En una publicación anterior , discutimos algunos enfoques para extraer las filas del marco de datos como una lista de Python. En esta publicación, veremos algunos métodos más para lograr ese objetivo.
Nota: para obtener un enlace al archivo CSV utilizado en el código, haga clic aquí .
Solución #1: para acceder a los datos de cada fila del marco de datos de Pandas, podemos usar el DataFrame.ilocatributo y luego podemos agregar los datos de cada fila al final de la lista.
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Create the dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame({'Date':['10/2/2011', '11/2/2011', '12/2/2011', '13/2/11'],
'Event':['Music', 'Poetry', 'Theatre', 'Comedy'],
'Cost':[10000, 5000, 15000, 2000]})
# Print the dataframe
print(df)
Producción :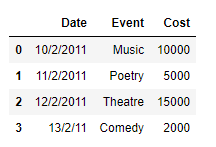
Ahora usaremos el DataFrame.ilocatributo para acceder a los valores de cada fila en el marco de datos y luego construiremos una lista a partir de él.
# Create an empty list Row_list =[] # Iterate over each row for i in range((df.shape[0])): # Using iloc to access the values of # the current row denoted by "i" Row_list.append(list(df.iloc[i, :])) # Print the list print(Row_list)
Salida:
como podemos ver en la salida, hemos extraído con éxito cada fila del marco de datos dado en una lista. Al igual que cualquier otra lista de Python, podemos realizar cualquier operación de lista en la lista extraída.
# Find the length of the newly # created list print(len(Row_list)) # Print the first 3 elements print(Row_list[:3])
Salida: 

Solución n.º 2: para acceder a los datos de cada fila del marco de datos de Pandas, podemos usar el DataFrame.iatatributo y luego podemos agregar los datos de cada fila al final de la lista.
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Create the dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame({'Date':['10/2/2011', '11/2/2011', '12/2/2011', '13/2/11'],
'Event':['Music', 'Poetry', 'Theatre', 'Comedy'],
'Cost':[10000, 5000, 15000, 2000]})
# Create an empty list
Row_list =[]
# Iterate over each row
for i in range((df.shape[0])):
# Create a list to store the data
# of the current row
cur_row =[]
# iterate over all the columns
for j in range(df.shape[1]):
# append the data of each
# column to the list
cur_row.append(df.iat[i, j])
# append the current row to the list
Row_list.append(cur_row)
# Print the list
print(Row_list)
Producción :
# Find the length of the newly # created list print(len(Row_list)) # Print the first 3 elements print(Row_list[:3])
Producción :

Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por Shubham__Ranjan y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA