Hay n ciudades y hay carreteras entre algunas de las ciudades. De alguna manera todos los caminos están dañados simultáneamente. Tenemos que reparar las carreteras para volver a conectar las ciudades. Hay un costo fijo para reparar un camino en particular. Descubre el coste mínimo para conectar todas las ciudades reparando carreteras. La entrada está en forma de array (ciudad), si ciudad[i][j] = 0, entonces no hay ningún camino entre la ciudad i y la ciudad j, si ciudad[i][j] = a > 0, entonces el costo de reconstruir el camino entre la ciudad i y la ciudad j es a. Imprime el costo mínimo para conectar todas las ciudades.
Es seguro que todas las ciudades estaban conectadas antes de que se dañaran las carreteras.
Ejemplos:
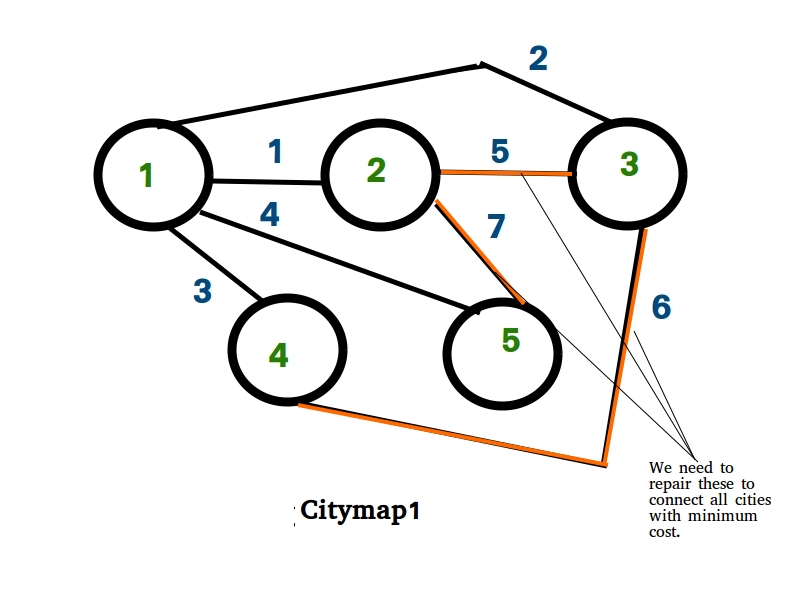
Input : {{0, 1, 2, 3, 4},
{1, 0, 5, 0, 7},
{2, 5, 0, 6, 0},
{3, 0, 6, 0, 0},
{4, 7, 0, 0, 0}};
Output : 10
Input : {{0, 1, 1, 100, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{100, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2},
{0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 2},
{0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 0}};
Output : 106
Método: Aquí tenemos que conectar todas las ciudades por el camino que menos nos cueste. La forma de hacerlo es averiguar el árbol de expansión mínimo ( MST ) del mapa de las ciudades (es decir, cada ciudad es un Node del gráfico y todas las carreteras dañadas entre ciudades son bordes). Y el costo total es la suma de los valores del borde de la ruta en el árbol de expansión mínimo.
Prerrequisito: Algoritmo de MST Prim
C++
// C++ code to find out minimum cost
// path to connect all the cities
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to find out minimum valued node
// among the nodes which are not yet included in MST
int minnode(int n, int keyval[], bool mstset[]) {
int mini = numeric_limits<int>::max();
int mini_index;
// Loop through all the values of the nodes
// which are not yet included in MST and find
// the minimum valued one.
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (mstset[i] == false && keyval[i] < mini) {
mini = keyval[i], mini_index = i;
}
}
return mini_index;
}
// Function to find out the MST and
// the cost of the MST.
void findcost(int n, vector<vector<int>> city) {
// Array to store the parent node of a
// particular node.
int parent[n];
// Array to store key value of each node.
int keyval[n];
// Boolean Array to hold bool values whether
// a node is included in MST or not.
bool mstset[n];
// Set all the key values to infinite and
// none of the nodes is included in MST.
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
keyval[i] = numeric_limits<int>::max();
mstset[i] = false;
}
// Start to find the MST from node 0.
// Parent of node 0 is none so set -1.
// key value or minimum cost to reach
// 0th node from 0th node is 0.
parent[0] = -1;
keyval[0] = 0;
// Find the rest n-1 nodes of MST.
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
// First find out the minimum node
// among the nodes which are not yet
// included in MST.
int u = minnode(n, keyval, mstset);
// Now the uth node is included in MST.
mstset[u] = true;
// Update the values of neighbor
// nodes of u which are not yet
// included in MST.
for (int v = 0; v < n; v++) {
if (city[u][v] && mstset[v] == false &&
city[u][v] < keyval[v]) {
keyval[v] = city[u][v];
parent[v] = u;
}
}
}
// Find out the cost by adding
// the edge values of MST.
int cost = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
cost += city[parent[i]][i];
cout << cost << endl;
}
// Utility Program:
int main() {
// Input 1
int n1 = 5;
vector<vector<int>> city1 = {{0, 1, 2, 3, 4},
{1, 0, 5, 0, 7},
{2, 5, 0, 6, 0},
{3, 0, 6, 0, 0},
{4, 7, 0, 0, 0}};
findcost(n1, city1);
// Input 2
int n2 = 6;
vector<vector<int>> city2 = {{0, 1, 1, 100, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{100, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2},
{0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 2},
{0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 0}};
findcost(n2, city2);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java code to find out minimum cost
// path to connect all the cities
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to find out minimum valued node
// among the nodes which are not yet included
// in MST
static int minnode(int n, int keyval[],
boolean mstset[])
{
int mini = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int mini_index = 0;
// Loop through all the values of the nodes
// which are not yet included in MST and find
// the minimum valued one.
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (mstset[i] == false &&
keyval[i] < mini)
{
mini = keyval[i];
mini_index = i;
}
}
return mini_index;
}
// Function to find out the MST and
// the cost of the MST.
static void findcost(int n, int city[][])
{
// Array to store the parent node of a
// particular node.
int parent[] = new int[n];
// Array to store key value of each node.
int keyval[] = new int[n];
// Boolean Array to hold bool values whether
// a node is included in MST or not.
boolean mstset[] = new boolean[n];
// Set all the key values to infinite and
// none of the nodes is included in MST.
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
keyval[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
mstset[i] = false;
}
// Start to find the MST from node 0.
// Parent of node 0 is none so set -1.
// key value or minimum cost to reach
// 0th node from 0th node is 0.
parent[0] = -1;
keyval[0] = 0;
// Find the rest n-1 nodes of MST.
for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
// First find out the minimum node
// among the nodes which are not yet
// included in MST.
int u = minnode(n, keyval, mstset);
// Now the uth node is included in MST.
mstset[u] = true;
// Update the values of neighbor
// nodes of u which are not yet
// included in MST.
for(int v = 0; v < n; v++)
{
if (city[u][v] > 0 &&
mstset[v] == false &&
city[u][v] < keyval[v])
{
keyval[v] = city[u][v];
parent[v] = u;
}
}
}
// Find out the cost by adding
// the edge values of MST.
int cost = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)
cost += city[parent[i]][i];
System.out.println(cost);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Input 1
int n1 = 5;
int city1[][] = { { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 1, 0, 5, 0, 7 },
{ 2, 5, 0, 6, 0 },
{ 3, 0, 6, 0, 0 },
{ 4, 7, 0, 0, 0 } };
findcost(n1, city1);
// Input 2
int n2 = 6;
int city2[][] = { { 0, 1, 1, 100, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 100, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 2 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 0 } };
findcost(n2, city2);
}
}
// This code is contributed by adityapande88
Python3
# Python3 code to find out minimum cost # path to connect all the cities # Function to find out minimum valued # node among the nodes which are not # yet included in MST def minnode(n, keyval, mstset): mini = 999999999999 mini_index = None # Loop through all the values of # the nodes which are not yet # included in MST and find the # minimum valued one. for i in range(n): if (mstset[i] == False and keyval[i] < mini): mini = keyval[i] mini_index = i return mini_index # Function to find out the MST and # the cost of the MST. def findcost(n, city): # Array to store the parent # node of a particular node. parent = [None] * n # Array to store key value # of each node. keyval = [None] * n # Boolean Array to hold bool # values whether a node is # included in MST or not. mstset = [None] * n # Set all the key values to infinite and # none of the nodes is included in MST. for i in range(n): keyval[i] = 9999999999999 mstset[i] = False # Start to find the MST from node 0. # Parent of node 0 is none so set -1. # key value or minimum cost to reach # 0th node from 0th node is 0. parent[0] = -1 keyval[0] = 0 # Find the rest n-1 nodes of MST. for i in range(n - 1): # First find out the minimum node # among the nodes which are not yet # included in MST. u = minnode(n, keyval, mstset) # Now the uth node is included in MST. mstset[u] = True # Update the values of neighbor # nodes of u which are not yet # included in MST. for v in range(n): if (city[u][v] and mstset[v] == False and city[u][v] < keyval[v]): keyval[v] = city[u][v] parent[v] = u # Find out the cost by adding # the edge values of MST. cost = 0 for i in range(1, n): cost += city[parent[i]][i] print(cost) # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': # Input 1 n1 = 5 city1 = [[0, 1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 0, 5, 0, 7], [2, 5, 0, 6, 0], [3, 0, 6, 0, 0], [4, 7, 0, 0, 0]] findcost(n1, city1) # Input 2 n2 = 6 city2 = [[0, 1, 1, 100, 0, 0], [1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0], [1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0], [100, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2], [0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 2], [0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 0]] findcost(n2, city2) # This code is contributed by PranchalK
C#
// C# code to find out minimum cost
// path to connect all the cities
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to find out minimum valued node
// among the nodes which are not yet included
// in MST
static int minnode(int n, int[] keyval,
bool[] mstset)
{
int mini = Int32.MaxValue;
int mini_index = 0;
// Loop through all the values of the nodes
// which are not yet included in MST and find
// the minimum valued one.
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (mstset[i] == false && keyval[i] < mini)
{
mini = keyval[i];
mini_index = i;
}
}
return mini_index;
}
// Function to find out the MST and
// the cost of the MST.
static void findcost(int n, int[,] city)
{
// Array to store the parent node of a
// particular node.
int[] parent = new int[n];
// Array to store key value of each node.
int[] keyval = new int[n];
// Boolean Array to hold bool values whether
// a node is included in MST or not.
bool[] mstset = new bool[n];
// Set all the key values to infinite and
// none of the nodes is included in MST.
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
keyval[i] = Int32.MaxValue;
mstset[i] = false;
}
// Start to find the MST from node 0.
// Parent of node 0 is none so set -1.
// key value or minimum cost to reach
// 0th node from 0th node is 0.
parent[0] = -1;
keyval[0] = 0;
// Find the rest n-1 nodes of MST.
for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
// First find out the minimum node
// among the nodes which are not yet
// included in MST.
int u = minnode(n, keyval, mstset);
// Now the uth node is included in MST.
mstset[u] = true;
// Update the values of neighbor
// nodes of u which are not yet
// included in MST.
for(int v = 0; v < n; v++)
{
if (city[u, v] > 0 && mstset[v] == false &&
city[u, v] < keyval[v])
{
keyval[v] = city[u, v];
parent[v] = u;
}
}
}
// Find out the cost by adding
// the edge values of MST.
int cost = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)
cost += city[parent[i], i];
Console.WriteLine(cost);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Input 1
int n1 = 5;
int[,] city1 = { { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 1, 0, 5, 0, 7 },
{ 2, 5, 0, 6, 0 },
{ 3, 0, 6, 0, 0 },
{ 4, 7, 0, 0, 0 } };
findcost(n1, city1);
// Input 2
int n2 = 6;
int[,] city2 = { { 0, 1, 1, 100, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 100, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 2 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 0 } };
findcost(n2, city2);
}
}
// This code is contributed by ukasp
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript code to find out minimum cost
// path to connect all the cities
// Function to find out minimum valued node
// among the nodes which are not yet included
// in MST
function minnode(n, keyval,
mstset)
{
let mini = Number.MAX_VALUE;
let mini_index = 0;
// Loop through all the values of the nodes
// which are not yet included in MST and find
// the minimum valued one.
for(let i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (mstset[i] == false &&
keyval[i] < mini)
{
mini = keyval[i];
mini_index = i;
}
}
return mini_index;
}
// Function to find out the MST and
// the cost of the MST.
function findcost(n, city)
{
// Array to store the parent node of a
// particular node.
let parent = Array(n).fill(0);
// Array to store key value of each node.
let keyval = Array(n).fill(0);
// Boolean Array to hold bool values whether
// a node is included in MST or not.
let mstset = Array(n).fill(0);
// Set all the key values to infinite and
// none of the nodes is included in MST.
for(let i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
keyval[i] = Number.MAX_VALUE;
mstset[i] = false;
}
// Start to find the MST from node 0.
// Parent of node 0 is none so set -1.
// key value or minimum cost to reach
// 0th node from 0th node is 0.
parent[0] = -1;
keyval[0] = 0;
// Find the rest n-1 nodes of MST.
for(let i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
// First find out the minimum node
// among the nodes which are not yet
// included in MST.
let u = minnode(n, keyval, mstset);
// Now the uth node is included in MST.
mstset[u] = true;
// Update the values of neighbor
// nodes of u which are not yet
// included in MST.
for(let v = 0; v < n; v++)
{
if (city[u][v] > 0 &&
mstset[v] == false &&
city[u][v] < keyval[v])
{
keyval[v] = city[u][v];
parent[v] = u;
}
}
}
// Find out the cost by adding
// the edge values of MST.
let cost = 0;
for(let i = 1; i < n; i++)
cost += city[parent[i]][i];
document.write(cost + "<br/>") ;
}
// driver code
// Input 1
let n1 = 5;
let city1 = [[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 ],
[ 1, 0, 5, 0, 7 ],
[ 2, 5, 0, 6, 0 ],
[ 3, 0, 6, 0, 0 ],
[ 4, 7, 0, 0, 0 ]];
findcost(n1, city1);
// Input 2
let n2 = 6;
let city2 = [[ 0, 1, 1, 100, 0, 0 ],
[ 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 ],
[ 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 ],
[ 100, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2 ],
[ 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 2 ],
[ 0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 0 ]];
findcost(n2, city2);
</script>
10 106
Complejidad: el ciclo externo (es decir, el ciclo para agregar un nuevo Node a MST) se ejecuta n veces y en cada iteración del ciclo se necesita O (n) tiempo para encontrar el minnode y O (n) tiempo para actualizar los Nodes vecinos de u -th Node. Por lo tanto, la complejidad global es O(n 2 )