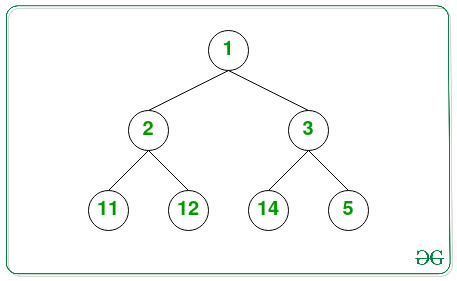
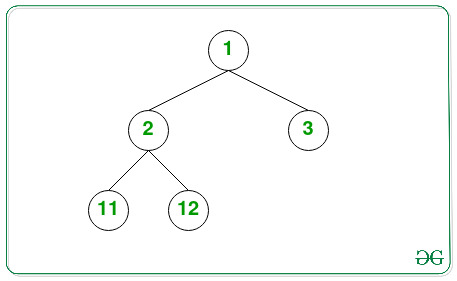
Dada la raíz de un árbol binario completo que consta de N Nodes, la tarea es encontrar el número total de Nodes en el árbol binario dado .
Ejemplos:
Aporte:
Salida: 7
Aporte:
Salida: 5
Enfoque ingenuo: el enfoque simple para resolver el árbol dado es realizar el DFS Traversal en el árbol dado y contar la cantidad de Nodes en él. Después del recorrido, imprima el recuento total de Nodes obtenidos.
Complejidad temporal: O(N)
Espacio auxiliar: O(1)
Enfoque eficiente: El enfoque anterior también se puede optimizar por el hecho de que:
Un árbol binario completo tiene (2 h – 1) Nodes en total.
Según esta lógica, en el primer caso, compare la altura del subárbol izquierdo con la altura del subárbol derecho. Si son iguales es un árbol completo, entonces la respuesta será 2^altura – 1 . De lo contrario, si no son iguales, solicite recursivamente el subárbol izquierdo y el subárbol derecho para contar la cantidad de Nodes. Siga los pasos a continuación para resolver el problema:
- Defina una función left_height(root) y encuentre la altura izquierda del árbol dado atravesando en la dirección izquierda de la raíz y guárdela en una variable, digamos leftHeight .
- Defina una función right_height(root) y encuentre la altura correcta del árbol dado atravesando en la dirección correcta de la raíz y guárdela en una variable, digamos rightHeight .
- Encuentre la altura izquierda y derecha del árbol dado para el valor raíz actual y, si es igual, devuelva el valor de (2 altura – 1) como el recuento resultante de Nodes.
- De lo contrario, llame recursivamente a la función para los subárboles izquierdo y derecho y devuelva la suma de ellos + 1 como el recuento resultante de Nodes.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior.
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Structure of a Tree Node
class node {
public:
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
};
node* newNode(int data);
// Function to get the left height of
// the binary tree
int left_height(node* node)
{
int ht = 0;
while (node) {
ht++;
node = node->left;
}
// Return the left height obtained
return ht;
}
// Function to get the right height
// of the binary tree
int right_height(node* node)
{
int ht = 0;
while (node) {
ht++;
node = node->right;
}
// Return the right height obtained
return ht;
}
// Function to get the count of nodes
// in complete binary tree
int TotalNodes(node* root)
{
// Base Case
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
// Find the left height and the
// right heights
int lh = left_height(root);
int rh = right_height(root);
// If left and right heights are
// equal return 2^height(1<<height) -1
if (lh == rh)
return (1 << lh) - 1;
// Otherwise, recursive call
return 1 + TotalNodes(root->left)
+ TotalNodes(root->right);
}
// Helper function to allocate a new node
// with the given data
node* newNode(int data)
{
node* Node = new node();
Node->data = data;
Node->left = NULL;
Node->right = NULL;
return (Node);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left = newNode(9);
root->right->right = newNode(8);
root->left->left->left = newNode(6);
root->left->left->right = newNode(7);
cout << TotalNodes(root);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by aditya kumar (adityakumar129)
C
// C program for the above approach
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Structure of a Tree Node
typedef struct node {
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
}node;
// Helper function to allocate a new node
// with the given data
node* newNode(int data)
{
node * Node = (node *)malloc(sizeof(node));
Node->data = data;
Node->left = NULL;
Node->right = NULL;
return (Node);
}
// Function to get the left height of
// the binary tree
int left_height(node* node)
{
int ht = 0;
while (node) {
ht++;
node = node->left;
}
// Return the left height obtained
return ht;
}
// Function to get the right height
// of the binary tree
int right_height(node* node)
{
int ht = 0;
while (node) {
ht++;
node = node->right;
}
// Return the right height obtained
return ht;
}
// Function to get the count of nodes
// in complete binary tree
int TotalNodes(node* root)
{
// Base Case
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
// Find the left height and the
// right heights
int lh = left_height(root);
int rh = right_height(root);
// If left and right heights are
// equal return 2^height(1<<height) -1
if (lh == rh)
return (1 << lh) - 1;
// Otherwise, recursive call
return 1 + TotalNodes(root->left) + TotalNodes(root->right);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left = newNode(9);
root->right->right = newNode(8);
root->left->left->left = newNode(6);
root->left->left->right = newNode(7);
printf("%d",TotalNodes(root));
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by aditya kumar (adityakumar129)
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Structure of a Tree Node
static class node {
int data;
node left;
node right;
};
// Function to get the left height of
// the binary tree
static int left_height(node node)
{
int ht = 0;
while (node!=null) {
ht++;
node = node.left;
}
// Return the left height obtained
return ht;
}
// Function to get the right height
// of the binary tree
static int right_height(node node)
{
int ht = 0;
while (node!=null) {
ht++;
node = node.right;
}
// Return the right height obtained
return ht;
}
// Function to get the count of nodes
// in complete binary tree
static int TotalNodes(node root)
{
// Base Case
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Find the left height and the
// right heights
int lh = left_height(root);
int rh = right_height(root);
// If left and right heights are
// equal return 2^height(1<<height) -1
if (lh == rh)
return (1 << lh) - 1;
// Otherwise, recursive call
return 1 + TotalNodes(root.left)
+ TotalNodes(root.right);
}
// Helper function to allocate a new node
// with the given data
static node newNode(int data)
{
node Node = new node();
Node.data = data;
Node.left = null;
Node.right = null;
return (Node);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.right.left = newNode(9);
root.right.right = newNode(8);
root.left.left.left = newNode(6);
root.left.left.right = newNode(7);
System.out.print(TotalNodes(root));
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput
Python3
# Python program for the above approach # Structure of a Tree Node class node: def __init__(self, key): self.left = None self.right = None self.val = key # Function to get the left height of # the binary tree def left_height(node): ht = 0 while(node): ht += 1 node = node.left # Return the left height obtained return ht # Function to get the right height # of the binary tree def right_height(node): ht = 0 while(node): ht += 1 node = node.right # Return the right height obtained return ht # Function to get the count of nodes # in complete binary tree def TotalNodes(root): # Base case if(root == None): return 0 # Find the left height and the # right heights lh = left_height(root) rh = right_height(root) # If left and right heights are # equal return 2^height(1<<height) -1 if(lh == rh): return (1 << lh) - 1 # Otherwise, recursive call return 1 + TotalNodes(root.left) + TotalNodes(root.right) # Driver code root = node(1) root.left = node(2) root.right = node(3) root.left.left = node(4) root.left.right = node(5) root.right.left = node(9) root.right.right = node(8) root.left.left.left = node(6) root.left.left.right = node(7) print(TotalNodes(root)) # This code is contributed by parthmanchanda81
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
public class GFG{
// Structure of a Tree Node
class node {
public int data;
public node left;
public node right;
};
// Function to get the left height of
// the binary tree
static int left_height(node node)
{
int ht = 0;
while (node != null) {
ht++;
node = node.left;
}
// Return the left height obtained
return ht;
}
// Function to get the right height
// of the binary tree
static int right_height(node node)
{
int ht = 0;
while (node != null) {
ht++;
node = node.right;
}
// Return the right height obtained
return ht;
}
// Function to get the count of nodes
// in complete binary tree
static int TotalNodes(node root)
{
// Base Case
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Find the left height and the
// right heights
int lh = left_height(root);
int rh = right_height(root);
// If left and right heights are
// equal return 2^height(1<<height) -1
if (lh == rh)
return (1 << lh) - 1;
// Otherwise, recursive call
return 1 + TotalNodes(root.left)
+ TotalNodes(root.right);
}
// Helper function to allocate a new node
// with the given data
static node newNode(int data)
{
node Node = new node();
Node.data = data;
Node.left = null;
Node.right = null;
return (Node);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.right.left = newNode(9);
root.right.right = newNode(8);
root.left.left.left = newNode(6);
root.left.left.right = newNode(7);
Console.Write(TotalNodes(root));
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript Program to implement
// the above approach
// Structure of a Tree Node
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
};
// Function to get the left height of
// the binary tree
function left_height(node) {
let ht = 0;
while (node) {
ht++;
node = node.left;
}
// Return the left height obtained
return ht;
}
// Function to get the right height
// of the binary tree
function right_height(node) {
let ht = 0;
while (node) {
ht++;
node = node.right;
}
// Return the right height obtained
return ht;
}
// Function to get the count of nodes
// in complete binary tree
function TotalNodes(root) {
// Base Case
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Find the left height and the
// right heights
let lh = left_height(root);
let rh = right_height(root);
// If left and right heights are
// equal return 2^height(1<<height) -1
if (lh == rh)
return (1 << lh) - 1;
// Otherwise, recursive call
return 1 + TotalNodes(root.left)
+ TotalNodes(root.right);
}
// Helper function to allocate a new node
// with the given data
// Driver Code
let root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(9);
root.right.right = new Node(8);
root.left.left.left = new Node(6);
root.left.left.right = new Node(7);
document.write(TotalNodes(root));
// This code is contributed by Potta Lokesh
</script>
9
Complejidad de tiempo: O((log N) 2 )
Espacio auxiliar: O(log N) debido al espacio de pila de recursión