Dado un árbol binario, conviértalo en una lista circular doblemente enlazada (in situ).
- Los punteros izquierdo y derecho en los Nodes se utilizarán como punteros anterior y siguiente, respectivamente, en la Lista enlazada circular convertida.
- El orden de los Nodes en la Lista debe ser el mismo que en Inorder para el Árbol Binario dado.
- El primer Node del recorrido Inorder debe ser el Node principal de la Lista circular.
Ejemplo:
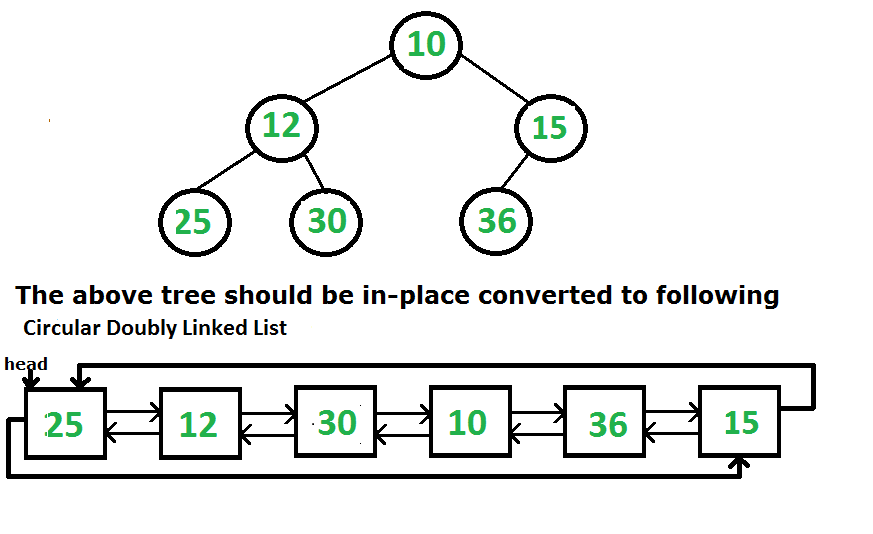
La idea se puede describir usando los pasos a continuación.
- Escriba una función de propósito general que concatene dos listas dobles circulares dadas (esta función se explica a continuación).
- Ahora atraviesa el árbol dado
- Convierta recursivamente el subárbol izquierdo en una DLL circular. Deje que la lista convertida sea leftList.
- Convierta recursivamente el subárbol derecho en una DLL circular. Deje que la lista convertida sea rightList.
- Haga una lista enlazada circular de la raíz del árbol, haga que la raíz izquierda y derecha apunten a sí misma.
- Concatene leftList con la lista del Node raíz único.
- Concatene la lista producida en el paso anterior (d) con rightList.
Tenga en cuenta que el código anterior atraviesa el árbol en modo Postorder. También podemos atravesar en orden. Primero podemos concatenar el subárbol izquierdo y la raíz, luego recurrir al subárbol derecho y concatenar el resultado con la concatenación de la raíz izquierda.
¿Cómo concatenar dos archivos DLL circulares?
- Obtenga el último Node de la lista de la izquierda. Recuperar el último Node es una operación O(1) ya que el puntero anterior del encabezado apunta al último Node de la lista.
- Conéctelo con el primer Node de la lista de la derecha
- Obtener el último Node de la segunda lista
- Conéctelo con el encabezado de la lista.
A continuación se presentan implementaciones de la idea anterior.
C++
// C++ Program to convert a Binary Tree
// to a Circular Doubly Linked List
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// To represents a node of a Binary Tree
struct Node {
struct Node *left, *right;
int data;
};
// A function that appends rightList at the end
// of leftList.
Node* concatenate(Node* leftList, Node* rightList)
{
// If either of the list is empty
// then return the other list
if (leftList == NULL)
return rightList;
if (rightList == NULL)
return leftList;
// Store the last Node of left List
Node* leftLast = leftList->left;
// Store the last Node of right List
Node* rightLast = rightList->left;
// Connect the last node of Left List
// with the first Node of the right List
leftLast->right = rightList;
rightList->left = leftLast;
// Left of first node points to
// the last node in the list
leftList->left = rightLast;
// Right of last node refers to the first
// node of the List
rightLast->right = leftList;
return leftList;
}
// Function converts a tree to a circular Linked List
// and then returns the head of the Linked List
Node* bTreeToCList(Node* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
// Recursively convert left and right subtrees
Node* left = bTreeToCList(root->left);
Node* right = bTreeToCList(root->right);
// Make a circular linked list of single node
// (or root). To do so, make the right and
// left pointers of this node point to itself
root->left = root->right = root;
// Step 1 (concatenate the left list with the list
// with single node, i.e., current node)
// Step 2 (concatenate the returned list with the
// right List)
return concatenate(concatenate(left, root), right);
}
// Display Circular Link List
void displayCList(Node* head)
{
cout << "Circular Linked List is :\n";
Node* itr = head;
do {
cout << itr->data << " ";
itr = itr->right;
} while (head != itr);
cout << "\n";
}
// Create a new Node and return its address
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node* temp = new Node();
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Driver Program to test above function
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(10);
root->left = newNode(12);
root->right = newNode(15);
root->left->left = newNode(25);
root->left->right = newNode(30);
root->right->left = newNode(36);
Node* head = bTreeToCList(root);
displayCList(head);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Aditya Kumar (adityakumar129)
C
// C Program to convert a Binary Tree
// to a Circular Doubly Linked List
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// To represents a node of a Binary Tree
typedef struct Node {
struct Node *left, *right;
int data;
} Node;
// A function that appends rightList at the end
// of leftList.
Node* concatenate(Node* leftList, Node* rightList)
{
// If either of the list is empty
// then return the other list
if (leftList == NULL)
return rightList;
if (rightList == NULL)
return leftList;
// Store the last Node of left List
Node* leftLast = leftList->left;
// Store the last Node of right List
Node* rightLast = rightList->left;
// Connect the last node of Left List
// with the first Node of the right List
leftLast->right = rightList;
rightList->left = leftLast;
// Left of first node points to
// the last node in the list
leftList->left = rightLast;
// Right of last node refers to the first
// node of the List
rightLast->right = leftList;
return leftList;
}
// Function converts a tree to a circular Linked List
// and then returns the head of the Linked List
Node* bTreeToCList(Node* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
// Recursively convert left and right subtrees
Node* left = bTreeToCList(root->left);
Node* right = bTreeToCList(root->right);
// Make a circular linked list of single node
// (or root). To do so, make the right and
// left pointers of this node point to itself
root->left = root->right = root;
// Step 1 (concatenate the left list with the list
// with single node, i.e., current node)
// Step 2 (concatenate the returned list with the
// right List)
return concatenate(concatenate(left, root), right);
}
// Display Circular Link List
void displayCList(Node* head)
{
printf("Circular Linked List is :\n");
Node* itr = head;
do {
printf("%d ", itr->data);
itr = itr->right;
} while (head != itr);
printf("\n");
}
// Create a new Node and return its address
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node* temp = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Driver Program to test above function
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(10);
root->left = newNode(12);
root->right = newNode(15);
root->left->left = newNode(25);
root->left->right = newNode(30);
root->right->left = newNode(36);
Node* head = bTreeToCList(root);
displayCList(head);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Aditya Kumar (adityakumar129)
Java
// Java Program to convert a Binary Tree to a
// Circular Doubly Linked List
// Node class represents a Node of a Tree
class Node
{
int val;
Node left,right;
public Node(int val)
{
this.val = val;
left = right = null;
}
}
// A class to represent a tree
class Tree
{
Node root;
public Tree()
{
root = null;
}
// concatenate both the lists and returns the head
// of the List
public Node concatenate(Node leftList,Node rightList)
{
// If either of the list is empty, then
// return the other list
if (leftList == null)
return rightList;
if (rightList == null)
return leftList;
// Store the last Node of left List
Node leftLast = leftList.left;
// Store the last Node of right List
Node rightLast = rightList.left;
// Connect the last node of Left List
// with the first Node of the right List
leftLast.right = rightList;
rightList.left = leftLast;
// left of first node refers to
// the last node in the list
leftList.left = rightLast;
// Right of last node refers to the first
// node of the List
rightLast.right = leftList;
// Return the Head of the List
return leftList;
}
// Method converts a tree to a circular
// Link List and then returns the head
// of the Link List
public Node bTreeToCList(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
return null;
// Recursively convert left and right subtrees
Node left = bTreeToCList(root.left);
Node right = bTreeToCList(root.right);
// Make a circular linked list of single node
// (or root). To do so, make the right and
// left pointers of this node point to itself
root.left = root.right = root;
// Step 1 (concatenate the left list with the list
// with single node, i.e., current node)
// Step 2 (concatenate the returned list with the
// right List)
return concatenate(concatenate(left, root), right);
}
// Display Circular Link List
public void display(Node head)
{
System.out.println("Circular Linked List is :");
Node itr = head;
do
{
System.out.print(itr.val+ " " );
itr = itr.right;
}
while (itr != head);
System.out.println();
}
}
// Driver Code
class Main
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Build the tree
Tree tree = new Tree();
tree.root = new Node(10);
tree.root.left = new Node(12);
tree.root.right = new Node(15);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(25);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(30);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(36);
// head refers to the head of the Link List
Node head = tree.bTreeToCList(tree.root);
// Display the Circular LinkedList
tree.display(head);
}
}
Python3
# Python3 Program to convert a Binary
# Tree to a Circular Doubly Linked List
class newNode:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = self.right = None
# A function that appends rightList
# at the end of leftList.
def concatenate(leftList, rightList):
# If either of the list is empty
# then return the other list
if (leftList == None):
return rightList
if (rightList == None):
return leftList
# Store the last Node of left List
leftLast = leftList.left
# Store the last Node of right List
rightLast = rightList.left
# Connect the last node of Left List
# with the first Node of the right List
leftLast.right = rightList
rightList.left = leftLast
# Left of first node points to
# the last node in the list
leftList.left = rightLast
# Right of last node refers to
# the first node of the List
rightLast.right = leftList
return leftList
# Function converts a tree to a circular
# Linked List and then returns the head
# of the Linked List
def bTreeToCList(root):
if (root == None):
return None
# Recursively convert left and
# right subtrees
left = bTreeToCList(root.left)
right = bTreeToCList(root.right)
# Make a circular linked list of single
# node (or root). To do so, make the
# right and left pointers of this node
# point to itself
root.left = root.right = root
# Step 1 (concatenate the left list
# with the list with single
# node, i.e., current node)
# Step 2 (concatenate the returned list
# with the right List)
return concatenate(concatenate(left,
root), right)
# Display Circular Link List
def displayCList(head):
print("Circular Linked List is :")
itr = head
first = 1
while (head != itr or first):
print(itr.data, end = " ")
itr = itr.right
first = 0
print()
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = newNode(10)
root.left = newNode(12)
root.right = newNode(15)
root.left.left = newNode(25)
root.left.right = newNode(30)
root.right.left = newNode(36)
head = bTreeToCList(root)
displayCList(head)
# This code is contributed by PranchalK
C#
// C# Program to convert a Binary Tree
// to a Circular Doubly Linked List
using System;
// Node class represents a Node of a Tree
public class Node
{
public int val;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int val)
{
this.val = val;
left = right = null;
}
}
// A class to represent a tree
public class Tree
{
internal Node root;
public Tree()
{
root = null;
}
// concatenate both the lists
// and returns the head of the List
public virtual Node concatenate(Node leftList,
Node rightList)
{
// If either of the list is empty,
// then return the other list
if (leftList == null)
{
return rightList;
}
if (rightList == null)
{
return leftList;
}
// Store the last Node of left List
Node leftLast = leftList.left;
// Store the last Node of right List
Node rightLast = rightList.left;
// Connect the last node of Left List
// with the first Node of the right List
leftLast.right = rightList;
rightList.left = leftLast;
// left of first node refers to
// the last node in the list
leftList.left = rightLast;
// Right of last node refers to
// the first node of the List
rightLast.right = leftList;
// Return the Head of the List
return leftList;
}
// Method converts a tree to a circular
// Link List and then returns the head
// of the Link List
public virtual Node bTreeToCList(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
{
return null;
}
// Recursively convert left
// and right subtrees
Node left = bTreeToCList(root.left);
Node right = bTreeToCList(root.right);
// Make a circular linked list of single
// node (or root). To do so, make the
// right and left pointers of this node
// point to itself
root.left = root.right = root;
// Step 1 (concatenate the left list with
// the list with single node,
// i.e., current node)
// Step 2 (concatenate the returned list
// with the right List)
return concatenate(concatenate(left, root), right);
}
// Display Circular Link List
public virtual void display(Node head)
{
Console.WriteLine("Circular Linked List is :");
Node itr = head;
do
{
Console.Write(itr.val + " ");
itr = itr.right;
} while (itr != head);
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// Driver Code
public class GFG
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Build the tree
Tree tree = new Tree();
tree.root = new Node(10);
tree.root.left = new Node(12);
tree.root.right = new Node(15);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(25);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(30);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(36);
// head refers to the head of the Link List
Node head = tree.bTreeToCList(tree.root);
// Display the Circular LinkedList
tree.display(head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13
Javascript
<script>
// javascript Program to convert a Binary Tree to a
// Circular Doubly Linked List
// Node class represents a Node of a Tree
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.val = val;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
// A class to represent a
var root = null;
// concatenate both the lists and returns the head
// of the List
function concatenate(leftList, rightList) {
// If either of the list is empty, then
// return the other list
if (leftList == null)
return rightList;
if (rightList == null)
return leftList;
// Store the last Node of left List
var leftLast = leftList.left;
// Store the last Node of right List
var rightLast = rightList.left;
// Connect the last node of Left List
// with the first Node of the right List
leftLast.right = rightList;
rightList.left = leftLast;
// left of first node refers to
// the last node in the list
leftList.left = rightLast;
// Right of last node refers to the first
// node of the List
rightLast.right = leftList;
// Return the Head of the List
return leftList;
}
// Method converts a to a circular
// Link List and then returns the head
// of the Link List
function bTreeToCList(root) {
if (root == null)
return null;
// Recursively convert left and right subtrees
var left = bTreeToCList(root.left);
var right = bTreeToCList(root.right);
// Make a circular linked list of single node
// (or root). To do so, make the right and
// left pointers of this node point to itself
root.left = root.right = root;
// Step 1 (concatenate the left list with the list
// with single node, i.e., current node)
// Step 2 (concatenate the returned list with the
// right List)
return concatenate(concatenate(left, root), right);
}
// Display Circular Link List
function display(head) {
document.write("Circular Linked List is :<br/>");
var itr = head;
do {
document.write(itr.val + " ");
itr = itr.right;
} while (itr != head);
document.write();
}
// Driver Code
// Build the
root = new Node(10);
root.left = new Node(12);
root.right = new Node(15);
root.left.left = new Node(25);
root.left.right = new Node(30);
root.right.left = new Node(36);
// head refers to the head of the Link List
var head = bTreeToCList(root);
// Display the Circular LinkedList
display(head);
// This code contributed by umadevi9616
</script>
Circular Linked List is : 25 12 30 10 36 15
Complejidad de tiempo: O(N)
Como cada Node se visita como máximo una vez.
Espacio auxiliar: O(log N)
El espacio adicional se usa en la pila de llamadas recursivas que puede crecer hasta un tamaño máximo de logN, ya que es un árbol binario.
Otro enfoque:
el algoritmo anterior puede ser difícil de entender, por lo que aquí hay otro enfoque que tiene las mismas complejidades de tiempo y espacio, pero utiliza la idea de esta publicación Convertir un árbol binario dado en una lista doblemente vinculada . Primero convertimos el árbol binario dado en una lista doblemente enlazada y luego convertimos esta lista doblemente enlazada en una lista circular enlazada.
Este enfoque fue aportado por Abhijeet Kumar
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// A C++ program for in-place conversion of Binary Tree to CDLL
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has - data , left and right pointers */
struct Node
{
int data;
Node* left;
Node* right;
};
// A utility function that converts given binary tree to
// a doubly linked list
// root --> the root of the binary tree
// head --> head of the created doubly linked list
Node *BTree2DoublyLinkedList(Node *root, Node **head)
{
// Base case
if (root == NULL)
return root;
// Initialize previously visited node as NULL. This is
// static so that the same value is accessible in all recursive
// calls
static Node* prev = NULL;
// Recursively convert left subtree
BTree2DoublyLinkedList(root->left, head);
// Now convert this node
if (prev == NULL)
*head = root;
else
{
root->left = prev;
prev->right = root;
}
prev = root;
// Finally convert right subtree
BTree2DoublyLinkedList(root->right, head);
return prev;
}
// A simple recursive function to convert a given Binary tree to
// Circular Doubly Linked List using a utility function
// root --> Root of Binary Tree
// tail --> Pointer to tail node of created circular doubly linked list
Node* BTree2CircularDoublyLinkedList(Node *root)
{
Node *head = NULL;
Node *tail = BTree2DoublyLinkedList(root, &head);
// make the changes to convert a DLL to CDLL
tail->right = head;
head->left = tail;
// return the head of the created CDLL
return head;
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node* new_node = new Node;
new_node->data = data;
new_node->left = new_node->right = NULL;
return (new_node);
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given circular doubly linked list */
void printList(Node *head)
{
if(head==NULL)
return;
Node *ptr = head;
do
{
cout << ptr->data << " ";
ptr = ptr->right;
}while(ptr!=head);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
// Let us create the tree shown in above diagram
Node *root = newNode(10);
root->left = newNode(12);
root->right = newNode(15);
root->left->left = newNode(25);
root->left->right = newNode(30);
root->right->left = newNode(36);
// Convert to DLL
Node *head = BTree2CircularDoublyLinkedList(root);
// Print the converted list
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// This code was contributed by Abhijeet Kumar(abhijeet19403)
Java
// A Java program for in-place conversion of Binary Tree to CDLL
// A binary tree node has - data, left pointer and right pointer
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
// head --> Pointer to head node of created doubly linked list
Node head;
// Initialize previously visited node as NULL. This is
// static so that the same value is accessible in all recursive
// calls
static Node prev = null;
// A simple utility recursive function to convert a given Binary tree
// to Doubly Linked List
// root --> Root of Binary Tree
void BTree2DoublyLinkedList(Node root)
{
// Base case
if (root == null)
return;
// Recursively convert left subtree
BTree2DoublyLinkedList(root.left);
// Now convert this node
if (prev == null)
head = root;
else
{
root.left = prev;
prev.right = root;
}
prev = root;
// Finally convert right subtree
BTree2DoublyLinkedList(root.right);
}
// A simple function to convert a given binary tree to Circular doubly linked list
// using a utility function
void BTree2CircularDoublyLinkedList(Node root)
{
BTree2DoublyLinkedList(root);
// make the changes to convert a DLL to CDLL
prev.right = head;
head.left = prev;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list */
void printList(Node node)
{
if(node == null)
return;
Node curr = node;
do
{
System.out.print(curr.data + " ");
curr = curr.right;
}while(curr!=node);
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Let us create the tree as shown in above diagram
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(10);
tree.root.left = new Node(12);
tree.root.right = new Node(15);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(25);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(30);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(36);
// convert to DLL
tree.BTree2CircularDoublyLinkedList(tree.root);
// Print the converted List
tree.printList(tree.head);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Abhijeet Kumar(abhijeet19403)
C#
// A C# program for in-place conversion of Binary Tree to
// CDLL
using System;
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree {
Node root;
// head --> Pointer to head node of created doubly
// linked list
Node head;
// Initialize previously visited node as NULL. This is
// static so that the same value is accessible in all
// recursive calls
static Node prev = null;
// A simple utility recursive function to convert a
// given Binary tree to Doubly Linked List root --> Root
// of Binary Tree
void BTree2DoublyLinkedList(Node root)
{
// Base case
if (root == null)
return;
// Recursively convert left subtree
BTree2DoublyLinkedList(root.left);
// Now convert this node
if (prev == null)
head = root;
else {
root.left = prev;
prev.right = root;
}
prev = root;
// Finally convert right subtree
BTree2DoublyLinkedList(root.right);
}
// A simple function to convert a given binary tree to
// Circular doubly linked list
// using a utility function
void BTree2CircularDoublyLinkedList(Node root)
{
BTree2DoublyLinkedList(root);
// make the changes to convert a DLL to CDLL
prev.right = head;
head.left = prev;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list
*/
void printList(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
Node curr = node;
do {
Console.Write(curr.data + " ");
curr = curr.right;
} while (curr != node);
}
static public void Main()
{
// Let us create the tree as shown in above diagram
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(10);
tree.root.left = new Node(12);
tree.root.right = new Node(15);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(25);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(30);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(36);
// convert to DLL
tree.BTree2CircularDoublyLinkedList(tree.root);
// Print the converted List
tree.printList(tree.head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by lokesh(lokeshmvs21).
25 12 30 10 36 15
Complejidad de tiempo: O(N)
Como cada Node se visita como máximo una vez.
Espacio auxiliar: O(log N)
El espacio adicional se usa en la pila de llamadas de funciones recursivas que puede crecer hasta un tamaño máximo de logN.
Este artículo es una contribución de Chirag Agarwal . Si te gusta GeeksforGeeks y te gustaría contribuir, también puedes escribir un artículo usando write.geeksforgeeks.org o enviar tu artículo por correo a review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA
