Dado un gráfico dirigido, compruebe si el gráfico contiene un ciclo o no. Su función debería devolver verdadero si el gráfico dado contiene al menos un ciclo, de lo contrario devolverá falso.
Ejemplo,
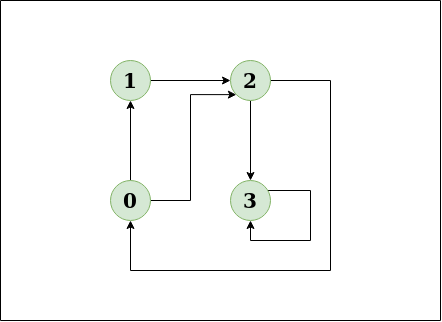
Input: n = 4, e = 6 0 -> 1, 0 -> 2, 1 -> 2, 2 -> 0, 2 -> 3, 3 -> 3 Output: Yes Explanation: Diagram:
C++
// A C++ Program to detect cycle in a graph
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Graph
{
int V; // No. of vertices
list<int> *adj; // Pointer to an array containing adjacency lists
bool isCyclicUtil(int v, bool visited[], bool *rs); // used by isCyclic()
public:
Graph(int V); // Constructor
void addEdge(int v, int w); // to add an edge to graph
bool isCyclic(); // returns true if there is a cycle in this graph
};
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list<int>[V];
}
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].push_back(w); // Add w to v’s list.
}
// This function is a variation of DFSUtil() in
// https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/archives/18212
bool Graph::isCyclicUtil(int v, bool visited[], bool *recStack)
{
if(visited[v] == false)
{
// Mark the current node as visited and part of recursion stack
visited[v] = true;
recStack[v] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
list<int>::iterator i;
for(i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i)
{
if ( !visited[*i] && isCyclicUtil(*i, visited, recStack) )
return true;
else if (recStack[*i])
return true;
}
}
recStack[v] = false; // remove the vertex from recursion stack
return false;
}
// Returns true if the graph contains a cycle, else false.
// This function is a variation of DFS() in
// https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/archives/18212
bool Graph::isCyclic()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited and not part of recursion
// stack
bool *visited = new bool[V];
bool *recStack = new bool[V];
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
visited[i] = false;
recStack[i] = false;
}
// Call the recursive helper function to detect cycle in different
// DFS trees
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if ( !visited[i] && isCyclicUtil(i, visited, recStack))
return true;
return false;
}
int main()
{
// Create a graph given in the above diagram
Graph g(4);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 3);
if(g.isCyclic())
cout << "Graph contains cycle";
else
cout << "Graph doesn't contain cycle";
return 0;
}
Java
// A Java Program to detect cycle in a graph
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
class Graph {
private final int V;
private final List<List<Integer>> adj;
public Graph(int V)
{
this.V = V;
adj = new ArrayList<>(V);
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
adj.add(new LinkedList<>());
}
// This function is a variation of DFSUtil() in
// https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/archives/18212
private boolean isCyclicUtil(int i, boolean[] visited,
boolean[] recStack)
{
// Mark the current node as visited and
// part of recursion stack
if (recStack[i])
return true;
if (visited[i])
return false;
visited[i] = true;
recStack[i] = true;
List<Integer> children = adj.get(i);
for (Integer c: children)
if (isCyclicUtil(c, visited, recStack))
return true;
recStack[i] = false;
return false;
}
private void addEdge(int source, int dest) {
adj.get(source).add(dest);
}
// Returns true if the graph contains a
// cycle, else false.
// This function is a variation of DFS() in
// https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/archives/18212
private boolean isCyclic()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited and
// not part of recursion stack
boolean[] visited = new boolean[V];
boolean[] recStack = new boolean[V];
// Call the recursive helper function to
// detect cycle in different DFS trees
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (isCyclicUtil(i, visited, recStack))
return true;
return false;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Graph graph = new Graph(4);
graph.addEdge(0, 1);
graph.addEdge(0, 2);
graph.addEdge(1, 2);
graph.addEdge(2, 0);
graph.addEdge(2, 3);
graph.addEdge(3, 3);
if(graph.isCyclic())
System.out.println("Graph contains cycle");
else
System.out.println("Graph doesn't "
+ "contain cycle");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sagar Shah.
Python
# Python program to detect cycle # in a graph from collections import defaultdict class Graph(): def __init__(self,vertices): self.graph = defaultdict(list) self.V = vertices def addEdge(self,u,v): self.graph[u].append(v) def isCyclicUtil(self, v, visited, recStack): # Mark current node as visited and # adds to recursion stack visited[v] = True recStack[v] = True # Recur for all neighbours # if any neighbour is visited and in # recStack then graph is cyclic for neighbour in self.graph[v]: if visited[neighbour] == False: if self.isCyclicUtil(neighbour, visited, recStack) == True: return True elif recStack[neighbour] == True: return True # The node needs to be popped from # recursion stack before function ends recStack[v] = False return False # Returns true if graph is cyclic else false def isCyclic(self): visited = [False] * (self.V + 1) recStack = [False] * (self.V + 1) for node in range(self.V): if visited[node] == False: if self.isCyclicUtil(node,visited,recStack) == True: return True return False g = Graph(4) g.addEdge(0, 1) g.addEdge(0, 2) g.addEdge(1, 2) g.addEdge(2, 0) g.addEdge(2, 3) g.addEdge(3, 3) if g.isCyclic() == 1: print "Graph has a cycle" else: print "Graph has no cycle" # Thanks to Divyanshu Mehta for contributing this code
C#
// A C# Program to detect cycle in a graph
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class Graph {
private readonly int V;
private readonly List<List<int>> adj;
public Graph(int V)
{
this.V = V;
adj = new List<List<int>>(V);
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
adj.Add(new List<int>());
}
// This function is a variation of DFSUtil() in
// https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/archives/18212
private bool isCyclicUtil(int i, bool[] visited,
bool[] recStack)
{
// Mark the current node as visited and
// part of recursion stack
if (recStack[i])
return true;
if (visited[i])
return false;
visited[i] = true;
recStack[i] = true;
List<int> children = adj[i];
foreach (int c in children)
if (isCyclicUtil(c, visited, recStack))
return true;
recStack[i] = false;
return false;
}
private void addEdge(int sou, int dest) {
adj[sou].Add(dest);
}
// Returns true if the graph contains a
// cycle, else false.
// This function is a variation of DFS() in
// https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/archives/18212
private bool isCyclic()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited and
// not part of recursion stack
bool[] visited = new bool[V];
bool[] recStack = new bool[V];
// Call the recursive helper function to
// detect cycle in different DFS trees
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (isCyclicUtil(i, visited, recStack))
return true;
return false;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Graph graph = new Graph(4);
graph.addEdge(0, 1);
graph.addEdge(0, 2);
graph.addEdge(1, 2);
graph.addEdge(2, 0);
graph.addEdge(2, 3);
graph.addEdge(3, 3);
if(graph.isCyclic())
Console.WriteLine("Graph contains cycle");
else
Console.WriteLine("Graph doesn't "
+ "contain cycle");
}
}
// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji
Javascript
<script>
// A JavaScript Program to detect cycle in a graph
let V;
let adj=[];
function Graph(v)
{
V=v;
for (let i = 0; i < V; i++)
adj.push([]);
}
// This function is a variation of DFSUtil() in
// https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/archives/18212
function isCyclicUtil(i,visited,recStack)
{
// Mark the current node as visited and
// part of recursion stack
if (recStack[i])
return true;
if (visited[i])
return false;
visited[i] = true;
recStack[i] = true;
let children = adj[i];
for (let c=0;c< children.length;c++)
if (isCyclicUtil(children, visited, recStack))
return true;
recStack[i] = false;
return false;
}
function addEdge(source,dest)
{
adj.push(dest);
}
// Returns true if the graph contains a
// cycle, else false.
// This function is a variation of DFS() in
// https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/archives/18212
function isCyclic()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited and
// not part of recursion stack
let visited = new Array(V);
let recStack = new Array(V);
for(let i=0;i<V;i++)
{
visited[i]=false;
recStack[i]=false;
}
// Call the recursive helper function to
// detect cycle in different DFS trees
for (let i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (isCyclicUtil(i, visited, recStack))
return true;
return false;
}
// Driver code
Graph(4);
addEdge(0, 1);
addEdge(0, 2);
addEdge(1, 2);
addEdge(2, 0);
addEdge(2, 3);
addEdge(3, 3);
if(isCyclic())
document.write("Graph contains cycle");
else
document.write("Graph doesn't "
+ "contain cycle");
// This code is contributed by patel2127
</script>
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA