Dado un entero ![]() y dos arrays
y dos arrays ![]() y
y ![]() , la tarea es contar los pares totales (formados después de elegir un elemento de
, la tarea es contar los pares totales (formados después de elegir un elemento de ![]() y otro de
y otro de ![]() ) de estas arrays cuya operación de módulo da como resultado
) de estas arrays cuya operación de módulo da como resultado ![]() .
.
Nota: Si en un par (a, b) , a > b entonces el módulo debe realizarse como a % b . Además, los pares que ocurran más de una vez se contarán solo una vez.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: arr1[] = {1, 3, 7}, arr2[] = {5, 3, 1}, K = 2
Salida: 2
(3, 5) y (7, 5) son los únicos pares posibles.
Ya que, 5 % 3 = 2 y 7 % 5 = 2
Entrada: arr1[] = {2, 5, 99}, arr2[] = {2, 8, 1, 4}, K = 0
Salida: 6
Todos los pares posibles son (2, 2), (2, 8), (2, 4), (2, 1), (5, 1) y (99, 1).
Acercarse:
- Tome un elemento de
 a la vez y realice su operación de módulo con todos los demás elementos de
a la vez y realice su operación de módulo con todos los demás elementos de  uno en uno.
uno en uno. - Si el resultado del paso anterior es igual a
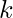 entonces almacene el par (a, b) en un conjunto para evitar duplicados donde a es el elemento más pequeño yb es el más grande.
entonces almacene el par (a, b) en un conjunto para evitar duplicados donde a es el elemento más pequeño yb es el más grande. - El total de pares requeridos será el tamaño del conjunto al final.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation of above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to return the total pairs
// of elements whose modulo yield K
int totalPairs(int arr1[], int arr2[], int K, int n, int m)
{
// set is used to avoid duplicate pairs
set<pair<int, int> > s;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
// check which element is greater and
// proceed according to it
if (arr1[i] > arr2[j]) {
// check if modulo is equal to K
if (arr1[i] % arr2[j] == K)
s.insert(make_pair(arr1[i], arr2[j]));
}
else {
if (arr2[j] % arr1[i] == K)
s.insert(make_pair(arr2[j], arr1[i]));
}
}
}
// return size of the set
return s.size();
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr1[] = { 8, 3, 7, 50 };
int arr2[] = { 5, 1, 10, 4 };
int K = 3;
int n = sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(arr1[0]);
int m = sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(arr2[0]);
cout << totalPairs(arr1, arr2, K, n, m);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation of above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static class pair
{
int first, second;
public pair(int first, int second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
// Function to return the total pairs
// of elements whose modulo yield K
static int totalPairs(int []arr1, int []arr2,
int K, int n, int m)
{
// set is used to avoid duplicate pairs
HashSet<pair> s = new HashSet<pair>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
// check which element is greater and
// proceed according to it
if (arr1[i] > arr2[j])
{
// check if modulo is equal to K
if (arr1[i] % arr2[j] == K)
s.add(new pair(arr1[i], arr2[j]));
}
else
{
if (arr2[j] % arr1[i] == K)
s.add(new pair(arr2[j], arr1[i]));
}
}
}
// return size of the set
return s.size();
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String []args)
{
int []arr1 = { 8, 3, 7, 50 };
int []arr2 = { 5, 1, 10, 4 };
int K = 3;
int n = arr1.length;
int m = arr2.length;
System.out.println(totalPairs(arr1, arr2, K, n, m));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh
Python3
# Python3 implementation of above approach
# Function to return the total pairs
# of elements whose modulo yield K
def totalPairs(arr1, arr2, K, n, m):
# set is used to avoid duplicate pairs
s={}
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
# check which element is greater and
# proceed according to it
if (arr1[i] > arr2[j]):
# check if modulo is equal to K
if (arr1[i] % arr2[j] == K):
s[(arr1[i], arr2[j])]=1
else:
if (arr2[j] % arr1[i] == K):
s[(arr2[j], arr1[i])]=1
# return size of the set
return len(s)
# Driver code
arr1 = [ 8, 3, 7, 50 ]
arr2 = [5, 1, 10, 4 ]
K = 3
n = len(arr1)
m = len(arr2)
print(totalPairs(arr1, arr2, K, n, m))
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29
C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
public class pair
{
public int first, second;
public pair(int first, int second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
// Function to return the total pairs
// of elements whose modulo yield K
static int totalPairs(int []arr1, int []arr2,
int K, int n, int m)
{
// set is used to avoid duplicate pairs
HashSet<pair> s = new HashSet<pair>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
// check which element is greater and
// proceed according to it
if (arr1[i] > arr2[j])
{
// check if modulo is equal to K
if (arr1[i] % arr2[j] == K)
s.Add(new pair(arr1[i], arr2[j]));
}
else
{
if (arr2[j] % arr1[i] == K)
s.Add(new pair(arr2[j], arr1[i]));
}
}
}
// return size of the set
return s.Count;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
int []arr1 = { 8, 3, 7, 50 };
int []arr2 = { 5, 1, 10, 4 };
int K = 3;
int n = arr1.Length;
int m = arr2.Length;
Console.WriteLine(totalPairs(arr1, arr2, K, n, m));
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript implementation of above approach
// Function to return the total pairs
// of elements whose modulo yield K
function totalPairs(arr1, arr2, K, n, m)
{
// set is used to avoid duplicate pairs
var s = new Set();
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (var j = 0; j < m; j++) {
// check which element is greater and
// proceed according to it
if (arr1[i] > arr2[j]) {
// check if modulo is equal to K
if (arr1[i] % arr2[j] == K)
s.add([arr1[i], arr2[j]]);
}
else {
if (arr2[j] % arr1[i] == K)
s.add([arr2[j], arr1[i]]);
}
}
}
// return size of the set
return s.size;
}
// Driver code
var arr1 = [ 8, 3, 7, 50 ];
var arr2 = [ 5, 1, 10, 4 ];
var K = 3;
var n = arr1.length;
var m = arr2.length;
document.write( totalPairs(arr1, arr2, K, n, m));
</script>
3
Complejidad temporal: O(n * m)
Espacio Auxiliar: O(n * m)
Nota: Para imprimir todos los pares solo imprima los elementos del conjunto.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por Shashank_Sharma y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA