Pairing Heap es como una forma simplificada de Fibonacci Heap . También mantiene la propiedad del montón mínimo , cuyo valor principal es menor que el valor de los Nodes secundarios. Se puede considerar como un montón binomial autoajustable.
Cada Node tiene un puntero hacia el hijo izquierdo y el hijo izquierdo apunta hacia el siguiente hermano del hijo.
A continuación se muestra un ejemplo de montón de emparejamiento:

Unirse o fusionarse en un montón de emparejamiento
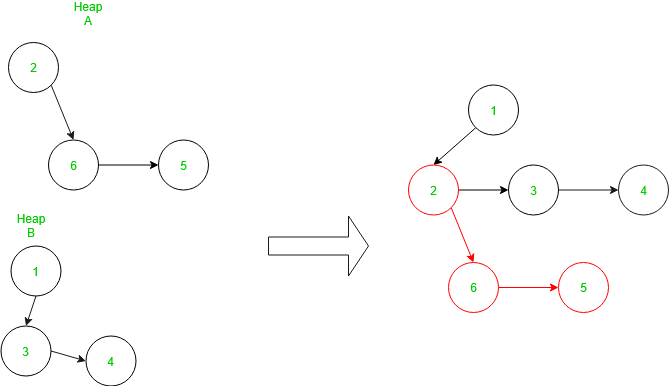
Para unir los dos montones, primero, comparamos el Node raíz del montón si el Node raíz del primer montón es más pequeño que el Node raíz del segundo montón, entonces el Node raíz del segundo montón se convierte en un Node izquierdo hijo del Node raíz del primer montón, de lo contrario, viceversa. La complejidad temporal de este proceso es O(1).
A continuación se muestra un ejemplo de combinación:
Inserción en el montón de emparejamiento :
para insertar un nuevo Node en el montón, cree un nuevo Node y combínelo con el montón existente como se explicó anteriormente. Por lo tanto, la complejidad temporal de esta función es O(1).
A continuación se muestra un ejemplo de inserción:

Eliminación en el montón de emparejamiento :
la eliminación en el montón de emparejamiento solo ocurre en el Node raíz. Primero elimine los enlaces entre la raíz, el hijo izquierdo y todos los hermanos del hijo izquierdo. Luego, fusione los subárboles que se obtienen al separar el hijo izquierdo y todos los hermanos mediante el método de dos pases y elimine el Node raíz. Combine los subárboles separados de izquierda a derecha en una sola pasada y luego combine los subárboles de derecha a izquierda para formar el nuevo montón sin violar las condiciones del montón mínimo. Este proceso toma un tiempo O(log n) donde n es el número de Nodes.
A continuación se muestra un ejemplo de eliminación:

A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
CPP14
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Heap structure
struct HeapNode {
int key;
HeapNode *leftChild;
HeapNode *nextSibling;
HeapNode():
leftChild(NULL), nextSibling(NULL) {}
// creates a new node
HeapNode(int key_, HeapNode *leftChild_, HeapNode *nextSibling_):
key(key_), leftChild(leftChild_), nextSibling(nextSibling_) {}
// Adds a child and sibling to the node
void addChild(HeapNode *node) {
if(leftChild == NULL)
leftChild = node;
else {
node->nextSibling = leftChild;
leftChild = node;
}
}
};
// Returns true if root of the tree
// is null otherwise returns false
bool Empty(HeapNode *node) {
return (node == NULL);
}
// Function to merge two heaps
HeapNode *Merge(HeapNode *A, HeapNode *B)
{
// If any of the two-nodes is null
// the return the not null node
if(A == NULL) return B;
if(B == NULL) return A;
// To maintain the min heap condition compare
// the nodes and node with minimum value become
// parent of the other node
if(A->key < B->key) {
A->addChild(B);
return A;
}
else {
B->addChild(A);
return B;
}
return NULL; // Unreachable
}
// Returns the root value of the heap
int Top(HeapNode *node) {
return node->key;
}
// Function to insert the new node in the heap
HeapNode *Insert(HeapNode *node, int key) {
return Merge(node, new HeapNode(key, NULL, NULL));
}
// This method is used when we want to delete root node
HeapNode *TwoPassMerge(HeapNode *node) {
if(node == NULL || node->nextSibling == NULL)
return node;
else {
HeapNode *A, *B, *newNode;
A = node;
B = node->nextSibling;
newNode = node->nextSibling->nextSibling;
A->nextSibling = NULL;
B->nextSibling = NULL;
return Merge(Merge(A, B), TwoPassMerge(newNode));
}
return NULL; // Unreachable
}
// Function to delete the root node in heap
HeapNode *Delete(HeapNode *node) {
return TwoPassMerge(node->leftChild);
}
struct PairingHeap {
HeapNode *root;
PairingHeap():
root(NULL) {}
bool Empty(void) {
return ::Empty(root);
}
int Top(void) {
return ::Top(root);
}
void Insert(int key) {
root = ::Insert(root, key);
}
void Delete(void) {
root = ::Delete(root);
}
void Join(PairingHeap other) {
root = ::Merge(root, other.root);
}
};
// Driver Code
int main(void) {
PairingHeap heap1, heap2;
heap2.Insert(5);
heap2.Insert(2);
heap2.Insert(6);
heap1.Insert(1);
heap1.Insert(3);
heap1.Insert(4);
heap1.Join(heap2);
cout << heap1.Top() << endl;
heap1.Delete();
cout << heap1.Top() << endl;
cout<< (heap1.Empty()?"True":"False");
return 0;
}
Python3
# Heap structure class HeapNode: # creates a new node def __init__(self, key_=None, leftChild_=None, nextSibling_=None): self.key = key_ self.leftChild = leftChild_ self.nextSibling = nextSibling_ # Adds a child and sibling to the node def addChild(self, node): if(self.leftChild == None): self.leftChild = node else: node.nextSibling = self.leftChild self.leftChild = node # Returns true if root of the tree # is None otherwise returns false def Empty(node): return (node == None) # Function to merge two heaps def Merge(A, B): # If any of the two-nodes is None # the return the not None node if(A == None): return B if(B == None): return A # To maintain the min heap condition compare # the nodes and node with minimum value become # parent of the other node if(A.key < B.key): A.addChild(B) return A B.addChild(A) return B # Returns the root value of the heap def Top(node): return node.key # Function to insert the new node in the heap def Insert(node, key): return Merge(node, HeapNode(key,)) # This method is used when we want to delete root node def TwoPassMerge(node): if(node == None or node.nextSibling == None): return node A = node B = node.nextSibling newNode = node.nextSibling.nextSibling A.nextSibling = None B.nextSibling = None return Merge(Merge(A, B), TwoPassMerge(newNode)) # Function to delete the root node in heap def Delete(node): return TwoPassMerge(node.leftChild) class PairingHeap: def __init__(self): self.root = None def Empty(self): return Empty(self.root) def Top(self): return Top(self.root) def Insert(self, key): self.root = Insert(self.root, key) def Delete(self): self.root = Delete(self.root) def Join(self, other): self.root = Merge(self.root, other.root) # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': heap1, heap2 = PairingHeap(), PairingHeap() heap2.Insert(5) heap2.Insert(2) heap2.Insert(6) heap1.Insert(1) heap1.Insert(3) heap1.Insert(4) heap1.Join(heap2) print(heap1.Top()) heap1.Delete() print(heap1.Top()) print(heap1.Empty()) # This code is contributed by Amartya Ghosh
1 2 False
Complejidad de tiempo:
Inserción: O(1)
Fusión: O(1)
Eliminación: O(logN)
Espacio auxiliar : O(1).
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por ParthManiyar y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA