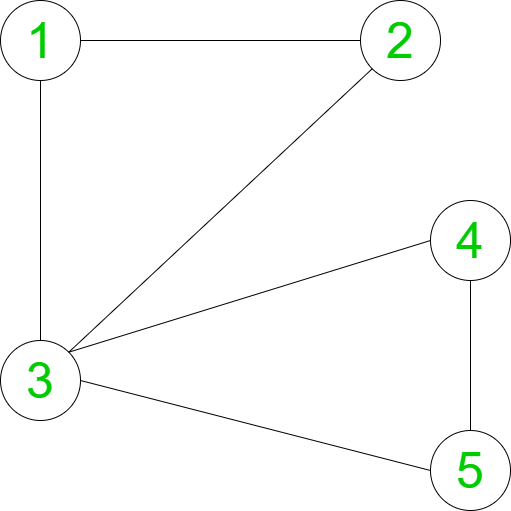
Dado un gráfico con N Nodes y E aristas, la tarea es contar el número de camarillas que tienen su tamaño como número primo o número primo de Nodes en el gráfico dado.
Una camarilla es un subgrafo completo de un grafo dado.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: N = 5, aristas[] = { {1, 2}, {2, 3}, {3, 1}, {4, 3}, {4, 5}, {5, 3} }
Salida: 8
Explicación:
En el gráfico no dirigido dado, 1->2->3 y 3->4->5 son los dos subgrafos completos, ambos de tamaño 3, que es un número primo.
Además, 1-2, 2->3, 3->1, 4->3, 4->5 y 5->3 son subgrafos completos de tamaño 2.
Por lo tanto, hay 8 camarillas principales.
Enfoque: Para resolver el problema mencionado anteriormente, la idea principal es utilizar la recursividad . Se encuentran todos los vértices cuyo grado es mayor o igual a (K-1) y se comprueba qué subconjunto de K vértices forman una camarilla. Cuando se agrega otro borde a la lista actual, se verifica si al agregar ese borde, la lista todavía forma una camarilla o no. Se pueden seguir los siguientes pasos para calcular el resultado:
- Para comprobar si el tamaño de la camarilla es primo o no, la idea es usar Sieve Of eratosthenes . Crea un tamiz que nos ayude a identificar si el tamaño es primo o no en tiempo O(1) .
- Forme una función recursiva con tres parámetros, Node inicial, longitud del conjunto actual de Nodes y arreglo primo (para comprobar los números primos).
- El índice inicial parece que no se puede agregar ningún Node al conjunto actual menos que ese índice. Entonces se ejecuta un bucle desde ese índice hasta n.
- Encuentre que después de agregar un Node al conjunto actual , el conjunto de Nodes sigue siendo una camarilla. En caso afirmativo, se agrega ese Node, luego se verifica el tamaño actual de la camarilla, si es primo, la respuesta aumenta en 1 y luego se llama a la función recursiva con los parámetros índice del nuevo Node agregado + 1, longitud del conjunto actual + 1 y la array principal.
- Los vértices se suman hasta que la lista no forma una camarilla. Al final, se imprime la respuesta que contiene el número de camarillas principales.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation to Count the number
// of Prime Cliques in an undirected graph
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 100;
// Stores the vertices
int store[MAX], n;
// Graph
int graph[MAX][MAX];
// Degree of the vertices
int d[MAX];
// To store the count of prime cliques
int ans;
// Function to create
// Sieve to check primes
void SieveOfEratosthenes(
bool prime[], int p_size)
{
// false here indicates
// that it is not prime
prime[0] = false;
prime[1] = false;
for (int p = 2; p * p <= p_size; p++) {
// Condition if prime[p]
// is not changed,
// then it is a prime
if (prime[p]) {
// Update all multiples of p,
// set them to non-prime
for (int i = p * 2; i <= p_size; i += p)
prime[i] = false;
}
}
}
// Function to check
// if the given set of
// vertices in store array
// is a clique or not
bool is_clique(int b)
{
// Run a loop for all set of edges
for (int i = 1; i < b; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < b; j++)
// If any edge is missing
if (graph[store[i]][store[j]] == 0)
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Function to find the count of
// all the cliques having prime size
void primeCliques(int i, int l,
bool prime[])
{
// Check if any vertices from i+1
// can be inserted
for (int j = i + 1; j <= n; j++) {
// Add the vertex to store
store[l] = j;
// If the graph is not
// a clique of size k then
// it cannot be a clique
// by adding another edge
if (is_clique(l + 1)) {
// increase the count of
// prime cliques if the size
// of current clique is prime
if (prime[l])
ans++;
// Check if another edge
// can be added
primeCliques(j, l + 1, prime);
}
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int edges[][2] = { { 1, 2 },
{ 2, 3 },
{ 3, 1 },
{ 4, 3 },
{ 4, 5 },
{ 5, 3 } };
int size = sizeof(edges)
/ sizeof(edges[0]);
n = 5;
bool prime[n + 1];
memset(prime, true, sizeof(prime));
SieveOfEratosthenes(prime, n + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
graph[edges[i][0]][edges[i][1]] = 1;
graph[edges[i][1]][edges[i][0]] = 1;
d[edges[i][0]]++;
d[edges[i][1]]++;
}
ans = 0;
primeCliques(0, 1, prime);
cout << ans << "\n";
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation to Count the number
// of Prime Cliques in an undirected graph
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static final int MAX = 100;
// Stores the vertices
static int[] store = new int[MAX];
static int n;
// Graph
static int[][] graph = new int[MAX][MAX];
// Degree of the vertices
static int[] d = new int[MAX];
// To store the count of prime cliques
static int ans;
// Function to create
// Sieve to check primes
static void SieveOfEratosthenes(boolean prime[],
int p_size)
{
// False here indicates
// that it is not prime
prime[0] = false;
prime[1] = false;
for(int p = 2; p * p <= p_size; p++)
{
// Condition if prime[p]
// is not changed,
// then it is a prime
if (prime[p])
{
// Update all multiples of p,
// set them to non-prime
for(int i = p * 2; i <= p_size; i += p)
prime[i] = false;
}
}
}
// Function to check
// if the given set of
// vertices in store array
// is a clique or not
static boolean is_clique(int b)
{
// Run a loop for all set of edges
for(int i = 1; i < b; i++)
{
for(int j = i + 1; j < b; j++)
// If any edge is missing
if (graph[store[i]][store[j]] == 0)
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Function to find the count of
// all the cliques having prime size
static void primeCliques(int i, int l,
boolean prime[])
{
// Check if any vertices from i+1
// can be inserted
for(int j = i + 1; j <= n; j++)
{
// Add the vertex to store
store[l] = j;
// If the graph is not
// a clique of size k then
// it cannot be a clique
// by adding another edge
if (is_clique(l + 1))
{
// Increase the count of
// prime cliques if the size
// of current clique is prime
if (prime[l])
ans++;
// Check if another edge
// can be added
primeCliques(j, l + 1, prime);
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int edges[][] = { { 1, 2 },
{ 2, 3 },
{ 3, 1 },
{ 4, 3 },
{ 4, 5 },
{ 5, 3 } };
int size = edges.length;
n = 5;
boolean[] prime = new boolean[n + 1];
Arrays.fill(prime, true);
SieveOfEratosthenes(prime, n);
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
graph[edges[i][0]][edges[i][1]] = 1;
graph[edges[i][1]][edges[i][0]] = 1;
d[edges[i][0]]++;
d[edges[i][1]]++;
}
ans = 0;
primeCliques(0, 1, prime);
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
// This code is contributed by coder001
Python3
# Python3 implementation to Count the number # of Prime Cliques in an undirected graph MAX = 100 # Stores the vertices store = [0 for i in range(MAX)] n = 0 # Graph graph = [[0 for j in range(MAX)] for i in range(MAX)] # Degree of the vertices d = [0 for i in range(MAX)] # To store the count of prime cliques ans = 0 # Function to create # Sieve to check primes def SieveOfEratosthenes(prime, p_size): # false here indicates # that it is not prime prime[0] = False prime[1] = False p = 2 while (p * p <= p_size): # Condition if prime[p] # is not changed, # then it is a prime if (prime[p]): # Update all multiples of p, # set them to non-prime for i in range(p * 2, p_size + 1, p): prime[i] = False p += 1 # Function to check if the given # set of vertices in store array # is a clique or not def is_clique(b): # Run a loop for all set of edges for i in range(1, b): for j in range(i + 1, b): # If any edge is missing if (graph[store[i]][store[j]] == 0): return False return True # Function to find the count of # all the cliques having prime size def primeCliques(i, l, prime): global ans # Check if any vertices from i+1 # can be inserted for j in range(i + 1, n + 1): # Add the vertex to store store[l] = j # If the graph is not # a clique of size k then # it cannot be a clique # by adding another edge if (is_clique(l + 1)): # Increase the count of # prime cliques if the size # of current clique is prime if (prime[l]): ans += 1 # Check if another edge # can be added primeCliques(j, l + 1, prime) # Driver code if __name__=='__main__': edges = [ [ 1, 2 ], [ 2, 3 ], [ 3, 1 ], [ 4, 3 ], [ 4, 5 ], [ 5, 3 ] ] size = len(edges) n = 5 prime = [True for i in range(n + 2)] SieveOfEratosthenes(prime, n + 1) for i in range(size): graph[edges[i][0]][edges[i][1]] = 1 graph[edges[i][1]][edges[i][0]] = 1 d[edges[i][0]] += 1 d[edges[i][1]] += 1 ans = 0 primeCliques(0, 1, prime) print(ans) # This code is contributed by rutvik_56
C#
// C# implementation to count the number
// of Prime Cliques in an undirected graph
using System;
class GFG{
static readonly int MAX = 100;
// Stores the vertices
static int[] store = new int[MAX];
static int n;
// Graph
static int[,] graph = new int[MAX, MAX];
// Degree of the vertices
static int[] d = new int[MAX];
// To store the count of prime cliques
static int ans;
// Function to create
// Sieve to check primes
static void SieveOfEratosthenes(bool []prime,
int p_size)
{
// False here indicates
// that it is not prime
prime[0] = false;
prime[1] = false;
for(int p = 2; p * p <= p_size; p++)
{
// Condition if prime[p]
// is not changed,
// then it is a prime
if (prime[p])
{
// Update all multiples of p,
// set them to non-prime
for(int i = p * 2; i <= p_size;
i += p)
prime[i] = false;
}
}
}
// Function to check if the given
// set of vertices in store array
// is a clique or not
static bool is_clique(int b)
{
// Run a loop for all set of edges
for(int i = 1; i < b; i++)
{
for(int j = i + 1; j < b; j++)
// If any edge is missing
if (graph[store[i],store[j]] == 0)
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Function to find the count of
// all the cliques having prime size
static void primeCliques(int i, int l,
bool []prime)
{
// Check if any vertices from i+1
// can be inserted
for(int j = i + 1; j <= n; j++)
{
// Add the vertex to store
store[l] = j;
// If the graph is not
// a clique of size k then
// it cannot be a clique
// by adding another edge
if (is_clique(l + 1))
{
// Increase the count of
// prime cliques if the size
// of current clique is prime
if (prime[l])
ans++;
// Check if another edge
// can be added
primeCliques(j, l + 1, prime);
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int [,]edges = { { 1, 2 },
{ 2, 3 },
{ 3, 1 },
{ 4, 3 },
{ 4, 5 },
{ 5, 3 } };
int size = edges.GetLength(0);
n = 5;
bool[] prime = new bool[n + 1];
for(int i = 0; i < prime.Length; i++)
prime[i] = true;
SieveOfEratosthenes(prime, n);
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
graph[edges[i, 0],edges[i, 1]] = 1;
graph[edges[i, 1],edges[i, 0]] = 1;
d[edges[i, 0]]++;
d[edges[i, 1]]++;
}
ans = 0;
primeCliques(0, 1, prime);
Console.WriteLine(ans);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript implementation to count the number
// of Prime Cliques in an undirected graph
let MAX = 100;
// Stores the vertices
let store = new Array(MAX);
store.fill(0);
let n;
// Graph
let graph = new Array(MAX);
for(let i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
{
graph[i] = new Array(MAX);
}
// Degree of the vertices
let d = new Array(MAX);
d.fill(0);
// To store the count of prime cliques
let ans;
// Function to create
// Sieve to check primes
function SieveOfEratosthenes(prime, p_size)
{
// False here indicates
// that it is not prime
prime[0] = false;
prime[1] = false;
for(let p = 2; p * p <= p_size; p++)
{
// Condition if prime[p]
// is not changed,
// then it is a prime
if (prime[p])
{
// Update all multiples of p,
// set them to non-prime
for(let i = p * 2; i <= p_size;
i += p)
prime[i] = false;
}
}
}
// Function to check if the given
// set of vertices in store array
// is a clique or not
function is_clique(b)
{
// Run a loop for all set of edges
for(let i = 1; i < b; i++)
{
for(let j = i + 1; j < b; j++)
// If any edge is missing
if (graph[store[i]][store[j]] == 0)
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// Function to find the count of
// all the cliques having prime size
function primeCliques(i, l, prime)
{
// Check if any vertices from i+1
// can be inserted
for(let j = i + 1; j <= n; j++)
{
// Add the vertex to store
store[l] = j;
// If the graph is not
// a clique of size k then
// it cannot be a clique
// by adding another edge
if (is_clique(l + 1))
{
// Increase the count of
// prime cliques if the size
// of current clique is prime
if (prime[l])
ans++;
else
{
ans-=1.3;
}
// Check if another edge
// can be added
primeCliques(j, l + 1, prime);
}
}
}
let edges = [ [ 1, 2 ],
[ 2, 3 ],
[ 3, 1 ],
[ 4, 3 ],
[ 4, 5 ],
[ 5, 3 ] ];
let size = edges.length;
n = 5;
let prime = new Array(n + 1);
for(let i = 0; i < prime.length; i++)
prime[i] = true;
SieveOfEratosthenes(prime, n);
for(let i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
graph[edges[i][0],edges[i][1]] = 1;
graph[edges[i][1],edges[i][0]] = 1;
d[edges[i][0]]++;
d[edges[i][1]]++;
}
ans = 0;
primeCliques(0, 1, prime);
document.write(ans);
// This code is contributed by suresh07.
</script>
8
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por muskan_garg y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA