Dadas las raíces de un árbol. imprima todas sus rutas de raíz a hoja, una por línea.
Algoritmo:
initialize: pathlen = 0, path[1000]
/*1000 is some max limit for paths, it can change*/
/*printPathsRecur traverses nodes of tree in preorder */
printPathsRecur(tree, path[], pathlen)
1) If node is not NULL then
a) push data to path array:
path[pathlen] = node->data.
b) increment pathlen
pathlen++
2) If node is a leaf node then print the path array.
3) Else
a) Call printPathsRecur for left subtree
printPathsRecur(node->left, path, pathLen)
b) Call printPathsRecur for right subtree.
printPathsRecur(node->right, path, pathLen)
Ejemplo:
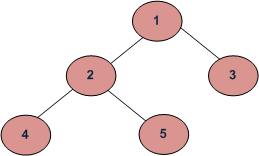
La salida para el ejemplo anterior será
1 2 4 1 2 5 1 3
Implementación:
C++
/* C++ program to print all of its
root-to-leaf paths for a tree*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
class node
{
public:
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
};
void printArray(int [], int);
void printPathsRecur(node*, int [], int);
node* newNode(int );
void printPaths(node*);
/* Given a binary tree, print out
all of its root-to-leaf paths,
one per line. Uses a recursive helper
to do the work.*/
void printPaths(node* node)
{
int path[1000];
printPathsRecur(node, path, 0);
}
/* Recursive helper function -- given
a node, and an array containing the
path from the root node up to but not
including this node, print out all the
root-leaf paths. */
void printPathsRecur(node* node, int path[], int pathLen)
{
if (node == NULL) return;
/* append this node to the path array */
path[pathLen] = node->data;
pathLen++;
/* it's a leaf, so print the path that led to here */
if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL)
{
printArray(path, pathLen);
}
else
{
/* otherwise try both subtrees */
printPathsRecur(node->left, path, pathLen);
printPathsRecur(node->right, path, pathLen);
}
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
node* newNode(int data)
{
node* Node = new node();
Node->data = data;
Node->left = NULL;
Node->right = NULL;
return(Node);
}
/* Utility that prints out an array on a line */
void printArray(int ints[], int len)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
cout << ints[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
/* Driver code */
int main()
{
node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
/* Print all root-to-leaf
paths of the input tree */
printPaths(root);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra
C
/*program to print all of its root-to-leaf paths for a tree*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct node
{
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
void printArray(int [], int);
void printPathsRecur(struct node*, int [], int);
struct node* newNode(int );
void printPaths(struct node*);
/* Given a binary tree, print out all of its root-to-leaf
paths, one per line. Uses a recursive helper to do the work.*/
void printPaths(struct node* node)
{
int path[1000];
printPathsRecur(node, path, 0);
}
/* Recursive helper function -- given a node, and an array containing
the path from the root node up to but not including this node,
print out all the root-leaf paths. */
void printPathsRecur(struct node* node, int path[], int pathLen)
{
if (node==NULL) return;
/* append this node to the path array */
path[pathLen] = node->data;
pathLen++;
/* it's a leaf, so print the path that led to here */
if (node->left==NULL && node->right==NULL)
{
printArray(path, pathLen);
}
else
{
/* otherwise try both subtrees */
printPathsRecur(node->left, path, pathLen);
printPathsRecur(node->right, path, pathLen);
}
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node = (struct node*)
malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return(node);
}
/* Utility that prints out an array on a line */
void printArray(int ints[], int len)
{
int i;
for (i=0; i<len; i++) {
printf("%d ", ints[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
/* Driver program to test mirror() */
int main()
{
struct node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
/* Print all root-to-leaf paths of the input tree */
printPaths(root);
getchar();
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to print all root to leaf paths
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
/* Given a binary tree, print out all of its root-to-leaf
paths, one per line. Uses a recursive helper to do the work.*/
void printPaths(Node node)
{
int path[] = new int[1000];
printPathsRecur(node, path, 0);
}
/* Recursive helper function -- given a node, and an array containing
the path from the root node up to but not including this node,
print out all the root-leaf paths. */
void printPathsRecur(Node node, int path[], int pathLen)
{
if (node == null)
return;
/* append this node to the path array */
path[pathLen] = node.data;
pathLen++;
/* it's a leaf, so print the path that led to here */
if (node.left == null && node.right == null)
printArray(path, pathLen);
else
{
/* otherwise try both subtrees */
printPathsRecur(node.left, path, pathLen);
printPathsRecur(node.right, path, pathLen);
}
}
/* Utility that prints out an array on a line */
void printArray(int ints[], int len)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
System.out.print(ints[i] + " ");
System.out.println("");
}
/* Driver program to test all above functions */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
/* Print all root-to-leaf paths of the input tree */
tree.printPaths(tree.root);
}
}
Python3
# Python3 program to print all of its
# root-to-leaf paths for a tree
class Node:
# A binary tree node has data,
# pointer to left child and a
# pointer to right child
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.right = None
self.left = None
def printRoute(stack, root):
if root == None:
return
# append this node to the path array
stack.append(root.data)
if(root.left == None and root.right == None):
# print out all of its
# root - to - leaf
print(' '.join([str(i) for i in stack]))
# otherwise try both subtrees
printRoute(stack, root.left)
printRoute(stack, root.right)
stack.pop()
# Driver Code
root = Node(1);
root.left = Node(2);
root.right = Node(3);
root.left.left = Node(4);
root.left.right = Node(5);
printRoute([], root)
# This code is contributed
# by Farheen Nilofer
C#
using System;
// C# program to print all root to leaf paths
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
public Node root;
/* Given a binary tree, print out all of its root-to-leaf
paths, one per line. Uses a recursive helper to do the work.*/
public virtual void printPaths(Node node)
{
int[] path = new int[1000];
printPathsRecur(node, path, 0);
}
/* Recursive helper function -- given a node, and an array containing
the path from the root node up to but not including this node,
print out all the root-leaf paths. */
public virtual void printPathsRecur(Node node, int[] path, int pathLen)
{
if (node == null)
{
return;
}
/* append this node to the path array */
path[pathLen] = node.data;
pathLen++;
/* it's a leaf, so print the path that led to here */
if (node.left == null && node.right == null)
{
printArray(path, pathLen);
}
else
{
/* otherwise try both subtrees */
printPathsRecur(node.left, path, pathLen);
printPathsRecur(node.right, path, pathLen);
}
}
/* Utility that prints out an array on a line */
public virtual void printArray(int[] ints, int len)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
Console.Write(ints[i] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine("");
}
/* Driver program to test all above functions */
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
/* Print all root-to-leaf paths of the input tree */
tree.printPaths(tree.root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program to print all root to leaf paths
class Node
{
constructor(data) {
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
this.data = data;
}
}
let root;
/* Given a binary tree, print out all of its root-to-leaf
paths, one per line. Uses a recursive helper to do the work.*/
function printPaths(node)
{
let path = new Array(1000);
printPathsRecur(node, path, 0);
}
/* Recursive helper function -- given
a node, and an array containing
the path from the root node up to but
not including this node,
print out all the root-leaf paths. */
function printPathsRecur(node, path, pathLen)
{
if (node == null)
return;
/* append this node to the path array */
path[pathLen] = node.data;
pathLen++;
/* it's a leaf, so print the path that led to here */
if (node.left == null && node.right == null)
printArray(path, pathLen);
else
{
/* otherwise try both subtrees */
printPathsRecur(node.left, path, pathLen);
printPathsRecur(node.right, path, pathLen);
}
}
/* Utility that prints out an array on a line */
function printArray(ints, len)
{
let i;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
document.write(ints[i] + " ");
document.write("</br>");
}
root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
/* Print all root-to-leaf paths of the input tree */
printPaths(root);
</script>
Producción:
1 2 4 1 2 5 1 3
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA