, 2 * si + 1), getGcdUtil(mid + 1, se, qs, qe, 2 * si + 2));
}
// A recursive function to update the nodes which have the given
// index in their range. The following are parameters
// si, ss and se are same as getSumUtil()
// i --> index of the element to be updated. This index is
// in the input array.
// diff --> Value to be added to all nodes which have i in range
function updateValueUtil(ss , se , i , diff , si) {
// Base Case: If the input index lies outside the range of
// this segment
if (i < ss || i > se)
return;
// If the input index is in range of this node, then update
// the value of the node and its children
st[si] = st[si] + diff;
if (se != ss) {
var mid = getMid(ss, se);
updateValueUtil(ss, mid, i, diff, 2 * si + 1);
updateValueUtil(mid + 1, se, i, diff, 2 * si + 2);
}
}
// The function to update a value in input array and segment tree.
// It uses updateValueUtil() to update the value in segment tree
function updateValue(arr , n , i , new_val) {
// Check for erroneous input index
if (i < 0 || i > n - 1) {
document.write("Invalid Input");
return;
}
// Get the difference between new value and old value
var diff = new_val - arr[i];
// Update the value in array
arr[i] = new_val;
// Update the values of nodes in segment tree
updateValueUtil(0, n - 1, i, diff, 0);
}
// Function to return the sum of elements in range
// from index qs (query start) to qe (query end)
// It mainly uses getSumUtil()
function getGcd(n , qs , qe) {
// Check for erroneous input values
if (qs < 0 || qe > n - 1 || qs > qe) {
document.write("Invalid Input");
return -1;
}
return getGcdUtil(0, n - 1, qs, qe, 0);
}
// A recursive function that constructs Segment Tree for array[ss..se].
// si is index of current node in segment tree st
function constructGcdUtil(arr , ss , se , si) {
// If there is one element in array, store it in current node of
// segment tree and return
if (ss == se) {
st[si] = arr[ss];
return arr[ss];
}
// If there are more than one element then recur for left and
// right subtrees and store the sum of values in this node
var mid = getMid(ss, se);
st[si] = __gcd(constructGcdUtil(arr, ss, mid, si * 2 + 1), constructGcdUtil(arr, mid + 1, se, si * 2 + 2));
return st[si];
}
// Function to construct segment tree from given array. This function
// allocates memory for segment tree and calls constructSTUtil() to
// fill the allocated memory
function constructGcd(arr , n) {
// Allocate memory for the segment tree
// Height of segment tree
var x = parseInt( (Math.ceil(Math.log(n) / Math.log(2))));
// Maximum size of segment tree
var max_size = 2 * parseInt( Math.pow(2, x) - 1);
// Allocate memory
st = Array(max_size).fill(0);
// Fill the allocated memory st
constructGcdUtil(arr, 0, n - 1, 0);
}
// Driver code
var arr = [ 1, 3, 6, 9, 9, 11 ];
var n = arr.length;
// Build segment tree from given array
constructGcd(arr, n);
// Print GCD of values in array from index 1 to 3
document.write(getGcd(n, 1, 3)+"<br/>");
// Update: set arr[1] = 10 and update corresponding
// segment tree nodes
updateValue(arr, n, 1, 10);
// Find GCD after the value is updated
document.write(getGcd(n, 1, 3));
// This code contributed by umadevi9616
</script>
3 1
Complejidad de tiempo: O (n log n), ya que la construcción del árbol de segmentos tomará O (n log n) tiempo. Donde n es el número de elementos de la array.
Espacio auxiliar: O(n log n), ya que estamos usando espacio adicional para el árbol de segmentos. Donde n es el número de elementos de la array.