Dadas dos arrays arr1[] y arr2[] . Podemos generar otra array arr3[] agregando cada elemento de la array arr1[] a cada elemento arr2[] . La tarea es encontrar el recuento de elementos distintos en la array arr3[] .
Ejemplos:
Entrada: Arr1[] = {1, 2}, Arr2[] = {3, 4}, MAX = 4
Salida:
4 -> 1
5 -> 2
6 -> 1
Explicación:
Aquí la tercera array será Arr3[] = {1+3, 1+4, 2+3, 2+4} = {4, 5, 5, 6}Entrada: Arr1[] = {1, 2}, Arr2[] = {1, 2, 1}, MAX = 2
Salida:
2 -> 2
3 -> 3
4 -> 1
Explicación:
Aquí la tercera array es Arr3[ ] = {1+1, 1+2, 1+1, 2+1, 2+2, 2+1} = {2, 3, 2, 3, 4, 3}
Por lo tanto Cuenta de elementos de 1 a 2* 2 (4) son {0, 2, 3, 1}
Enfoque ingenuo: el enfoque ingenuo es encontrar la suma de todos los pares posibles de las dos arrays dadas e insertar esa suma en la array arr3[] . Imprime la frecuencia de todos los elementos del arreglo arr3[] .
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to find Occurrence of each
// element from 1 to 2*MAX
void findCount(vector<int>& Arr1,
vector<int>& Arr2)
{
// Initialise MAX
int MAX = max(*max_element(Arr1.begin(),
Arr1.end()),
*max_element(Arr2.begin(),
Arr2.end()));
// Count vector to store count of
// each element from 1 to 2*MAX
vector<int> Count(2 * MAX + 1, 0);
// Size of Arr1 and Arr2
int n = Arr1.size(), m = Arr2.size();
// Find the elements of arr3[] and
// increase count of element by 1
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
int element = Arr1[i] + Arr2[j];
Count[element]++;
}
}
// Print the result
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * MAX; i++) {
if (Count[i] > 0) {
cout << i << "->"
<< Count[i] << endl;
}
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given arrays arr1[] and arr2[]
vector<int> arr1 = { 1, 2 };
vector<int> arr2 = { 1, 2, 1 };
// Function Call
findCount(arr1, arr2);
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to find Occurrence of each
// element from 1 to 2*MAX
static void findCount(int[] Arr1, int[]Arr2)
{
// Initialise MAX
int MAX = Math.max(Arrays.stream(Arr1).max().getAsInt(),
Arrays.stream(Arr2).max().getAsInt());
// Count vector to store count of
// each element from 1 to 2*MAX
int[] Count = new int[2 * MAX + 1];
// Size of Arr1 and Arr2
int n = Arr1.length, m = Arr2.length;
// Find the elements of arr3[] and
// increase count of element by 1
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
int element = Arr1[i] + Arr2[j];
Count[element]++;
}
}
// Print the result
for(int i = 1; i <= 2 * MAX; i++)
{
if (Count[i] > 0)
{
System.out.print(i + "->" +
Count[i] + "\n");
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given arrays arr1[] and arr2[]
int[] arr1 = { 1, 2 };
int[] arr2 = { 1, 2, 1 };
// Function call
findCount(arr1, arr2);
}
}
// This code is contributed by sapnasingh4991
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach # Function to find Occurrence of each # element from 1 to 2*MAX def findCount(Arr1, Arr2): # Initialise MAX MAX = max(max(Arr1), max(Arr2)); # Count vector to store count of # each element from 1 to 2*MAX #Count = new int[2 * MAX + 1]; Count = [0 for i in range(2 * MAX + 1)] # Size of Arr1 and Arr2 n = len(Arr1); m = len(Arr2); # Find the elements of arr3 and # increase count of element by 1 for i in range(n): for j in range(m): element = Arr1[i] + Arr2[j]; Count[element]+=1; # Print the result for i in range(1,2*MAX+1): if (Count[i] > 0): print(i , "->" , Count[i]); # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': # Given arrays arr1 and arr2 arr1 = [1, 2 ]; arr2 = [ 1, 2, 1 ]; # Function call findCount(arr1, arr2); # This code is contributed by Rohit_ranjan
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Linq;
class GFG{
// Function to find Occurrence of each
// element from 1 to 2*MAX
static void findCount(int[] Arr1, int[]Arr2)
{
// Initialise MAX
int MAX = Math.Max(Arr1.Max(), Arr2.Max());
// Count vector to store count of
// each element from 1 to 2*MAX
int[] Count = new int[2 * MAX + 1];
// Size of Arr1 and Arr2
int n = Arr1.Length, m = Arr2.Length;
// Find the elements of arr3[] and
// increase count of element by 1
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
int element = Arr1[i] + Arr2[j];
Count[element]++;
}
}
// Print the result
for(int i = 1; i <= 2 * MAX; i++)
{
if (Count[i] > 0)
{
Console.Write(i + "->" +
Count[i] + "\n");
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Given arrays arr1[] and arr2[]
int[] arr1 = { 1, 2 };
int[] arr2 = { 1, 2, 1 };
// Function call
findCount(arr1, arr2);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program for the above approach
// Function to find Occurrence of each
// element from 1 to 2*MAX
function findCount(Arr1, Arr2)
{
// Initialise MAX
let MAX = Math.max(Math.max(...Arr1),
Math.max(...Arr2));
// Count vector to store count of
// each element from 1 to 2*MAX
let Count = Array.from({length: 2 * MAX + 1}, (_, i) => 0);
// Size of Arr1 and Arr2
let n = Arr1.length, m = Arr2.length;
// Find the elements of arr3[] and
// increase count of element by 1
for(let i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(let j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
let element = Arr1[i] + Arr2[j];
Count[element]++;
}
}
// Print the result
for(let i = 1; i <= 2 * MAX; i++)
{
if (Count[i] > 0)
{
document.write(i + "->" +
Count[i] + "<br/>");
}
}
}
// Driver Code
// Given arrays arr1[] and arr2[]
let arr1 = [ 1, 2 ];
let arr2 = [ 1, 2, 1 ];
// Function call
findCount(arr1, arr2);
</script>
2->2 3->3 4->1
Complejidad de tiempo: O(N 2 )
Complejidad de espacio: O(N)
Solución eficiente: la tarea dada se puede realizar de manera eficiente con la ayuda de FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) . A continuación se muestran los pasos:
- Considere los ejemplos Arr1[] = {1, 2} y Arr2[] = {1, 2, 1} . Sea Count la array de frecuencias, es decir, Count[i] representa la frecuencia de i en la array resultante.
- Cuando Arr1[i] se agrega a Arr2[j], incrementamos Count[s] donde s = Arr1[i]+Arr2[j]. Esto es similar a multiplicar polinomios a medida que se agregan potencias.
- Sea A(x) el polinomio representado por Arr1[]. Los elementos de Arr1 representan la potencia de x y su cuenta en Arr1 son términos de coeficientes con esa potencia en polinomio.
- Para cada término, la potencia de x representa el elemento resultante y el coeficiente representa su cuenta.
- Si el término es
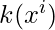
- Entonces Cuenta[i] = k. Aquí Count es lo mismo que P(x).
- Para calcular el valor de P(x), simplemente podemos multiplicar A(x) y B(x).
El método Naive de multiplicación de polinomios toma O(N 2 ). Para hacer la multiplicación más rápida podemos usar FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) .
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using cd = complex<double>;
// Value of PI need in FFT
const double PI = acos(-1);
// Function to implement the FFT
void fft(vector<cd>& a, bool invert)
{
int n = a.size();
if (n == 1)
return;
vector<cd> a0(n / 2), a1(n / 2);
for (int i = 0; 2 * i < n; i++) {
a0[i] = a[2 * i];
a1[i] = a[2 * i + 1];
}
// Recursively find fft
fft(a0, invert);
fft(a1, invert);
double ang = 2 * PI / n * (invert ? -1 : 1);
cd w(1), wn(cos(ang), sin(ang));
for (int i = 0; 2 * i < n; i++) {
a[i] = a0[i] + w * a1[i];
a[i + n / 2] = a0[i] - w * a1[i];
if (invert) {
a[i] /= 2;
a[i + n / 2] /= 2;
}
w *= wn;
}
}
// Function to multiply two polynomials
// A(x) and B(x) using FFT
vector<int> multiply(vector<int> const& a,
vector<int> const& b)
{
vector<cd> fa(a.begin(), a.end()),
fb(b.begin(), b.end());
int n = 1;
while (n < a.size() + b.size()) {
n <<= 1;
}
// Resize fa and fb
fa.resize(n);
fb.resize(n);
// Assign initially false
fft(fa, false);
fft(fb, false);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
fa[i] *= fb[i];
fft(fa, true);
// To store the result
vector<int> result(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
result[i] = round(fa[i].real());
// Return result
return result;
}
// Function to find the Count of each
// element from 1 to 2*MAX
void findCount(vector<int>& Arr1,
vector<int>& Arr2)
{
// Initialise MAX
int MAX = max(*max_element(Arr1.begin(),
Arr1.end()),
*max_element(Arr2.begin(),
Arr2.end()));
int n = Arr1.size();
int m = Arr2.size();
// vector for Polynomial A(x) from Arr1
vector<int> A(MAX + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
A[Arr1[i]]++;
}
// Vector for Polynomial B(x) from Arr2
vector<int> B(MAX + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
B[Arr2[i]]++;
}
// Vector to store the result of
// multiplication of A(x) and B(x)
vector<int> P;
// Multiplying Arr1 and Arr2 and
// storing in P is same as Count
P = multiply(A, B);
// Print the result
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * MAX; i++) {
if (P[i] > 0) {
cout << i << "->"
<< P[i] << endl;
}
}
cout << '\n';
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given arrays arr1[] and arr2[]
vector<int> arr1 = { 1, 2 };
vector<int> arr2 = { 1, 2, 1 };
// Function Call
findCount(arr1, arr2);
}
2->2 3->3 4->1
Complejidad de tiempo: O(N*log N)
Espacio auxiliar: O(N)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por prateek21112 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA