N líneas dadas tienen la forma a*x + b*y = c (a>0 o a==0 & b>0). Halla el número de pares de rectas que se cortan en un punto. Ejemplos:
Entrada: N=5 x + y = 2 x + y = 4 x = 1 x – y = 2 y = 3 Salida: 9 Entrada: N=2 x + 2y = 2 x + 2y = 4 Salida: 0
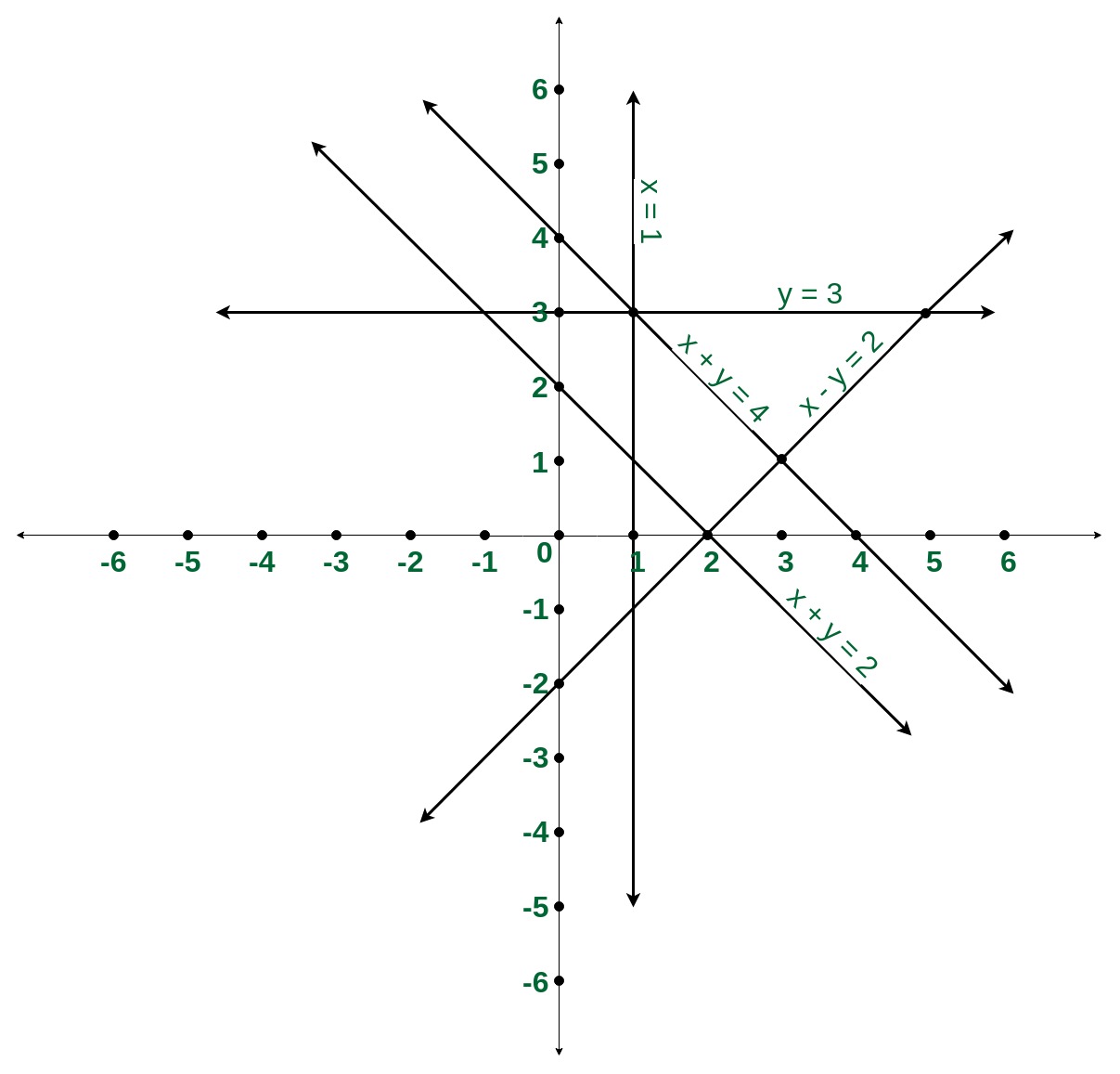
Acercarse:
- Las líneas paralelas nunca se cruzan, por lo que se necesita un método para excluir líneas paralelas para cada línea.
- La pendiente de una línea se puede representar como un par (a, b). Construya un mapa con clave como pendiente y valor como un conjunto con c como entradas para que tenga una cuenta de las líneas paralelas.
- Itere sobre las líneas, agréguelas al mapa y mantenga una variable Tot que cuente el número total de líneas hasta ahora.
- Ahora, para cada línea, actualice la variable Tot , luego agregue Tot a la respuesta y reste el número de líneas paralelas a esa línea, incluyéndose a sí misma.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
CPP
// C++ implementation to calculate
// pair of intersecting lines
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to return the number
// of intersecting pair of lines
void numberOfPairs(int a[],int b[],int c[],int N){
int count = 0, Tot = 0;
// Construct a map of slope and
// corresponding c value
map<pair<int, int>, set<int> > LineMap;
// iterate over each line
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// Slope can be represented
// as pair(a, b)
pair<int, int> Slope =
make_pair(a[i], b[i]);
// Checking if the line does
// not already exist
if (!LineMap[Slope].count(c[i])){
// maintaining a count
// of total lines
Tot++;
LineMap[Slope].insert(c[i]);
// subtracting the count of
// parallel lines including itself
count += Tot -
LineMap[Slope].size();
}
}
cout << count << endl;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// A line can be represented as ax+by=c
// such that (a>0 || (a==0 & b>0) )
// a and b are already in there lowest
// form i.e gcd(a, b)=1
int N = 5;
int a[] = { 1, 1, 1, 1, 0 };
int b[] = { 1, 1, 0, -1, 1 };
int c[] = { 2, 4, 1, 2, 3 };
numberOfPairs(a,b,c,N);
return 0;
}
Javascript
// JavaScript implementation to calculate
// pair of intersecting lines
// Function to return the number
// of intersecting pair of lines
function numberOfPairs(a, b, c, N){
let count = 0;
let Tot = 0;
// Construct a map of slope and
// corresponding c value
let LineMap = new Map();
// map<pair<int, int>, set<int> > LineMap;
// iterate over each line
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// Slope can be represented
// as pair(a, b)
let Slope = [a[i], b[i]].join();
// Checking if the line does
// not already exist
if (!LineMap.has(Slope) || !LineMap.get(Slope).has(c[i])){
// maintaining a count
// of total lines
Tot = Tot + 1;
if(!LineMap.has(Slope))
LineMap.set(Slope, new Set().add(c[i]));
else
LineMap.set(Slope, LineMap.get(Slope).add(c[i]));
// subtracting the count of
// parallel lines including itself
count = count + Tot - LineMap.get(Slope).size;
}
}
console.log(count);
}
// Driver code
// A line can be represented as ax+by=c
// such that (a>0 || (a==0 & b>0) )
// a and b are already in there lowest
// form i.e gcd(a, b)=1
let N = 5;
let a = [1, 1, 1, 1, 0];
let b = [1, 1, 0, -1, 1];
let c = [2, 4, 1, 2, 3 ];
numberOfPairs(a,b,c,N);
// The code is contributed by Gatuam goel (gautamgoel962)
Producción:
9
Complejidad del tiempo: ![]()
Complejidad espacial : O (N) desde que se usa un mapa