Dado un elemento x, la tarea es encontrar el valor de su elemento más pequeño inmediato.
// C++ program to find immediate Smaller
// Element of a given element in a n-ary tree.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// class of a node of an n-ary tree
class Node {
public:
int key;
vector<Node*> child;
// constructor
Node(int data)
{
key = data;
}
};
// Function to find immediate Smaller Element
// of a given number x
void immediateSmallerElementUtil(Node* root,
int x, Node** res)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
// if root is greater than res, but less
// than x, then update res
if (root->key < x)
if (!(*res) || (*res)->key < root->key)
*res = root; // Updating res
// Number of children of root
int numChildren = root->child.size();
// Recursive calling for every child
for (int i = 0; i < numChildren; i++)
immediateSmallerElementUtil(root->child[i], x, res);
return;
}
// Function to return immediate Smaller
// Element of x in tree
Node* immediateSmallerElement(Node* root, int x)
{
// resultant node
Node* res = NULL;
// calling helper function and using
// pass by reference
immediateSmallerElementUtil(root, x, &res);
return res;
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
// Creating a generic tree
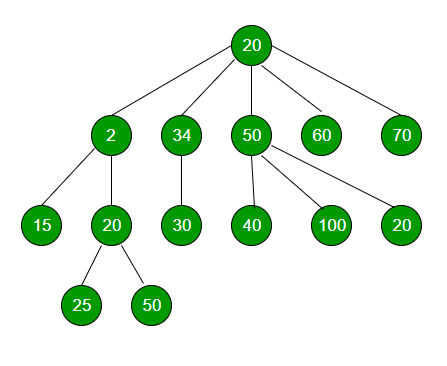
Node* root = new Node(20);
(root->child).push_back(new Node(2));
(root->child).push_back(new Node(34));
(root->child).push_back(new Node(50));
(root->child).push_back(new Node(60));
(root->child).push_back(new Node(70));
(root->child[0]->child).push_back(new Node(15));
(root->child[0]->child).push_back(new Node(20));
(root->child[1]->child).push_back(new Node(30));
(root->child[2]->child).push_back(new Node(40));
(root->child[2]->child).push_back(new Node(100));
(root->child[2]->child).push_back(new Node(20));
(root->child[0]->child[1]->child).push_back(new Node(25));
(root->child[0]->child[1]->child).push_back(new Node(50));
int x = 30;
cout << "Immediate smaller element of " << x << " is ";
cout << immediateSmallerElement(root, x)->key << endl;
return 0;
}
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por Sahil_Bansall y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA