Dada una array 2D casas[][] que consta de N coordenadas 2D {x, y} donde cada coordenada representa la ubicación de cada casa, la tarea es encontrar el costo mínimo para conectar todas las casas de la ciudad.
El costo de conectar dos casas es la Distancia Manhattan entre los dos puntos (x i , y i ) y (x j , y j ) es decir, |x i – x j | + |y yo – yj | , donde |p| denota el valor absoluto de p.
Ejemplos:
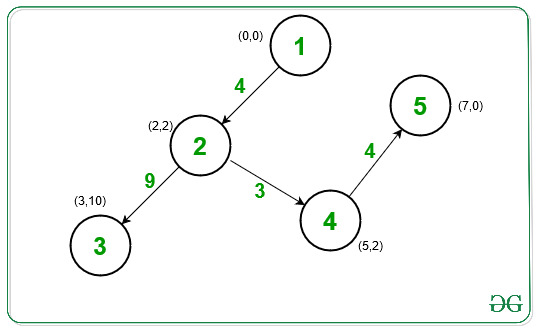
Entrada: casas[][] = [[0, 0], [2, 2], [3, 10], [5, 2], [7, 0]]
Salida: 20
Explicación:Conectar casa 1 (0, 0) con casa 2 (2, 2) con costo = 4
Conectar casa 2 (2, 2) con casa 3 (3, 10) con costo =9
Conectar casa 2 (2, 2) con casa 4 (5, 2) con costo =3
Por último, conecte la casa 4 (5, 2) con la casa 5 (7, 0) con costo 4.
Todas las casas están conectadas ahora.
El costo mínimo general es 4 + 9 + 3 + 4 = 20.Entrada: casas[][] = [[3, 12], [-2, 5], [-4, 1]]
Salida: 18
Explicación:
Conecte la casa 1 (3, 12) con la casa 2 (-2, 5 ) con costo = 12
Conecte la casa 2 (-2, 5) con la casa 3 (-4, 1) con costo = 6
Todas las casas están conectadas ahora.
El costo mínimo general es 12 + 6 = 18.
Enfoque: La idea es crear un gráfico ponderado a partir de la información dada con pesos entre cualquier par de aristas iguales al costo de conectarlos, digamos C i , es decir, la distancia de Manhattan entre las dos coordenadas. Una vez que se genera el gráfico, aplique el Algoritmo de Kruskal para encontrar el árbol de expansión mínimo del gráfico usando Disjoint Set . Finalmente, imprima el costo mínimo.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<int> parent, size;
// Utility function to find set of an
// element v using path compression
// technique
int find_set(int v)
{
// If v is the parent
if (v == parent[v])
return v;
// Otherwise, recursively
// find its parent
return parent[v]
= find_set(parent[v]);
}
// Function to perform union
// of the sets a and b
int union_sets(int a, int b)
{
// Find parent of a and b
a = find_set(a);
b = find_set(b);
// If parent are different
if (a != b) {
// Swap Operation
if (size[a] < size[b])
swap(a, b);
// Update parent of b as a
parent[b] = a;
size[a] += size[b];
return 1;
}
// Otherwise, return 0
return 0;
}
// Function to create a Minimum Cost
// Spanning tree for given houses
void MST(int houses[][2], int n)
{
// Stores adjacency list of graph
vector<pair<int, pair<int, int> > > v;
// Traverse each coordinate
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
// Find the Manhattan distance
int p = abs(houses[i][0]
- houses[j][0]);
p += abs(houses[i][1]
- houses[j][1]);
// Add the edges
v.push_back({ p, { i, j } });
}
}
parent.resize(n);
size.resize(n);
// Sort all the edges
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
// Initialize parent[] and size[]
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i, size[i] = 1;
}
/// Stores the minimum cost
int ans = 0;
// Finding the minimum cost
for (auto x : v) {
// Perform the unioun operation
if (union_sets(x.second.first,
x.second.second)) {
ans += x.first;
}
}
// Print the minimum cost
cout << ans;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given houses
int houses[][2] = { { 0, 0 }, { 2, 2 },
{ 3, 10 }, { 5, 2 },
{ 7, 0 }};
int N = sizeof(houses)
/ sizeof(houses[0]);
// Function Call
MST(houses, N);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
// Class for DSU implementation
class DSU{
int parent[];
int rank[];
// Constructor to initialize DSU
DSU(int n)
{
parent = new int[n];
rank = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
parent[i] = -1;
rank[i] = 1;
}
}
// Utility function to find set of an
// element v using path compression
// technique
int find_set(int v)
{
// If v is the parent
if (parent[v] == -1)
return v;
// Otherwise, recursively
// find its parent
return parent[v] = find_set(parent[v]);
}
// Function to perform union
// of the sets a and b
void union_sets(int a, int b)
{
// Find parent of a and b
int p1 = find_set(a);
int p2 = find_set(b);
// If parent are different
if (p1 != p2)
{
// Swap Operation
if (rank[p1] > rank[p2])
{
parent[p2] = p1;
rank[p1] += rank[p2];
}
else
{
parent[p1] = p2;
rank[p2] += rank[p1];
}
}
}
}
class GFG{
// Function to create a Minimum Cost
// Spanning tree for given houses
static void MST(int houses[][], int n)
{
int ans = 0;
ArrayList<int[]> edges = new ArrayList<>();
// Traverse each coordinate
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
// Find the Manhattan distance
int p = Math.abs(houses[i][0] -
houses[j][0]);
p += Math.abs(houses[i][1] -
houses[j][1]);
// Add the edges
edges.add(new int[]{ p, i, j });
}
}
// Sorting arraylist using custome comparator
// on the basis of weight i.e first element in
// array object stored in Arraylist
Collections.sort(edges, new Comparator<int[]>()
{
@Override public int compare(int[] o1, int[] o2)
{
return Integer.compare(o1[0], o2[0]);
}
});
// Calling DSU class
DSU d = new DSU(n);
for(int i = 0; i < edges.size(); i++)
{
int from = edges.get(i)[1];
int to = edges.get(i)[2];
// Checking if they lie in different component
// or not i.e they have same parent or not in
// DSU
if (d.find_set(from) != d.find_set(to))
{
// Calling union_sets
d.union_sets(from, to);
ans += edges.get(i)[0];
}
}
// Printing the minimum cost
System.out.println(ans);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Graph in form of 2D array
int houses[][] = { { 0, 0 }, { 2, 2 },
{ 3, 10 }, { 5, 2 },
{ 7, 0 } };
int n = houses.length;
// Function Call
MST(houses, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rahul Verma
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach parent = [0] * 100 size = [0] * 100 # Utility function to find set of an # element v using path compression # technique def find_set(v): # If v is the parent if (v == parent[v]): return v # Otherwise, recursively # find its parent parent[v] = find_set(parent[v]) return parent[v] # Function to perform union # of the sets a and b def union_sets(a, b): # Find parent of a and b a = find_set(a) b = find_set(b) # If parent are different if (a != b): # Swap Operation if (size[a] < size[b]): a, b = b, a # Update parent of b as a parent[b] = a size[a] += size[b] return 1 # Otherwise, return 0 return 0 # Function to create a Minimum Cost # Spanning tree for given houses def MST(houses, n): # Stores adjacency list of graph v = [] # Traverse each coordinate for i in range(n): for j in range(i + 1, n): # Find the Manhattan distance p = abs(houses[i][0] - houses[j][0]) p += abs(houses[i][1] - houses[j][1]) # Add the edges v.append([p, i, j]) # Sort all the edges v = sorted(v) # Initialize parent[] and size[] for i in range(n): parent[i] = i size[i] = 1 # Stores the minimum cost ans = 0 # Finding the minimum cost for x in v: # Perform the unioun operation if (union_sets(x[1], x[2])): ans += x[0] # Print the minimum cost print(ans) # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': # Given houses houses = [ [ 0, 0 ], [ 2, 2 ], [ 3, 10 ], [ 5, 2 ], [ 7, 0 ] ] N = len(houses) # Function Call MST(houses, N) # This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program for the above approach
let parent = new Array(100).fill(0)
let size = new Array(100).fill(0)
// Utility function to find set of an
// element v using path compression
// technique
function find_set(v){
// If v is the parent
if (v == parent[v])
return v
// Otherwise, recursively
// find its parent
parent[v] = find_set(parent[v])
return parent[v]
}
// Function to perform union
// of the sets a and b
function union_sets(a, b){
// Find parent of a and b
a = find_set(a)
b = find_set(b)
// If parent are different
if (a != b){
// Swap Operation
if (size[a] < size[b]){
a, b = b, a
}
// Update parent of b as a
parent[b] = a
size[a] += size[b]
return 1
}
// Otherwise, return 0
return 0
}
// Function to create a Minimum Cost
// Spanning tree for given houses
function MST(houses, n){
// Stores adjacency list of graph
let v = []
// Traverse each coordinate
for(let i=0;i<n;i++){
for(let j=i+1;j<n;j++){
// Find the Manhattan distance
let p = Math.abs(houses[i][0] -
houses[j][0])
p += Math.abs(houses[i][1] -
houses[j][1])
// Add the edges
v.push([p, i, j])
}
}
// Sort all the edges
v.sort((a,b)=>a[0]-b[0])
// Initialize parent[] and size[]
for(let i=0;i<n;i++){
parent[i] = i
size[i] = 1
}
// Stores the minimum cost
let ans = 0
// Finding the minimum cost
for(let x of v){
// Perform the unioun operation
if (union_sets(x[1], x[2]))
ans += x[0]
}
// Print the minimum cost
document.write(ans,"</br>")
}
// Driver Code
// Given houses
let houses = [ [ 0, 0 ], [ 2, 2 ], [ 3, 10 ], [ 5, 2 ],[ 7, 0 ] ]
let N = houses.length
// Function Call
MST(houses, N)
// This code is contributed by shinjanpatra
</script>
20
Tiempo Complejidad: O(N 2 )
Espacio Auxiliar: O(N 2 )
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por ankitlunia192 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA