Distribuciones
- uniform_int_distribution: Produce valores enteros aleatorios i, que se distribuyen uniformemente en el intervalo cerrado [a,b], que se describe mediante la siguiente función de masa de probabilidad:
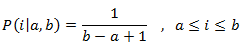
- operator(): Genera los números aleatorios que se distribuyen según la función de probabilidad.
- min: devuelve el mayor límite inferior del rango de valores devueltos por operator(), que es el parámetro de distribución ‘a’ para uniform_int_distribution.
- max: devuelve el límite superior mínimo del rango de valores devueltos por operator(), que es el parámetro de distribución ‘b’ para uniform_int_distribution.
- reset: Resetea la distribución, de forma que en los usos posteriores el resultado no dependa de los valores ya producidos por ella.
// C++ program to illustrate// the use of operator()// in uniform_int_distribution#include <iostream>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;// Driver programintmain(){// Constructing a trivial random generator engineunsigned s = 2;// The random number generatordefault_random_engine generator (s);uniform_int_distribution<int> distribution(1,10);cout <<"Some random numbers between 1 and 10";for(inti = 0; i < 10; ++i)cout << distribution(generator) ;cout << endl;return0;}Producción:
Some random numbers between 1 and 10: 1 3 6 10 1 5 1 4 4 9
// C++ program to illustrate// the use of reset// in uniform_int_distribution#include <iostream>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;//Driver programintmain(){//the random number generatordefault_random_engine generator;// Initialising the uniform distributionuniform_int_distribution<int> distribution(1, 1000);// First random number is generatedcout << distribution(generator) << endl;//Resets the distributiondistribution.reset();// Second random number is//generated independent of previous numbercout << distribution(generator) << endl;return0;}Producción:
1 132
- uniform_real_distribution: Es la distribución de números aleatorios que produce valores de punto flotante, que se describe mediante la siguiente función de densidad de probabilidad:
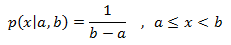
- operator(): Devuelve un nuevo número aleatorio que sigue los parámetros de la distribución.
- min: Devuelve el mayor límite inferior del rango de valores devuelto por operator(), que es el parámetro de distribución ‘a’ para uniform_real_distribution.
- max: devuelve el límite superior mínimo del rango de valores devueltos por operator(), que es el parámetro de distribución ‘b’ para uniform_real_distribution.
- reset: Resetea la distribución, de forma que en los usos posteriores el resultado no dependa de los valores ya producidos por ella.
// C++ program to illustrate// the use of operator()// in uniform_int_distribution#include <iostream>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;// Driver programintmain(){// Constructing a trivial random generator engineunsigned s = 2;// The random number generatordefault_random_engine generator (s);uniform_int_distribution<int> distribution(1,10);cout <<"Random numbers between 1 and 10";for(inti = 0; i< 10; ++i)cout << distribution(generator) ;cout << endl;return0;}Producción:
some random numbers between 0.0 and 10.0: 0.150031 9.77072 3.36669 7.06447 5.11455 8.43061 1.93792 7.78965 8.31532 5.14354
// C++ program to illustrate// the use of reset// in uniform_real_distribution#include <iostream>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;// Driver programintmain(){default_random_engine generator;uniform_real_distribution<double> distribution(0.0,100.0);// It prints two independent values:// First random number is generatedcout << distribution(generator) << endl;//Resets the distributiondistribution.reset();// Second random number is//generated independent of previous numbercout << distribution(generator) << endl;return0;}Producción:
13.1538 45.865
II. Relacionado con los juicios de Bernoulli:
- bernoulli_distribution: Es la distribución de números aleatorios que produce valores booleanos según una distribución de Bernoulli, dada por la siguiente función de masa de probabilidad:

- operator(): Devuelve un nuevo número aleatorio.
- min: Devuelve el mayor límite inferior del rango de valores devuelto por operator(), que para bernoulli_distribution es falso.
- max: devuelve el límite superior mínimo del rango de valores devueltos por operator(), que para bernoulli_distribution es verdadero.
// C++ program to illustrate// the bernoulli_distribution#include <iostream>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;//Driver programintmain(){constinttemp=500;//The random number generatordefault_random_engine generator;//Initialising the bernoulli distributionbernoulli_distribution distribution(0.7);// count number of truesintcount=0;for(inti = 0; i < temp; ++i){// checking for true conditionif(distribution(generator))count++;}cout <<"bernoulli_distribution (0.7) x 500:"<< endl;cout <<"true: "<< count << endl;cout <<"false: "<< temp-count << endl;return0;}Producción:
bernoulli_distribution (0.7) x 500: true: 360 false: 140
// C++ program to// illustrate the use of reset#include <iostream>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;//Driver programintmain(){// Random number generatordefault_random_engine generator;// Initialising the bernoulli distributionbernoulli_distribution distribution;// print two independent values:cout << distribution(generator) << endl;// use of reset// Generates second output without// the effect of first outputdistribution.reset();cout << distribution(generator) << endl;return0;}Producción:
1 1
- binomial_distribution: Es la distribución de números aleatorios que produce números enteros de acuerdo a una distribución binomial discreta, la cual viene dada por esta función de masa de probabilidad:

- operator(): Genera un nuevo número aleatorio.
- max: Devuelve el límite superior mínimo del rango dado por operator(), que para binomial_distribution es el parámetro de distribución t.
- min: Devuelve el mayor límite inferior del rango dado por el operador miembro(), que para binomial_distribution siempre es cero.
- reset: Resetea la distribución, de modo que los usos posteriores del objeto no dependan de los valores ya producidos por él.
// C++ program to illustrate// the use of binomial_distribution#include <iostream>#include <chrono>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;intmain(){// construct a trivial random//generator engine from a time-based seed:unsigned seed = chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count();default_random_engine generator (seed);// Initialising binomial distributionbinomial_distribution<int> distribution (15, 0.4);cout <<"some binomial results (t=15, p=0.4): ";for(inti = 0; i < 15; ++i){// Use of operator()cout << distribution(generator) <<" ";}cout << endl;return0;}Producción:
some binomial results (t=15, p=0.4): 7 6 7 8 4 6 7 6 9 3 5 6 4 6 7
// C++ program to illustrate// the use of binomial_distribution#include <iostream>#include <chrono>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;intmain(){// construct a trivial random//generator engine from a time-based seed:unsigned seed = chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count();default_random_engine generator (seed);// Initialising binomial distributionbinomial_distribution<int> distribution (15, 0.4);cout <<"some binomial results (t=15, p=0.4): ";for(inti = 0; i < 15; ++i){// Use of operator()cout << distribution(generator) <<" ";}cout << endl;return0;}Producción:
57 52
- distribución_geométrica : Es una distribución de números aleatorios que produce números enteros de acuerdo a una distribución geométrica discreta, dada por la siguiente función de masa de probabilidad:

- operator(): Devuelve un nuevo número aleatorio que sigue los parámetros de la distribución.
- max: Devuelve el límite superior mínimo del rango dado por operator().
- min: Devuelve el valor mínimo dado por operator().
- reset: Resetea la distribución, de modo que los usos posteriores del objeto no dependan de los valores ya producidos por él.
// C++ program to illustrate//the use of geometric_distribution#include <iostream>#include <chrono>#include <string>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;intmain(){// construct a trivial random// generator engine from a time-based seed:intseed = chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count();default_random_engine generator (seed);// Initialises the geometric distributiongeometric_distribution<int> distribution (1.0 / 5);cout <<"Plus sign is 5 spaces away from the next :"<< endl;for(inti = 0; i < 10 ; ++i){intnumber = distribution(generator);cout << string (number,' ') <<"+";}return0;}Producción:
each plus sign is 5 spaces away from the next : ++ + + + ++ + ++// C++ program to illustrate// the use of reset#include <iostream>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;// Driver programintmain(){// Random number generatordefault_random_engine generator;// Initialising the geometric distributiongeometric_distribution<int> distribution(0.3);// Prints two independent values:// Generates the first valuecout << distribution(generator) << endl;// Use of resetdistribution.reset();// Generates second valuecout << distribution(generator) << endl;return0;}Producción:
0 1
- distribución_binomial_negativa : Es una distribución de números aleatorios que produce números enteros de acuerdo con una distribución discreta binomial negativa (también conocida como distribución de Pascal), dada por la siguiente función de masa de probabilidad:
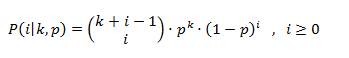
- operator(): Devuelve un nuevo número aleatorio que sigue los parámetros de la distribución.
- max: Devuelve el límite superior mínimo del rango dado por operator().
- min: Devuelve el valor mínimo dado por operator(), que para distribución_binomial_negativa siempre es cero.
- reset: Resetea la distribución, de modo que los usos posteriores del objeto no dependan de los valores ya producidos por él.
// C++ program to illustrate// the use of operator() in// negative_binomial_distribution#include <iostream>#include <chrono>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;// Driver programintmain(){// construct a trivial random// generator engine from a time-based seed:unsigned seed = chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count();default_random_engine generator (seed);// Initialising negative binomial distributionnegative_binomial_distribution<int> distribution (6,0.7);cout <<"Negative binomial results (t=6, p=0.7): ";for(inti = 0; i < 15; ++i){// Use of operatorcout << distribution(generator) <<" ";}cout << endl;return0;}Producción:
Negative binomial results (t=6, p=0.7): 2 6 3 1 4 1 4 1 2 0 7 3 4 4 4
// C++ program to illustrate// the use of reset in// negative_binomial_distribution::#include <iostream>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;// Driver programintmain(){// Random number generatordefault_random_engine generator;// Initialising the negative binomial distributionnegative_binomial_distribution<int> distribution(20, 0.5);// print two independent values:// Generates the first valuecout << distribution(generator) << endl;// Use of resetdistribution.reset();// Generates the second valuecout << distribution(generator) << endl;return0;}Producción:
23 30
III.Distribuciones por piezas:
- distribución_discreta : Es una distribución de números aleatorios que produce valores enteros de acuerdo a una distribución discreta.
- operator(): Devuelve un nuevo número aleatorio que sigue los parámetros de la distribución.
- max: Devuelve el límite superior mínimo del rango dado por operator().
- min: Devuelve el mayor límite inferior del rango dado por operator().
- reset: Resetea la distribución, de modo que los usos posteriores del objeto no dependan de los valores ya producidos por él.
// C++ program to illustrate the// use of operator() in// discrete_distribution#include <iostream>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;intmain(){// number of experimentsintn = 10000;// maximum number of stars to distributeintm = 100;// Random number generatordefault_random_engine generator;//Initialising discrete distributiondiscrete_distribution<int> distribution { 2, 2, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1, 1, 2, 2 };intp[10] = {};// use of operator()for(inti = 0; i < n; i++){intnumber = distribution(generator);p[number]++;}cout <<"a discrete_distribution:"<< endl;for(inti = 0; i < 10; ++i){cout << i <<": "<< string(p[i]*m/n,'*') << endl;}return0;}Producción:
a discrete_distribution: 0: ************ 1: ************* 2: ***** 3: ****** 4: ************ 5: ************ 6: ****** 7: ****** 8: ************ 9: ************
// C++ program to illustrate//the use of reset in//discrete_distribution#include <iostream>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;// Driver programintmain(){// Random number generatordefault_random_engine generator;// Initialising the discrete distributiondiscrete_distribution<int> distribution {20,20,30,40};// print two independent values:// Generates the first valuecout << distribution(generator) << endl;// Use of resetdistribution.reset();// Generates the secong valuecout << distribution(generator) << endl;return0;}Producción:
0 2
- piecewise_constant_distribution: Es una distribución de números aleatorios que produce valores de punto flotante que se distribuyen uniformemente sobre cada uno de una secuencia de subintervalos contiguos, dados por la siguiente función de densidad de probabilidad:
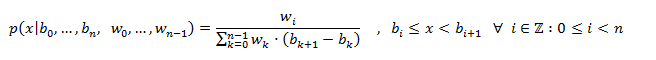
- operator(): Devuelve un nuevo número aleatorio que sigue los parámetros de la distribución.
- max: Devuelve el límite superior mínimo del rango dado por operator().
- min: Devuelve el mayor límite inferior del rango dado por operator().
- reset: Resetea la distribución, de modo que los usos posteriores del objeto no dependan de los valores ya producidos por él.
// C++ program to illustrate the// use of reset in// piecewise_constant_distribution#include <iostream>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;// Driver programintmain(){// Random number generatordefault_random_engine generator;// Initialisind piecewise_constant_distributionpiecewise_constant_distribution<double> distribution( 4, 0.0, 10.0, [](doublex){returnx;} );// print two independent values:// Generates the first value// Use of operator()cout << distribution(generator) << endl;// Use of resetdistribution.reset();// Generates second valuecout << distribution(generator) << endl;return0;}Producción:
3.4205 6.6692
- piecewise_linear_distribution: es una distribución de números aleatorios que produce valores de coma flotante que se distribuyen en una secuencia de subintervalos contiguos.
- operator(): Devuelve un nuevo número aleatorio que sigue los parámetros de la distribución.
- max: Devuelve el límite superior mínimo del rango dado por operator().
- min: Devuelve el mayor límite inferior del rango dado por operator().
- reset: Resetea la distribución, de modo que los usos posteriores del objeto no dependan de los valores ya producidos por él.
// C++ program to illustrate the// use of reset in// piecewise_linear_distribution#include <iostream>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;// Driver programintmain(){// Random number generatordefault_random_engine generator;// Initialising piecewise_linear_distributionpiecewise_linear_distribution<double>distribution ( 5, 0.0, 10.0, [](doublex){returnx+1.0;} );// print two independent values:// generates first value// use of operator()cout << distribution(generator) << endl;// Use of resetdistribution.reset();// generates second valuecout << distribution(generator) << endl;return0;}Producción:
2.48143 6.07656
Este artículo es una contribución de Shambhavi Singh . Si le gusta GeeksforGeeks y le gustaría contribuir, también puede escribir un artículo usando contribuya.geeksforgeeks.org o envíe su artículo por correo a contribuya@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA