requisitos previos:
Dado un árbol N-ario con N Nodes numerados de 0 a N-1 y una lista de aristas no dirigidas, la tarea es encontrar los Nodes en el centro del árbol dado.
Excentricidad: La excentricidad de cualquier vértice V en un árbol dado es la distancia máxima entre el vértice V dado y cualquier otro vértice del árbol.
Centro: El centro de un árbol es el vértice que tiene la mínima excentricidad. Por lo tanto, significa que para encontrar el centro tenemos que minimizar esta excentricidad.
Ejemplos:
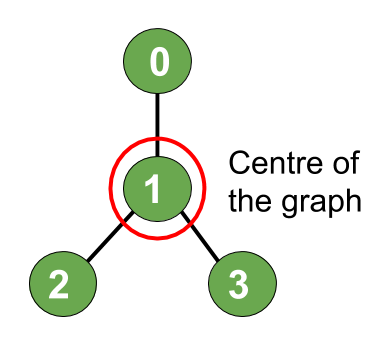
Entrada: N = 4, Edges[] = { (1, 0), (1, 2), (1, 3)}
Salida: 1
Explicación:
Entrada: N = 6, Edges[] = { (0, 3), (1, 3), (2, 3), (4, 3), (5, 4)}
Salida: 3, 4
Explicación:
Aproximación: Se puede observar que el camino de máxima excentricidad es el diámetro del árbol. Por lo tanto, el centro del diámetro del árbol será también el centro del árbol.
Prueba:
- Por ejemplo, consideremos un caso en el que el camino más largo consta de un número impar de vértices. Sea el camino más largo X —— O ——– Y donde X e Y son los dos extremos del camino y O es el vértice central.
- Para una contradicción, si el centro del árbol no es O sino algún otro vértice O’ , entonces al menos uno de los dos enunciados siguientes debe ser verdadero.
- La ruta XO’ es estrictamente más larga que la ruta XO
- La ruta YO’ es estrictamente más larga que la ruta YO
- Esto significa que O’ no cumplirá la condición de mínima excentricidad. Por lo tanto, por contradicción, hemos demostrado que el centro del árbol es en realidad el centro de la trayectoria del diámetro.
- Ahora, si el diámetro consta de un número impar de Nodes, entonces existe solo 1 centro (también conocido como Árbol central ).
- Si el diámetro consta de un número par de Nodes, entonces hay 2 Nodes centrales (también conocidos como árbol bicentral ).
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation of
// the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// To create tree
map<int, vector<int> > tree;
// Function to store the path
// from given vertex to the target
// vertex in a vector path
bool getDiameterPath(int vertex,
int targetVertex,
int parent,
vector<int>& path)
{
// If the target node is found,
// push it into path vector
if (vertex == targetVertex) {
path.push_back(vertex);
return true;
}
for (auto i : tree[vertex]) {
// To prevent visiting a
// node already visited
if (i == parent)
continue;
// Recursive call to the neighbours
// of current node inorder
// to get the path
if (getDiameterPath(i, targetVertex,
vertex, path)) {
path.push_back(vertex);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// Function to obtain and return the
// farthest node from a given vertex
void farthestNode(int vertex, int parent,
int height, int& maxHeight,
int& maxHeightNode)
{
// If the current height is maximum
// so far, then save the current node
if (height > maxHeight) {
maxHeight = height;
maxHeightNode = vertex;
}
// Iterate over all the neighbours
// of current node
for (auto i : tree[vertex]) {
// This is to prevent visiting
// a already visited node
if (i == parent)
continue;
// Next call will be at 1 height
// higher than our current height
farthestNode(i, vertex,
height + 1,
maxHeight,
maxHeightNode);
}
}
// Function to add edges
void addedge(int a, int b)
{
tree[a].push_back(b);
tree[b].push_back(a);
}
void FindCenter(int n)
{
// Now we will find the 1st farthest
// node from 0(any arbitrary node)
// Perform DFS from 0 and update
// the maxHeightNode to obtain
// the farthest node from 0
// Reset to -1
int maxHeight = -1;
// Reset to -1
int maxHeightNode = -1;
farthestNode(0, -1, 0, maxHeight,
maxHeightNode);
// Stores one end of the diameter
int leaf1 = maxHeightNode;
// Similarly the other end of
// the diameter
// Reset the maxHeight
maxHeight = -1;
farthestNode(maxHeightNode,
-1, 0, maxHeight,
maxHeightNode);
// Stores the second end
// of the diameter
int leaf2 = maxHeightNode;
// Store the diameter into
// the vector path
vector<int> path;
// Diameter is equal to the
// path between the two farthest
// nodes leaf1 and leaf2
getDiameterPath(leaf1, leaf2,
-1, path);
int pathSize = path.size();
if (pathSize % 2) {
cout << path[pathSize / 2]
<< endl;
}
else {
cout << path[pathSize / 2]
<< ", "
<< path[(pathSize - 1) / 2]
<< endl;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int N = 4;
addedge(1, 0);
addedge(1, 2);
addedge(1, 3);
FindCenter(N);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation of
// the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// To create tree
static Map<Integer, ArrayList<Integer>> tree;
static ArrayList<Integer> path;
static int maxHeight, maxHeightNode;
// Function to store the path
// from given vertex to the target
// vertex in a vector path
static boolean getDiameterPath(int vertex,
int targetVertex,
int parent,
ArrayList<Integer> path)
{
// If the target node is found,
// push it into path vector
if (vertex == targetVertex)
{
path.add(vertex);
return true;
}
for(Integer i : tree.get(vertex))
{
// To prevent visiting a
// node already visited
if (i == parent)
continue;
// Recursive call to the neighbours
// of current node inorder
// to get the path
if (getDiameterPath(i, targetVertex,
vertex, path))
{
path.add(vertex);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// Function to obtain and return the
// farthest node from a given vertex
static void farthestNode(int vertex, int parent,
int height)
{
// If the current height is maximum
// so far, then save the current node
if (height > maxHeight)
{
maxHeight = height;
maxHeightNode = vertex;
}
// Iterate over all the neighbours
// of current node
if (tree.get(vertex) != null)
for(Integer i : tree.get(vertex))
{
// This is to prevent visiting
// a already visited node
if (i == parent)
continue;
// Next call will be at 1 height
// higher than our current height
farthestNode(i, vertex,
height + 1);
}
}
// Function to add edges
static void addedge(int a, int b)
{
if (tree.get(a) == null)
tree.put(a, new ArrayList<>());
tree.get(a).add(b);
if (tree.get(b) == null)
tree.put(b, new ArrayList<>());
tree.get(b).add(a);
}
static void FindCenter(int n)
{
// Now we will find the 1st farthest
// node from 0(any arbitrary node)
// Perform DFS from 0 and update
// the maxHeightNode to obtain
// the farthest node from 0
// Reset to -1
maxHeight = -1;
// Reset to -1
maxHeightNode = -1;
farthestNode(0, -1, 0);
// Stores one end of the diameter
int leaf1 = maxHeightNode;
// Similarly the other end of
// the diameter
// Reset the maxHeight
maxHeight = -1;
farthestNode(maxHeightNode,
-1, 0);
// Stores the second end
// of the diameter
int leaf2 = maxHeightNode;
// Store the diameter into
// the vector path
path = new ArrayList<>();
// Diameter is equal to the
// path between the two farthest
// nodes leaf1 and leaf2
getDiameterPath(leaf1, leaf2,
-1, path);
int pathSize = path.size();
if (pathSize % 2 == 1)
{
System.out.println(path.get(pathSize / 2));
}
else {
System.out.println(path.get(pathSize / 2) +
", " + path.get((pathSize - 1) / 2));
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 4;
tree = new HashMap<>();
addedge(1, 0);
addedge(1, 2);
addedge(1, 3);
FindCenter(N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeat
Python3
# Python3 implementation of the above approach
# To create tree
tree = {}
path = []
maxHeight, maxHeightNode = -1, -1
# Function to store the path
# from given vertex to the target
# vertex in a vector path
def getDiameterPath(vertex, targetVertex, parent, path):
# If the target node is found,
# push it into path vector
if (vertex == targetVertex):
path.append(vertex)
return True
for i in range(len(tree[vertex])):
# To prevent visiting a
# node already visited
if (tree[vertex][i] == parent):
continue
# Recursive call to the neighbours
# of current node inorder
# to get the path
if (getDiameterPath(tree[vertex][i], targetVertex, vertex, path)):
path.append(vertex)
return True
return False
# Function to obtain and return the
# farthest node from a given vertex
def farthestNode(vertex, parent, height):
global maxHeight, maxHeightNode
# If the current height is maximum
# so far, then save the current node
if (height > maxHeight):
maxHeight = height
maxHeightNode = vertex
# Iterate over all the neighbours
# of current node
if (vertex in tree):
for i in range(len(tree[vertex])):
# This is to prevent visiting
# a already visited node
if (tree[vertex][i] == parent):
continue
# Next call will be at 1 height
# higher than our current height
farthestNode(tree[vertex][i], vertex, height + 1)
# Function to add edges
def addedge(a, b):
if (a not in tree):
tree[a] = []
tree[a].append(b)
if (b not in tree):
tree[b] = []
tree[b].append(a)
def FindCenter(n):
# Now we will find the 1st farthest
# node from 0(any arbitrary node)
# Perform DFS from 0 and update
# the maxHeightNode to obtain
# the farthest node from 0
# Reset to -1
maxHeight = -1
# Reset to -1
maxHeightNode = -1
farthestNode(0, -1, 0)
# Stores one end of the diameter
leaf1 = maxHeightNode
# Similarly the other end of
# the diameter
# Reset the maxHeight
maxHeight = -1
farthestNode(maxHeightNode, -1, 0)
# Stores the second end
# of the diameter
leaf2 = maxHeightNode
# Store the diameter into
# the vector path
path = []
# Diameter is equal to the
# path between the two farthest
# nodes leaf1 and leaf2
getDiameterPath(leaf1, leaf2, -1, path)
pathSize = len(path)
if (pathSize % 2 == 1):
print(path[int(pathSize / 2)]*-1)
else:
print(path[int(pathSize / 2)], ", ", path[int((pathSize - 1) / 2)], sep = "", end = "")
N = 4
tree = {}
addedge(1, 0)
addedge(1, 2)
addedge(1, 3)
FindCenter(N)
# This code is contributed by suresh07.
C#
// C# implementation of
// the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
// To create tree
static Dictionary<int, List<int>> tree;
static List<int> path;
static int maxHeight, maxHeightNode;
// Function to store the path
// from given vertex to the target
// vertex in a vector path
static bool getDiameterPath(int vertex,
int targetVertex,
int parent,
List<int> path)
{
// If the target node is found,
// push it into path vector
if (vertex == targetVertex)
{
path.Add(vertex);
return true;
}
foreach(int i in tree[vertex])
{
// To prevent visiting a
// node already visited
if (i == parent)
continue;
// Recursive call to the neighbours
// of current node inorder
// to get the path
if (getDiameterPath(i, targetVertex,
vertex, path))
{
path.Add(vertex);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// Function to obtain and return the
// farthest node from a given vertex
static void farthestNode(int vertex, int parent,
int height)
{
// If the current height is maximum
// so far, then save the current node
if (height > maxHeight)
{
maxHeight = height;
maxHeightNode = vertex;
}
// Iterate over all the neighbours
// of current node
if (tree.ContainsKey(vertex) && tree[vertex].Count > 0)
{
foreach(int i in tree[vertex])
{
// This is to prevent visiting
// a already visited node
if (i == parent)
continue;
// Next call will be at 1 height
// higher than our current height
farthestNode(i, vertex, height + 1);
}
}
}
// Function to add edges
static void addedge(int a, int b)
{
if (!tree.ContainsKey(a))
tree[a] = new List<int>();
tree[a].Add(b);
if (!tree.ContainsKey(b))
tree[b] = new List<int>();
tree[b].Add(a);
}
static void FindCenter(int n)
{
// Now we will find the 1st farthest
// node from 0(any arbitrary node)
// Perform DFS from 0 and update
// the maxHeightNode to obtain
// the farthest node from 0
// Reset to -1
maxHeight = -1;
// Reset to -1
maxHeightNode = -1;
farthestNode(0, -1, 0);
// Stores one end of the diameter
int leaf1 = maxHeightNode;
// Similarly the other end of
// the diameter
// Reset the maxHeight
maxHeight = -1;
farthestNode(maxHeightNode,
-1, 0);
// Stores the second end
// of the diameter
int leaf2 = maxHeightNode;
// Store the diameter into
// the vector path
path = new List<int>();
// Diameter is equal to the
// path between the two farthest
// nodes leaf1 and leaf2
getDiameterPath(leaf1, leaf2,
-1, path);
int pathSize = path.Count;
if (pathSize % 2 == 1)
{
Console.WriteLine(path[pathSize / 2]);
}
else {
Console.WriteLine(path[pathSize / 2] +
", " + path[(pathSize - 1) / 2]);
}
}
static void Main() {
int N = 4;
tree = new Dictionary<int, List<int>>();
addedge(1, 0);
addedge(1, 2);
addedge(1, 3);
FindCenter(N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyesh072019.
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript implementation of the above approach
// To create tree
let tree;
let path;
let maxHeight, maxHeightNode;
// Function to store the path
// from given vertex to the target
// vertex in a vector path
function getDiameterPath(vertex, targetVertex, parent, path)
{
// If the target node is found,
// push it into path vector
if (vertex == targetVertex)
{
path.push(vertex);
return true;
}
for(let i = 0; i < tree.get(vertex).length; i++)
{
// To prevent visiting a
// node already visited
if (tree.get(vertex)[i] == parent)
continue;
// Recursive call to the neighbours
// of current node inorder
// to get the path
if (getDiameterPath(tree.get(vertex)[i], targetVertex,
vertex, path))
{
path.push(vertex);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// Function to obtain and return the
// farthest node from a given vertex
function farthestNode(vertex, parent, height)
{
// If the current height is maximum
// so far, then save the current node
if (height > maxHeight)
{
maxHeight = height;
maxHeightNode = vertex;
}
// Iterate over all the neighbours
// of current node
if (tree.get(vertex) != null)
for(let i = 0; i < tree.get(vertex).length; i++)
{
// This is to prevent visiting
// a already visited node
if (tree.get(vertex)[i] == parent)
continue;
// Next call will be at 1 height
// higher than our current height
farthestNode(tree.get(vertex)[i], vertex, height + 1);
}
}
// Function to add edges
function addedge(a, b)
{
if (tree.get(a) == null)
tree.set(a, []);
tree.get(a).push(b);
if (tree.get(b) == null)
tree.set(b, []);
tree.get(b).push(a);
}
function FindCenter(n)
{
// Now we will find the 1st farthest
// node from 0(any arbitrary node)
// Perform DFS from 0 and update
// the maxHeightNode to obtain
// the farthest node from 0
// Reset to -1
maxHeight = -1;
// Reset to -1
maxHeightNode = -1;
farthestNode(0, -1, 0);
// Stores one end of the diameter
let leaf1 = maxHeightNode;
// Similarly the other end of
// the diameter
// Reset the maxHeight
maxHeight = -1;
farthestNode(maxHeightNode,
-1, 0);
// Stores the second end
// of the diameter
let leaf2 = maxHeightNode;
// Store the diameter into
// the vector path
path = [];
// Diameter is equal to the
// path between the two farthest
// nodes leaf1 and leaf2
getDiameterPath(leaf1, leaf2,
-1, path);
let pathSize = path.length;
if (pathSize % 2 == 1)
{
document.write(path[parseInt(pathSize / 2, 10)]);
}
else {
document.write(path[parseInt(pathSize / 2, 10)] +
", " + path[parseInt((pathSize - 1) / 2, 10)]);
}
}
let N = 4;
tree = new Map();
addedge(1, 0);
addedge(1, 2);
addedge(1, 3);
FindCenter(N);
</script>
1
Complejidad temporal: O(N)
Espacio auxiliar: O(N)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por red_devil09 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA