Dado un árbol binario (Bt), conviértalo en una lista doblemente enlazada (DLL). Los punteros izquierdo y derecho en los Nodes se utilizarán como punteros anterior y siguiente, respectivamente, en la DLL convertida. El orden de los Nodes en DLL debe ser el mismo que en Inorder para el árbol binario dado. El primer Node del recorrido Inorder (el Node más a la izquierda en BT) debe ser el Node principal de la DLL.
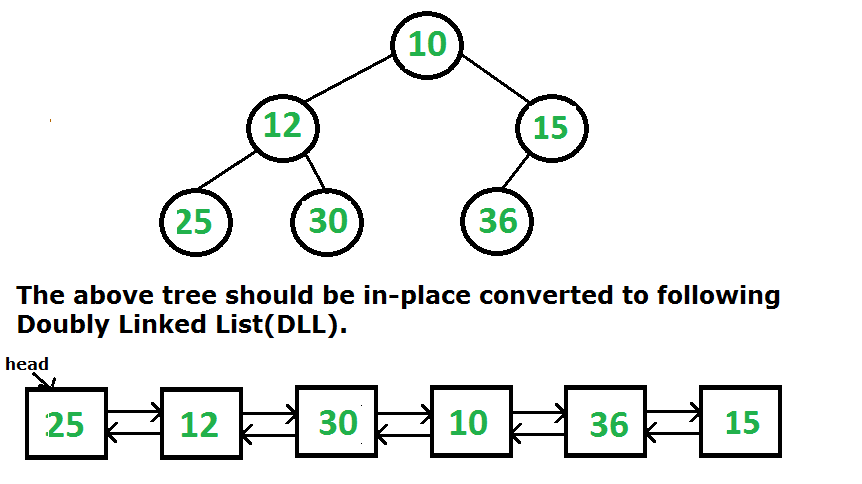
Me encontré con esta pregunta durante una de mis entrevistas. Un problema similar ha sido discutido en este post .
El problema aquí es más simple ya que no necesitamos crear una DLL circular, sino una DLL simple. La idea detrás de su solución es bastante simple y directa.
- Si existe el subárbol izquierdo, procesar el subárbol izquierdo
- Convierta recursivamente el subárbol izquierdo a DLL.
- Luego encuentre el predecesor en orden de la raíz en el subárbol izquierdo (el predecesor en orden es el Node más a la derecha en el subárbol izquierdo).
- Haga que el predecesor en orden sea la raíz anterior y la raíz como el siguiente predecesor en orden.
- Si existe el subárbol derecho, procese el subárbol derecho (los siguientes 3 pasos son similares al subárbol izquierdo).
- Convierte recursivamente el subárbol derecho a DLL.
- Luego encuentre el sucesor en orden de la raíz en el subárbol derecho (en orden, el sucesor es el Node más a la izquierda en el subárbol derecho).
- Haga que el sucesor en orden sea la siguiente raíz y la raíz como el sucesor en orden anterior.
- Busque el Node más a la izquierda y devuélvalo (el Node más a la izquierda es siempre el encabezado de una DLL convertida).
A continuación se muestra el código fuente del algoritmo anterior.
C++
// A C++ program for in-place
// conversion of Binary Tree to DLL
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data,
and left and right pointers */
class node {
public:
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
};
/* This is the core function to convert
Tree to list. This function follows
steps 1 and 2 of the above algorithm */
node* bintree2listUtil(node* root)
{
// Base case
if (root == NULL)
return root;
// Convert the left subtree and link to root
if (root->left != NULL) {
// Convert the left subtree
node* left = bintree2listUtil(root->left);
// Find inorder predecessor. After this loop, left
// will point to the inorder predecessor
for (; left->right != NULL; left = left->right)
;
// Make root as next of the predecessor
left->right = root;
// Make predecessor as previous of root
root->left = left;
}
// Convert the right subtree and link to root
if (root->right != NULL) {
// Convert the right subtree
node* right = bintree2listUtil(root->right);
// Find inorder successor. After this loop, right
// will point to the inorder successor
for (; right->left != NULL; right = right->left)
;
// Make root as previous of successor
right->left = root;
// Make successor as next of root
root->right = right;
}
return root;
}
// The main function that first calls
// bintree2listUtil(), then follows step 3
// of the above algorithm
node* bintree2list(node* root)
{
// Base case
if (root == NULL)
return root;
// Convert to DLL using bintree2listUtil()
root = bintree2listUtil(root);
// bintree2listUtil() returns root node of the converted
// DLL. We need pointer to the leftmost node which is
// head of the constructed DLL, so move to the leftmost
// node
while (root->left != NULL)
root = root->left;
return (root);
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
node* newNode(int data)
{
node* new_node = new node();
new_node->data = data;
new_node->left = new_node->right = NULL;
return (new_node);
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list */
void printList(node* node)
{
while (node != NULL) {
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->right;
}
}
/* Driver code*/
int main()
{
// Let us create the tree shown in above diagram
node* root = newNode(10);
root->left = newNode(12);
root->right = newNode(15);
root->left->left = newNode(25);
root->left->right = newNode(30);
root->right->left = newNode(36);
// Convert to DLL
node* head = bintree2list(root);
// Print the converted list
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra
C
// A C program for in-place conversion of Binary Tree to DLL
#include <stdio.h>
/* A binary tree node has data, and left and right pointers */
struct node
{
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
};
/* This is the core function to convert Tree to list. This function follows
steps 1 and 2 of the above algorithm */
node* bintree2listUtil(node* root)
{
// Base case
if (root == NULL)
return root;
// Convert the left subtree and link to root
if (root->left != NULL)
{
// Convert the left subtree
node* left = bintree2listUtil(root->left);
// Find inorder predecessor. After this loop, left
// will point to the inorder predecessor
for (; left->right!=NULL; left=left->right);
// Make root as next of the predecessor
left->right = root;
// Make predecessor as previous of root
root->left = left;
}
// Convert the right subtree and link to root
if (root->right!=NULL)
{
// Convert the right subtree
node* right = bintree2listUtil(root->right);
// Find inorder successor. After this loop, right
// will point to the inorder successor
for (; right->left!=NULL; right = right->left);
// Make root as previous of successor
right->left = root;
// Make successor as next of root
root->right = right;
}
return root;
}
// The main function that first calls bintree2listUtil(), then follows step 3
// of the above algorithm
node* bintree2list(node *root)
{
// Base case
if (root == NULL)
return root;
// Convert to DLL using bintree2listUtil()
root = bintree2listUtil(root);
// bintree2listUtil() returns root node of the converted
// DLL. We need pointer to the leftmost node which is
// head of the constructed DLL, so move to the leftmost node
while (root->left != NULL)
root = root->left;
return (root);
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
node* newNode(int data)
{
node* new_node = new node;
new_node->data = data;
new_node->left = new_node->right = NULL;
return (new_node);
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list */
void printList(node *node)
{
while (node!=NULL)
{
printf("%d ", node->data);
node = node->right;
}
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
// Let us create the tree shown in above diagram
node *root = newNode(10);
root->left = newNode(12);
root->right = newNode(15);
root->left->left = newNode(25);
root->left->right = newNode(30);
root->right->left = newNode(36);
// Convert to DLL
node *head = bintree2list(root);
// Print the converted list
printList(head);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to convert binary tree to double linked list
/* A binary tree node has data, and left and right pointers */
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
/* This is the core function to convert Tree to list. This function
follows steps 1 and 2 of the above algorithm */
Node bintree2listUtil(Node node)
{
// Base case
if (node == null)
return node;
// Convert the left subtree and link to root
if (node.left != null)
{
// Convert the left subtree
Node left = bintree2listUtil(node.left);
// Find inorder predecessor. After this loop, left
// will point to the inorder predecessor
for (; left.right != null; left = left.right);
// Make root as next of the predecessor
left.right = node;
// Make predecessor as previous of root
node.left = left;
}
// Convert the right subtree and link to root
if (node.right != null)
{
// Convert the right subtree
Node right = bintree2listUtil(node.right);
// Find inorder successor. After this loop, right
// will point to the inorder successor
for (; right.left != null; right = right.left);
// Make root as previous of successor
right.left = node;
// Make successor as next of root
node.right = right;
}
return node;
}
// The main function that first calls bintree2listUtil(), then follows
// step 3 of the above algorithm
Node bintree2list(Node node)
{
// Base case
if (node == null)
return node;
// Convert to DLL using bintree2listUtil()
node = bintree2listUtil(node);
// bintree2listUtil() returns root node of the converted
// DLL. We need pointer to the leftmost node which is
// head of the constructed DLL, so move to the leftmost node
while (node.left != null)
node = node.left;
return node;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list */
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null)
{
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.right;
}
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
// Let us create the tree shown in above diagram
tree.root = new Node(10);
tree.root.left = new Node(12);
tree.root.right = new Node(15);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(25);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(30);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(36);
// Convert to DLL
Node head = tree.bintree2list(tree.root);
// Print the converted list
tree.printList(head);
}
}
Python3
# Python program to convert # binary tree to doubly linked list class Node(object): """Binary tree Node class has data, left and right child""" def __init__(self, item): self.data = item self.left = None self.right = None def BTToDLLUtil(root): """This is a utility function to convert the binary tree to doubly linked list. Most of the core task is done by this function.""" if root is None: return root # Convert left subtree # and link to root if root.left: # Convert the left subtree left = BTToDLLUtil(root.left) # Find inorder predecessor, After # this loop, left will point to the # inorder predecessor of root while left.right: left = left.right # Make root as next of predecessor left.right = root # Make predecessor as # previous of root root.left = left # Convert the right subtree # and link to root if root.right: # Convert the right subtree right = BTToDLLUtil(root.right) # Find inorder successor, After # this loop, right will point to # the inorder successor of root while right.left: right = right.left # Make root as previous # of successor right.left = root # Make successor as # next of root root.right = right return root def BTToDLL(root): if root is None: return root # Convert to doubly linked # list using BLLToDLLUtil root = BTToDLLUtil(root) # We need pointer to left most # node which is head of the # constructed Doubly Linked list while root.left: root = root.left return root def print_list(head): """Function to print the given doubly linked list""" if head is None: return while head: print(head.data, end = " ") head = head.right # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': root = Node(10) root.left = Node(12) root.right = Node(15) root.left.left = Node(25) root.left.right = Node(30) root.right.left = Node(36) head = BTToDLL(root) print_list(head) # This code is contributed # by viveksyngh
C#
using System;
// C# program to convert binary tree to double linked list
/* A binary tree node has data, and left and right pointers */
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
public Node root;
/* This is the core function to convert Tree to list. This function
follows steps 1 and 2 of the above algorithm */
public virtual Node bintree2listUtil(Node node)
{
// Base case
if (node == null)
{
return node;
}
// Convert the left subtree and link to root
if (node.left != null)
{
// Convert the left subtree
Node left = bintree2listUtil(node.left);
// Find inorder predecessor. After this loop, left
// will point to the inorder predecessor
for (; left.right != null; left = left.right)
{
;
}
// Make root as next of the predecessor
left.right = node;
// Make predecessor as previous of root
node.left = left;
}
// Convert the right subtree and link to root
if (node.right != null)
{
// Convert the right subtree
Node right = bintree2listUtil(node.right);
// Find inorder successor. After this loop, right
// will point to the inorder successor
for (; right.left != null; right = right.left)
{
;
}
// Make root as previous of successor
right.left = node;
// Make successor as next of root
node.right = right;
}
return node;
}
// The main function that first calls bintree2listUtil(), then follows
// step 3 of the above algorithm
public virtual Node bintree2list(Node node)
{
// Base case
if (node == null)
{
return node;
}
// Convert to DLL using bintree2listUtil()
node = bintree2listUtil(node);
// bintree2listUtil() returns root node of the converted
// DLL. We need pointer to the leftmost node which is
// head of the constructed DLL, so move to the leftmost node
while (node.left != null)
{
node = node.left;
}
return node;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list */
public virtual void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null)
{
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
node = node.right;
}
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
// Let us create the tree shown in above diagram
tree.root = new Node(10);
tree.root.left = new Node(12);
tree.root.right = new Node(15);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(25);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(30);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(36);
// Convert to DLL
Node head = tree.bintree2list(tree.root);
// Print the converted list
tree.printList(head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13
Javascript
<script>
// javascript program to convert binary tree to double linked list
/* A binary tree node has data, and left and right pointers */
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
var root;
/*
* This is the core function to convert Tree to list. This function follows
* steps 1 and 2 of the above algorithm
*/
function bintree2listUtil(node) {
// Base case
if (node == null)
return node;
// Convert the left subtree and link to root
if (node.left != null) {
// Convert the left subtree
var left = bintree2listUtil(node.left);
// Find inorder predecessor. After this loop, left
// will point to the inorder predecessor
for (; left.right != null; left = left.right)
// Make root as next of the predecessor
left.right = node;
// Make predecessor as previous of root
node.left = left;
}
// Convert the right subtree and link to root
if (node.right != null) {
// Convert the right subtree
var right = bintree2listUtil(node.right);
// Find inorder successor. After this loop, right
// will point to the inorder successor
for (; right.left != null; right = right.left)
// Make root as previous of successor
right.left = node;
// Make successor as next of root
node.right = right;
}
return node;
}
// The main function that first calls bintree2listUtil(), then follows
// step 3 of the above algorithm
function bintree2list(node) {
// Base case
if (node == null)
return node;
// Convert to DLL using bintree2listUtil()
node = bintree2listUtil(node);
// bintree2listUtil() returns root node of the converted
// DLL. We need pointer to the leftmost node which is
// head of the constructed DLL, so move to the leftmost node
while (node.left != null)
node = node.left;
return node;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list */
function printList(node) {
while (node != null) {
document.write(node.data + " ");
node = node.right;
}
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
// Let us create the tree shown in above diagram
root = new Node(10);
root.left = new Node(12);
root.right = new Node(15);
root.left.left = new Node(25);
root.left.right = new Node(30);
root.right.left = new Node(36);
// Convert to DLL
var head = bintree2list(root);
// Print the converted list
printList(head);
// This code contributed by umadevi9616
</script>
25 12 30 10 36 15
Otro enfoque:
Algoritmo:
- Atraviesa el árbol en orden.
- Mientras visita cada Node, realice un seguimiento de los punteros de cabeza y cola de DLL, inserte cada Node visitado al final de DLL usando el puntero de cola.
- Vuelve a la cabeza de la lista.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// A C++ program for in-place
// conversion of Binary Tree to DLL
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data,
and left and right pointers */
class node {
public:
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
};
/* This is the core function to convert
Tree to list.*/
void bintree2listUtil(node* root, node** head, node** tail)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
bintree2listUtil(root->left, head, tail);
if (*head == NULL) {
*head = root;
}
root->left = *tail;
if (*tail != NULL) {
(*tail)->right = root;
}
*tail = root;
bintree2listUtil(root->right, head, tail);
}
// The main function that first calls
// bintree2listUtil()
node* bintree2list(node* root)
{
// Base case
if (root == NULL)
return root;
node* head = NULL;
node* tail = NULL;
bintree2listUtil(root, &head, &tail);
return head;
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
node* newNode(int data)
{
node* new_node = new node();
new_node->data = data;
new_node->left = new_node->right = NULL;
return (new_node);
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list */
void printList(node* node)
{
while (node != NULL) {
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->right;
}
}
/* Driver code*/
int main()
{
// Let us create the tree shown in above diagram
node* root = newNode(10);
root->left = newNode(12);
root->right = newNode(15);
root->left->left = newNode(25);
root->left->right = newNode(30);
root->right->left = newNode(36);
// Convert to DLL
node* head = bintree2list(root);
// Print the converted list
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra
Java
// A Java program for in-place
// conversion of Binary Tree to DLL
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
/* A binary tree node has data,
and left and right pointers */
static class node {
int data;
node left;
node right;
};
/*
* This is the core function to convert Tree to list.
*/
static node head, tail;
static void bintree2listUtil(node root)
{
if (root == null)
return ;
node left = root.left;
node right = root.right;
bintree2listUtil(root.left);
if (head == null) {
head = root;
}
root.left = tail;
if (tail != null) {
(tail).right = root;
}
tail = root;
bintree2listUtil(root.right);
}
// The main function that first calls
// bintree2listUtil()
static void bintree2list(node root)
{
// Base case
if (root == null)
head= root;
bintree2listUtil(root);
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and null left and right pointers. */
static node newNode(int data)
{
node new_node = new node();
new_node.data = data;
new_node.left = new_node.right = null;
return (new_node);
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list */
static void printList()
{
while (head != null) {
System.out.print(head.data+ " ");
head = head.right;
}
}
/* Driver code */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Let us create the tree shown in above diagram
node root = newNode(10);
root.left = newNode(12);
root.right = newNode(15);
root.left.left = newNode(25);
root.left.right = newNode(30);
root.right.left = newNode(36);
head = null;
tail = null;
// Convert to DLL
bintree2list(root);
// Print the converted list
printList();
}
}
// This code is contributed by umadevi9616
C#
// A C# program for in-place
// conversion of Binary Tree to DLL
using System;
public class GFG {
/*
* A binary tree node has data, and left and right pointers
*/
public class node {
public int data;
public node left;
public node right;
};
/*
* This is the core function to convert Tree to list.
*/
static node head, tail;
static void bintree2listUtil(node root) {
if (root == null)
return;
node left = root.left;
node right = root.right;
bintree2listUtil(root.left);
if (head == null) {
head = root;
}
root.left = tail;
if (tail != null) {
(tail).right = root;
}
tail = root;
bintree2listUtil(root.right);
}
// The main function that first calls
// bintree2listUtil()
static void bintree2list(node root) {
// Base case
if (root == null)
head = root;
bintree2listUtil(root);
}
/*
* Helper function that allocates a new node with the given data and null left
* and right pointers.
*/
static node newNode(int data) {
node new_node = new node();
new_node.data = data;
new_node.left = new_node.right = null;
return (new_node);
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list */
static void printList() {
while (head != null) {
Console.Write(head.data + " ");
head = head.right;
}
}
/* Driver code */
public static void Main(String[] args) {
// Let us create the tree shown in above diagram
node root = newNode(10);
root.left = newNode(12);
root.right = newNode(15);
root.left.left = newNode(25);
root.left.right = newNode(30);
root.right.left = newNode(36);
head = null;
tail = null;
// Convert to DLL
bintree2list(root);
// Print the converted list
printList();
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
Javascript
<script>
// A javascript program for in-place
// conversion of Binary Tree to DLL
/*
* A binary tree node has data, and left and right pointers
*/
class Node {
constructor() {
this.data = 0;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
/*
* This is the core function to convert Tree to list.
*/
var head, tail;
function bintree2listUtil(root) {
if (root == null)
return;
var left = root.left;
var right = root.right;
bintree2listUtil(root.left);
if (head == null) {
head = root;
}
root.left = tail;
if (tail != null) {
(tail).right = root;
}
tail = root;
bintree2listUtil(root.right);
}
// The main function that first calls
// bintree2listUtil()
function bintree2list( root) {
// Base case
if (root == null)
head = root;
bintree2listUtil(root);
}
/*
* Helper function that allocates a new node with the given data and null left
* and right pointers.
*/
function newNode(data) {
var new_node = new Node();
new_node.data = data;
new_node.left = new_node.right = null;
return (new_node);
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list */
function printList() {
while (head != null) {
document.write(head.data + " ");
head = head.right;
}
}
/* Driver code */
// Let us create the tree shown in above diagram
var root = newNode(10);
root.left = newNode(12);
root.right = newNode(15);
root.left.left = newNode(25);
root.left.right = newNode(30);
root.right.left = newNode(36);
head = null;
tail = null;
// Convert to DLL
bintree2list(root);
// Print the converted list
printList();
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
</script>
25 12 30 10 36 15
Este artículo fue compilado por Ashish Mangla y revisado por el equipo de GeeksforGeeks. Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
También le puede interesar ver Convertir un árbol binario dado en una lista doblemente enlazada | Set 2 para otra solución simple y eficiente.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA
