Dada una lista enlazada, la tarea es eliminar el último Node de la lista enlazada y actualizar el puntero principal de la lista enlazada.
Ejemplos:
Input: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> NULL Output: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> NULL Explanation: The last node of the linked list is 5, so 5 is deleted. Input: 2 -> 4 -> 6 -> 8 -> 33 -> 67 -> NULL Output: 2 -> 4 -> 6 -> 8 -> 33 -> NULL Explanation: The last node of the linked list is 67, so 67 is deleted.
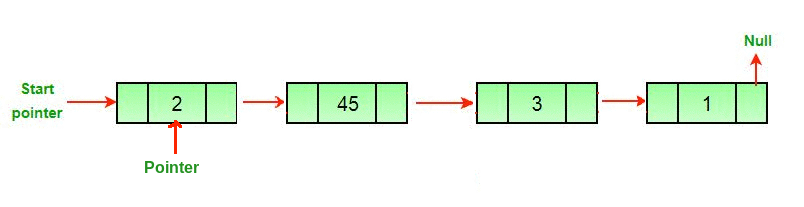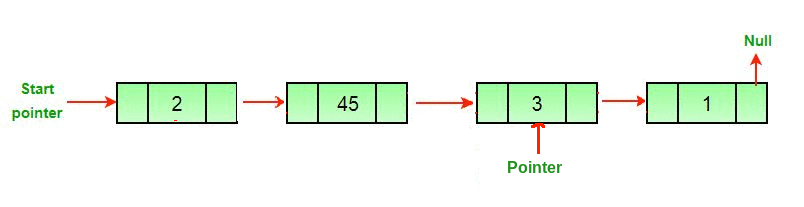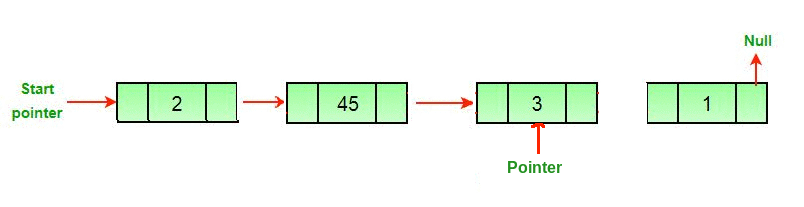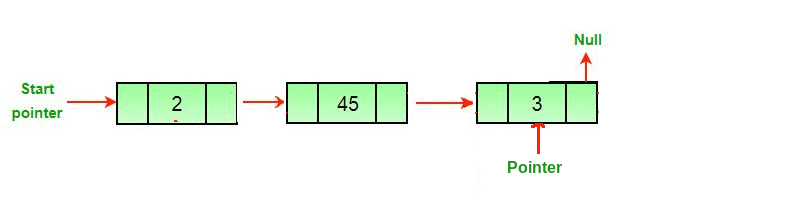
Enfoque: para eliminar el último Node de una lista vinculada, busque el penúltimo Node y haga que el siguiente puntero de ese Node sea nulo.
Algoritmo:
1. Si el primer Node es nulo o solo hay un Node, devuelven nulo.
if headNode == null then return null if headNode.nextNode == null then free head and return null
2. Cree un espacio adicional secondLast y recorra la lista enlazada hasta el penúltimo Node.
while secondLast.nextNode.nextNode != null
secondLast = secondLast.nextNode
3. elimine el último Node, es decir, el siguiente Node del penúltimo Node delete( secondLast .nextNode), y establezca el valor del siguiente penúltimo Node en nulo.
Implementación:
C++
// CPP program to remove last node of
// linked list.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/* Link list node */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
/* Function to remove the last node
of the linked list */
Node* removeLastNode(struct Node* head)
{
if (head == NULL)
return NULL;
if (head->next == NULL) {
delete head;
return NULL;
}
// Find the second last node
Node* second_last = head;
while (second_last->next->next != NULL)
second_last = second_last->next;
// Delete last node
delete (second_last->next);
// Change next of second last
second_last->next = NULL;
return head;
}
// Function to push node at head
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
struct Node* new_node = new Node;
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
Node* head = NULL;
/* Use push() function to construct
the below list 8 -> 23 -> 11 -> 29 -> 12 */
push(&head, 12);
push(&head, 29);
push(&head, 11);
push(&head, 23);
push(&head, 8);
head = removeLastNode(head);
for (Node* temp = head; temp != NULL; temp = temp->next)
cout << temp->data << " ";
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to remove last node of
// linked list.
class GFG {
// Link list node /
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
};
// Function to remove the last node
// of the linked list /
static Node removeLastNode(Node head)
{
if (head == null)
return null;
if (head.next == null) {
return null;
}
// Find the second last node
Node second_last = head;
while (second_last.next.next != null)
second_last = second_last.next;
// Change next of second last
second_last.next = null;
return head;
}
// Function to push node at head
static Node push(Node head_ref, int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node();
new_node.data = new_data;
new_node.next = (head_ref);
(head_ref) = new_node;
return head_ref;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Start with the empty list /
Node head = null;
// Use push() function to construct
// the below list 8 . 23 . 11 . 29 . 12 /
head = push(head, 12);
head = push(head, 29);
head = push(head, 11);
head = push(head, 23);
head = push(head, 8);
head = removeLastNode(head);
for (Node temp = head; temp != null; temp = temp.next)
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu
Python3
# Python3 program to remove the last node of
# linked list.
import sys
import math
# Link list node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
# Function to push node at head
def push(head, data):
if not head:
return Node(data)
temp = Node(data)
temp.next = head
head = temp
return head
# Function to remove the last node
# of the linked list
def removeLastNode(head):
if head == None:
return None
if head.next == None:
head = None
return None
second_last = head
while(second_last.next.next):
second_last = second_last.next
second_last.next = None
return head
# Driver code
if __name__=='__main__':
# Start with the empty list
head = None
# Use push() function to construct
# the below list 8 . 23 . 11 . 29 . 12
head = push(head, 12)
head = push(head, 29)
head = push(head, 11)
head = push(head, 23)
head = push(head, 8)
head = removeLastNode(head)
while(head):
print("{} ".format(head.data), end ="")
head = head.next
# This code is contributed by Vikash kumar 37
C#
// C# program to remove last node of
// linked list.
using System;
class GFG {
// Link list node /
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
};
// Function to remove the last node
// of the linked list /
static Node removeLastNode(Node head)
{
if (head == null)
return null;
if (head.next == null) {
return null;
}
// Find the second last node
Node second_last = head;
while (second_last.next.next != null)
second_last = second_last.next;
// Change next of second last
second_last.next = null;
return head;
}
// Function to push node at head
static Node push(Node head_ref, int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node();
new_node.data = new_data;
new_node.next = (head_ref);
(head_ref) = new_node;
return head_ref;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Start with the empty list /
Node head = null;
// Use push() function to construct
// the below list 8 . 23 . 11 . 29 . 12 /
head = push(head, 12);
head = push(head, 29);
head = push(head, 11);
head = push(head, 23);
head = push(head, 8);
head = removeLastNode(head);
for (Node temp = head; temp != null; temp = temp.next)
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
}
}
/* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */
Javascript
<script>
// javascript program to remove last node of
// linked list. // Link list node /
class Node {
constructor() {
this.data = 0;
this.next = null;
}
}
// Function to remove the last node
// of the linked list /
function removeLastNode(head)
{
if (head == null)
return null;
if (head.next == null) {
return null;
}
// Find the second last node
var second_last = head;
while (second_last.next.next != null)
second_last = second_last.next;
// Change next of second last
second_last.next = null;
return head;
}
// Function to push node at head
function push(head_ref , new_data)
{
var new_node = new Node();
new_node.data = new_data;
new_node.next = (head_ref);
(head_ref) = new_node;
return head_ref;
}
// Driver code
// Start with the empty list /
var head = null;
// Use push() function to construct
// the below list 8 . 23 . 11 . 29 . 12 /
head = push(head, 12);
head = push(head, 29);
head = push(head, 11);
head = push(head, 23);
head = push(head, 8);
head = removeLastNode(head);
for (temp = head; temp != null; temp = temp.next)
document.write(temp.data + " ");
// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji
</script>
8 23 11 29
Análisis de Complejidad:
- Complejidad temporal: O(n).
El algoritmo implica el recorrido de la lista enlazada hasta su final, por lo que la complejidad de tiempo requerida es O(n) . - Complejidad espacial: O(1).
No se requiere espacio adicional, por lo que la complejidad del espacio es constante.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por VishalBachchas y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA
