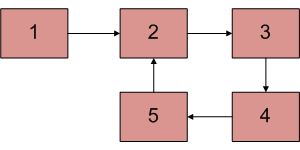
Escriba una función detectAndRemoveLoop() que compruebe si una lista enlazada determinada contiene un bucle y, si el bucle está presente, lo elimina y devuelve verdadero. Si la lista no contiene un bucle, devuelve falso. El siguiente diagrama muestra una lista enlazada con un bucle. detectAndRemoveLoop() debe cambiar la lista siguiente a 1->2->3->4->5->NULL.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* Link list node */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
/* Function to remove loop. */
void removeLoop(struct Node*, struct Node*);
/* This function detects and removes loop in the list
If loop was there in the list then it returns 1,
otherwise returns 0 */
int detectAndRemoveLoop(struct Node* list)
{
struct Node *slow_p = list, *fast_p = list;
// Iterate and find if loop exists or not
while (slow_p && fast_p && fast_p->next) {
slow_p = slow_p->next;
fast_p = fast_p->next->next;
/* If slow_p and fast_p meet at some point then there
is a loop */
if (slow_p == fast_p) {
removeLoop(slow_p, list);
/* Return 1 to indicate that loop is found */
return 1;
}
}
/* Return 0 to indicate that there is no loop*/
return 0;
}
/* Function to remove loop.
loop_node --> Pointer to one of the loop nodes
head --> Pointer to the start node of the linked list */
void removeLoop(struct Node* loop_node, struct Node* head)
{
struct Node* ptr1 = loop_node;
struct Node* ptr2 = loop_node;
// Count the number of nodes in loop
unsigned int k = 1, i;
while (ptr1->next != ptr2) {
ptr1 = ptr1->next;
k++;
}
// Fix one pointer to head
ptr1 = head;
// And the other pointer to k nodes after head
ptr2 = head;
for (i = 0; i < k; i++)
ptr2 = ptr2->next;
/* Move both pointers at the same pace,
they will meet at loop starting node */
while (ptr2 != ptr1) {
ptr1 = ptr1->next;
ptr2 = ptr2->next;
}
// Get pointer to the last node
while (ptr2->next != ptr1)
ptr2 = ptr2->next;
/* Set the next node of the loop ending node
to fix the loop */
ptr2->next = NULL;
}
/* Function to print linked list */
void printList(struct Node* node)
{
// Print the list after loop removal
while (node != NULL) {
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
}
struct Node* newNode(int key)
{
struct Node* temp = new Node();
temp->data = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
struct Node* head = newNode(50);
head->next = newNode(20);
head->next->next = newNode(15);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head->next->next;
detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
cout << "Linked List after removing loop \n";
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// This code has been contributed by Striver
Java
// Java program to detect and remove loop in linked list
class LinkedList {
static Node head;
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// Function that detects loop in the list
int detectAndRemoveLoop(Node node)
{
Node slow = node, fast = node;
while (slow != null && fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// If slow and fast meet at same point then loop is present
if (slow == fast) {
removeLoop(slow, node);
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
// Function to remove loop
void removeLoop(Node loop, Node head)
{
Node ptr1 = loop;
Node ptr2 = loop;
// Count the number of nodes in loop
int k = 1, i;
while (ptr1.next != ptr2) {
ptr1 = ptr1.next;
k++;
}
// Fix one pointer to head
ptr1 = head;
// And the other pointer to k nodes after head
ptr2 = head;
for (i = 0; i < k; i++) {
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
/* Move both pointers at the same pace,
they will meet at loop starting node */
while (ptr2 != ptr1) {
ptr1 = ptr1.next;
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
// Get pointer to the last node
while (ptr2.next != ptr1) {
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
/* Set the next node of the loop ending node
to fix the loop */
ptr2.next = null;
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.head = new Node(50);
list.head.next = new Node(20);
list.head.next.next = new Node(15);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
list.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
// Creating a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
list.detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
System.out.println("Linked List after removing loop : ");
list.printList(head);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal
Python3
# Python program to detect and remove loop in linked list
# Node class
class Node:
# Constructor to initialize the node object
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def detectAndRemoveLoop(self):
slow_p = fast_p = self.head
while(slow_p and fast_p and fast_p.next):
slow_p = slow_p.next
fast_p = fast_p.next.next
# If slow_p and fast_p meet at some point then
# there is a loop
if slow_p == fast_p:
self.removeLoop(slow_p)
# Return 1 to indicate that loop is found
return 1
# Return 0 to indicate that there is no loop
return 0
# Function to remove loop
# loop_node --> pointer to one of the loop nodes
# head --> Pointer to the start node of the linked list
def removeLoop(self, loop_node):
ptr1 = loop_node
ptr2 = loop_node
# Count the number of nodes in loop
k = 1
while(ptr1.next != ptr2):
ptr1 = ptr1.next
k += 1
# Fix one pointer to head
ptr1 = self.head
# And the other pointer to k nodes after head
ptr2 = self.head
for i in range(k):
ptr2 = ptr2.next
# Move both pointers at the same place
# they will meet at loop starting node
while(ptr2 != ptr1):
ptr1 = ptr1.next
ptr2 = ptr2.next
# Get pointer to the last node
while(ptr2.next != ptr1):
ptr2 = ptr2.next
# Set the next node of the loop ending node
# to fix the loop
ptr2.next = None
# Function to insert a new node at the beginning
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
# Utility function to print the LinkedList
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while(temp):
print(temp.data, end = ' ')
temp = temp.next
# Driver program
llist = LinkedList()
llist.push(10)
llist.push(4)
llist.push(15)
llist.push(20)
llist.push(50)
# Create a loop for testing
llist.head.next.next.next.next.next = llist.head.next.next
llist.detectAndRemoveLoop()
print("Linked List after removing loop")
llist.printList()
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)
C#
// A C# program to detect and remove loop in linked list
using System;
public class LinkedList {
Node head;
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// Function that detects loop in the list
int detectAndRemoveLoop(Node node)
{
Node slow = node, fast = node;
while (slow != null && fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// If slow and fast meet at same
// point then loop is present
if (slow == fast) {
removeLoop(slow, node);
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
// Function to remove loop
void removeLoop(Node loop, Node head)
{
Node ptr1 = loop;
Node ptr2 = loop;
// Count the number of nodes in loop
int k = 1, i;
while (ptr1.next != ptr2) {
ptr1 = ptr1.next;
k++;
}
// Fix one pointer to head
ptr1 = head;
// And the other pointer to k nodes after head
ptr2 = head;
for (i = 0; i < k; i++) {
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
/* Move both pointers at the same pace,
they will meet at loop starting node */
while (ptr2 != ptr1) {
ptr1 = ptr1.next;
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
// Get pointer to the last node
while (ptr2.next != ptr1) {
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
/* Set the next node of the loop ending node
to fix the loop */
ptr2.next = null;
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.head = new Node(50);
list.head.next = new Node(20);
list.head.next.next = new Node(15);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
list.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
// Creating a loop for testing
list.head.next.next.next.next.next = list.head.next.next;
list.detectAndRemoveLoop(list.head);
Console.WriteLine("Linked List after removing loop : ");
list.printList(list.head);
}
}
// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program to detect and
// remove loop in linked list
var head;
class Node
{
constructor(val)
{
this.data = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
// Function that detects loop in the list
function detectAndRemoveLoop(node)
{
var slow = node, fast = node;
while (slow != null &&
fast != null &&
fast.next != null)
{
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// If slow and fast meet at same
// point then loop is present
if (slow == fast)
{
removeLoop(slow, node);
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
// Function to remove loop
function removeLoop(loop, head)
{
var ptr1 = loop;
var ptr2 = loop;
// Count the number of nodes in loop
var k = 1, i;
while (ptr1.next != ptr2)
{
ptr1 = ptr1.next;
k++;
}
// Fix one pointer to head
ptr1 = head;
// And the other pointer to
// k nodes after head
ptr2 = head;
for(i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
/* Move both pointers at the same pace,
they will meet at loop starting node */
while (ptr2 != ptr1)
{
ptr1 = ptr1.next;
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
// Get pointer to the last node
while (ptr2.next != ptr1)
{
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
/* Set the next node of the loop ending node
to fix the loop */
ptr2.next = null;
}
// Function to print the linked list
function printList(node)
{
while (node != null)
{
document.write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver code
head = new Node(50);
head.next = new Node(20);
head.next.next = new Node(15);
head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
// Creating a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
document.write("Linked List after removing loop : ");
printList(head);
// This code is contributed by todaysgaurav
</script>
C++
// C++ program to detect and remove loop
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node* next;
};
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
void printList(Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
cout << head->key << " ";
head = head->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
// Function to detect and remove loop in a linked list that
// may contain loop
void detectAndRemoveLoop(Node* head)
{
// If list is empty or has only one node without loop
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL)
return;
Node *slow = head, *fast = head;
// Move slow and fast 1 and 2 steps ahead respectively.
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
// Search for loop using slow and fast pointers
while (fast && fast->next) {
if (slow == fast)
break;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
/* If loop exists */
if (slow == fast) {
slow = head;
// this check is needed when slow and fast both meet
// at the head of the LL eg: 1->2->3->4->5 and then
// 5->next = 1 i.e the head of the LL
if (slow == fast)
while (fast->next != slow)
fast = fast->next;
else {
while (slow->next != fast->next) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
}
/* since fast->next is the looping point */
fast->next = NULL; /* remove loop */
}
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
Node* head = newNode(50);
head->next = head;
head->next = newNode(20);
head->next->next = newNode(15);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head;
detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
printf("Linked List after removing loop \n");
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Aditya Kumar (adityakumar129)
C
// C++ program to detect and remove loop
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct Node {
int key;
struct Node* next;
} Node;
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
temp->key = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
void printList(Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
printf("%d ", head->key);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
// Function to detect and remove loop in a linked list that
// may contain loop
void detectAndRemoveLoop(Node* head)
{
// If list is empty or has only one node without loop
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL)
return;
Node *slow = head, *fast = head;
// Move slow and fast 1 and 2 steps ahead respectively.
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
// Search for loop using slow and fast pointers
while (fast && fast->next) {
if (slow == fast)
break;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
/* If loop exists */
if (slow == fast) {
slow = head;
// this check is needed when slow and fast both meet
// at the head of the LL eg: 1->2->3->4->5 and then
// 5->next = 1 i.e the head of the LL
if (slow == fast)
while (fast->next != slow)
fast = fast->next;
else {
while (slow->next != fast->next) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
}
/* since fast->next is the looping point */
fast->next = NULL; /* remove loop */
}
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
Node* head = newNode(50);
head->next = head;
head->next = newNode(20);
head->next->next = newNode(15);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head;
detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
printf("Linked List after removing loop \n");
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Aditya Kumar (adityakumar129)
Java
// Java program to detect
// and remove loop in linked list
class LinkedList {
static Node head;
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// Function that detects loop in the list
void detectAndRemoveLoop(Node node)
{
// If list is empty or has only one node
// without loop
if (node == null || node.next == null)
return;
Node slow = node, fast = node;
// Move slow and fast 1 and 2 steps
// ahead respectively.
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// Search for loop using slow and fast pointers
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
if (slow == fast)
break;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
/* If loop exists */
if (slow == fast) {
slow = node;
if (slow != fast) {
while (slow.next != fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
/* since fast->next is the looping point */
fast.next = null; /* remove loop */
}
/* This case is added if fast and slow pointer meet at first position. */
else {
while(fast.next != slow) {
fast = fast.next;
}
fast.next = null;
}
}
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.head = new Node(50);
list.head.next = new Node(20);
list.head.next.next = new Node(15);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
list.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
// Creating a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
list.detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
System.out.println("Linked List after removing loop : ");
list.printList(head);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal
Python3
# Python program to detect and remove loop
# Node class
class Node:
# Constructor to initialize the node object
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Function to insert a new node at the beginning
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
def detectAndRemoveLoop(self):
if self.head is None:
return
if self.head.next is None:
return
slow_p = self.head
fast_p = self.head
while(slow_p and fast_p and fast_p.next):
slow_p = slow_p.next
fast_p = fast_p.next.next
# If slow_p and fast_p meet at some point then
# there is a loop
if slow_p == fast_p:
slow_p = self.head
# Finding the beginning of the loop
while (slow_p.next != fast_p.next):
slow_p = slow_p.next
fast_p = fast_p.next
# Sinc fast.next is the looping point
fast_p.next = None # Remove loop
# Utility function to print the LinkedList
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while(temp):
print(temp.data, end = ' ')
temp = temp.next
# Driver program
llist = LinkedList()
llist.head = Node(50)
llist.head.next = Node(20)
llist.head.next.next = Node(15)
llist.head.next.next.next = Node(4)
llist.head.next.next.next.next = Node(10)
# Create a loop for testing
llist.head.next.next.next.next.next = llist.head.next.next
llist.detectAndRemoveLoop()
print("Linked List after removing loop")
llist.printList()
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)
C#
// C# program to detect and remove loop in linked list
using System;
public class LinkedList {
public Node head;
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// Function that detects loop in the list
void detectAndRemoveLoop(Node node)
{
// If list is empty or has only one node
// without loop
if (node == null || node.next == null)
return;
Node slow = node, fast = node;
// Move slow and fast 1 and 2 steps
// ahead respectively.
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// Search for loop using slow and fast pointers
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
if (slow == fast)
break;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
/* If loop exists */
if (slow == fast) {
slow = node;
while (slow.next != fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
/* since fast->next is the looping point */
fast.next = null; /* remove loop */
}
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.head = new Node(50);
list.head.next = new Node(20);
list.head.next.next = new Node(15);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
list.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
// Creating a loop for testing
list.head.next.next.next.next.next = list.head.next.next;
list.detectAndRemoveLoop(list.head);
Console.WriteLine("Linked List after removing loop : ");
list.printList(list.head);
}
}
// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji
Javascript
<script>
// javascript program to detect
// and remove loop in linked list
var head;
class Node
{
constructor(val)
{
this.data = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
// Function that detects loop in the list
function detectAndRemoveLoop(node) {
// If list is empty or has only one node
// without loop
if (node == null || node.next == null)
return;
var slow = node, fast = node;
// Move slow and fast 1 and 2 steps
// ahead respectively.
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// Search for loop using slow and fast pointers
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
if (slow == fast)
break;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
/* If loop exists */
if (slow == fast) {
slow = node;
if (slow != fast) {
while (slow.next != fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
/* since fast->next is the looping point */
fast.next = null; /* remove loop */
}
/* This case is added if fast and
slow pointer meet at first position. */
else {
while (fast.next != slow) {
fast = fast.next;
}
fast.next = null;
}
}
}
// Function to print the linked list
function printList(node) {
while (node != null) {
document.write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver code
head = new Node(50);
head.next = new Node(20);
head.next.next = new Node(15);
head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
// Creating a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
document.write("Linked List after removing loop : ");
printList(head);
// This code is contributed by umadevi9616
</script>
C++
// C++ program to detect and remove loop
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node* next;
};
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
void printList(Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
cout << head->key << " ";
head = head->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
// Function to detect and remove loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
void hashAndRemove(Node* head)
{
// hash map to hash addresses of the linked list nodes
unordered_map<Node*, int> node_map;
// pointer to last node
Node* last = NULL;
while (head != NULL) {
// if node not present in the map, insert it in the map
if (node_map.find(head) == node_map.end()) {
node_map[head]++;
last = head;
head = head->next;
}
// if present, it is a cycle, make the last node's next pointer NULL
else {
last->next = NULL;
break;
}
}
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
Node* head = newNode(50);
head->next = head;
head->next = newNode(20);
head->next->next = newNode(15);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head->next->next;
// printList(head);
hashAndRemove(head);
printf("Linked List after removing loop \n");
printList(head);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to detect and remove loop in a linked list
import java.util.*;
public class LinkedList {
static Node head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node*/
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
static public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Returns true if the loop is removed from the linked
// list else returns false.
static boolean removeLoop(Node h)
{
HashSet<Node> s = new HashSet<Node>();
Node prev = null;
while (h != null) {
// If we have already has this node
// in hashmap it means their is a cycle and we
// need to remove this cycle so set the next of
// the previous pointer with null.
if (s.contains(h)) {
prev.next = null;
return true;
}
// If we are seeing the node for
// the first time, insert it in hash
else {
s.add(h);
prev = h;
h = h.next;
}
}
return false;
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(20);
llist.push(4);
llist.push(15);
llist.push(10);
/*Create loop for testing */
llist.head.next.next.next.next = llist.head;
if (removeLoop(head)) {
System.out.println("Linked List after removing loop");
llist.printList(head);
}
else
System.out.println("No Loop found");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Animesh Nag.
C#
// C# program to detect and remove loop in a linked list
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class LinkedList {
public Node head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node*/
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Returns true if the loop is removed from the linked
// list else returns false.
bool removeLoop(Node h)
{
HashSet<Node> s = new HashSet<Node>();
Node prev = null;
while (h != null) {
// If we have already has this node
// in hashmap it means their is a cycle and we
// need to remove this cycle so set the next of
// the previous pointer with null.
if (s.Contains(h)) {
prev.next = null;
return true;
}
// If we are seeing the node for
// the first time, insert it in hash
else {
s.Add(h);
prev = h;
h = h.next;
}
}
return false;
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void Main()
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.head = new Node(50);
list.head.next = new Node(20);
list.head.next.next = new Node(15);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
list.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
/*Create loop for testing */
list.head.next.next.next.next.next = list.head.next.next;
if (list.removeLoop(list.head)) {
Console.WriteLine("Linked List after removing loop");
list.printList(list.head);
}
else
Console.WriteLine("No Loop found");
}
}
// This code is contributed by ihritik
Javascript
<script>
// javascript program to detect and remove loop in a linked list class LinkedList {
/* Linked list Node */
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
var head; // head of list
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
function push(new_data) {
/*
* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node & Put in the data
*/
var new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
return head;
}
// Function to print the linked list
function printList(node) {
while (node != null) {
document.write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Returns true if the loop is removed from the linked
// list else returns false.
function removeLoop(h)
{
var s = new Set();
var prev = null;
while (h != null)
{
// If we have already has this node
// in hashmap it means their is a cycle and we
// need to remove this cycle so set the next of
// the previous pointer with null.
if (s.has(h)) {
prev.next = null;
return true;
}
// If we are seeing the node for
// the first time, insert it in hash
else {
s.add(h);
prev = h;
h = h.next;
}
}
return false;
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
head = push(50);
head.next = push(20);
head.next.next=push(4);
head.next.next.next=push(15);
head.next.next.next.next=push(10);
/* Create loop for testing */
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
if (removeLoop(head)) {
document.write("Linked List after removing loop<br/>");
printList(head);
} else
document.write("No Loop found");
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
</script>
Python
class LinkedList:
head = None
# head of list
# Linked list Node
class Node:
data = 0
next = None
def __init__(self, d):
self.data = d
self.next = None
# Inserts a new Node at front of the list.
@staticmethod
def push(new_data):
# 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
# Put in the data
new_node = LinkedList.Node(new_data)
# 3. Make next of new Node as head
new_node.next = LinkedList.head
# 4. Move the head to point to new Node
LinkedList.head = new_node
# Function to print the linked list
def printList(self, node):
while (node != None):
print(node.data)
node = node.next
# Returns true if the loop is removed from the linked
# list else returns false.
@staticmethod
def removeLoop(h):
s = set()
prev = None
while (h != None):
# If we have already has this node
# in hashmap it means their is a cycle and we
# need to remove this cycle so set the next of
# the previous pointer with null.
if (h in s):
prev.next = None
return True
else:
s.add(h)
prev = h
h = h.next
return False
# Driver program to test above function
@staticmethod
def main(args):
llist = LinkedList()
llist.push(20)
llist.push(4)
llist.push(15)
llist.push(10)
# Create loop for testing
llist.head.next.next.next.next = llist.head
if (LinkedList.removeLoop(LinkedList.head)):
print("Linked List after removing loop")
llist.printList(LinkedList.head)
else:
print("No Loop found")
if __name__ == "__main__":
LinkedList.main([])
# This code is contributed by mukulsomukesh
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA