Escriba una función findFirstLoopNode() que verifique si una lista enlazada dada contiene un bucle. Si el bucle está presente, devuelve el punto al primer Node del bucle. De lo contrario, devuelve NULL.
Ejemplo :
Input : Head of below linked list
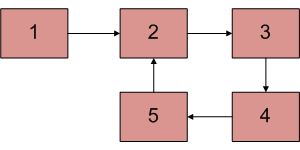
Output : Pointer to node 2
Hemos discutido el algoritmo de detección de bucles de Floyd . A continuación se muestran los pasos para encontrar el primer Node del ciclo.
1. Si se encuentra un bucle, inicialice un puntero lento en la cabeza, deje que el puntero rápido esté en su posición.
2. Mueva los punteros lento y rápido un Node a la vez.
3. El punto en el que se encuentran es el comienzo del bucle.
C++
// C++ program to return first node of loop.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node* next;
};
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
void printList(Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
cout << head->key << " ";
head = head->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
// Function to detect and remove loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
Node* detectAndRemoveLoop(Node* head)
{
// If list is empty or has only one node
// without loop
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL)
return NULL;
Node *slow = head, *fast = head;
// Move slow and fast 1 and 2 steps
// ahead respectively.
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
// Search for loop using slow and
// fast pointers
while (fast && fast->next) {
if (slow == fast)
break;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
// If loop does not exist
if (slow != fast)
return NULL;
// If loop exists. Start slow from
// head and fast from meeting point.
slow = head;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
Node* head = newNode(50);
head->next = newNode(20);
head->next->next = newNode(15);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head->next->next;
Node* res = detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
if (res == NULL)
cout << "Loop does not exist";
else
cout << "Loop starting node is " << res->key;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Aditya Kumar (adityakumar129)
C
// C++ program to return first node of loop.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct Node {
int key;
struct Node* next;
} Node;
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
temp->key = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
void printList(Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
printf("%d ",head->key);
head = head->next;
}
printf("/n");
}
// Function to detect and remove loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
Node* detectAndRemoveLoop(Node* head)
{
// If list is empty or has only one node
// without loop
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL)
return NULL;
Node *slow = head, *fast = head;
// Move slow and fast 1 and 2 steps
// ahead respectively.
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
// Search for loop using slow and
// fast pointers
while (fast && fast->next) {
if (slow == fast)
break;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
// If loop does not exist
if (slow != fast)
return NULL;
// If loop exists. Start slow from
// head and fast from meeting point.
slow = head;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
Node* head = newNode(50);
head->next = newNode(20);
head->next->next = newNode(15);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head->next->next;
Node* res = detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
if (res == NULL)
printf("Loop does not exist");
else
printf("Loop starting node is %d ",res->key);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Aditya Kumar (adityakumar129)
Java
// Java program to return
// first node of loop.
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static class Node
{
int key;
Node next;
};
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.next = null;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to
// print a linked list
static void printList(Node head)
{
while (head != null)
{
System.out.print(head.key + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// Function to detect and remove loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
static Node detectAndRemoveLoop(Node head)
{
// If list is empty or has
// only one node without loop
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return null;
Node slow = head, fast = head;
// Move slow and fast 1
// and 2 steps ahead
// respectively.
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// Search for loop using
// slow and fast pointers
while (fast != null &&
fast.next != null)
{
if (slow == fast)
break;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
// If loop does not exist
if (slow != fast)
return null;
// If loop exists. Start slow from
// head and fast from meeting point.
slow = head;
while (slow != fast)
{
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node head = newNode(50);
head.next = newNode(20);
head.next.next = newNode(15);
head.next.next.next = newNode(4);
head.next.next.next.next = newNode(10);
// Create a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
Node res = detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
if (res == null)
System.out.print("Loop does not exist");
else
System.out.print("Loop starting node is " + res.key);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput
Python3
# Python3 program to return first node of loop.
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.key = key
self.next = None
def newNode(key):
temp = Node(key)
return temp
# A utility function to print a linked list
def printList(head):
while (head != None):
print(head.key, end = ' ')
head = head.next
print()
# Function to detect and remove loop
# in a linked list that may contain loop
def detectAndRemoveLoop(head):
# If list is empty or has only one node
# without loop
if (head == None or head.next == None):
return None
slow = head
fast = head
# Move slow and fast 1 and 2 steps
# ahead respectively.
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
# Search for loop using slow and
# fast pointers
while (fast and fast.next):
if (slow == fast):
break
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
# If loop does not exist
if (slow != fast):
return None
# If loop exists. Start slow from
# head and fast from meeting point.
slow = head
while (slow != fast):
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
return slow
# Driver code
if __name__=='__main__':
head = newNode(50)
head.next = newNode(20)
head.next.next = newNode(15)
head.next.next.next = newNode(4)
head.next.next.next.next = newNode(10)
# Create a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next
res = detectAndRemoveLoop(head)
if (res == None):
print("Loop does not exist")
else:
print("Loop starting node is " +
str(res.key))
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56
C#
// C# program to return
// first node of loop.
using System;
class GFG{
class Node
{
public int key;
public Node next;
};
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.next = null;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to
// print a linked list
static void printList(Node head)
{
while (head != null)
{
Console.Write(head.key + " ");
head = head.next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Function to detect and remove loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
static Node detectAndRemoveLoop(Node head)
{
// If list is empty or has
// only one node without loop
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return null;
Node slow = head, fast = head;
// Move slow and fast 1
// and 2 steps ahead
// respectively.
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// Search for loop using
// slow and fast pointers
while (fast != null &&
fast.next != null)
{
if (slow == fast)
break;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
// If loop does not exist
if (slow != fast)
return null;
// If loop exists. Start slow from
// head and fast from meeting point.
slow = head;
while (slow != fast)
{
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node head = newNode(50);
head.next = newNode(20);
head.next.next = newNode(15);
head.next.next.next = newNode(4);
head.next.next.next.next = newNode(10);
// Create a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next =
head.next.next;
Node res = detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
if (res == null)
Console.Write("Loop does not exist");
else
Console.Write("Loop starting node is " +
res.key);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program to return
// first node of loop.
class Node
{
constructor(key)
{
this.key=key;
this.next=null;
}
}
// A utility function to
// print a linked list
function printList(head)
{
while (head != null)
{
document.write(head.key + " ");
head = head.next;
}
document.write("<br>");
}
// Function to detect and remove loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
function detectAndRemoveLoop(head)
{
// If list is empty or has
// only one node without loop
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return null;
let slow = head, fast = head;
// Move slow and fast 1
// and 2 steps ahead
// respectively.
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// Search for loop using
// slow and fast pointers
while (fast != null &&
fast.next != null)
{
if (slow == fast)
break;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
// If loop does not exist
if (slow != fast)
return null;
// If loop exists. Start slow from
// head and fast from meeting point.
slow = head;
while (slow != fast)
{
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
// Driver code
let head = new Node(50);
head.next = new Node(20);
head.next.next = new Node(15);
head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(10);
// Create a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
let res = detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
if (res == null)
document.write("Loop does not exist");
else
document.write("Loop starting node is " + res.key);
// This code is contributed by unknown2108
</script>
Loop starting node is 15
¿Cómo funciona este enfoque?
Deje que lento y rápido se encuentren en algún punto después del algoritmo de búsqueda del ciclo de Floyd. El siguiente diagrama muestra la situación cuando se encuentra el ciclo.
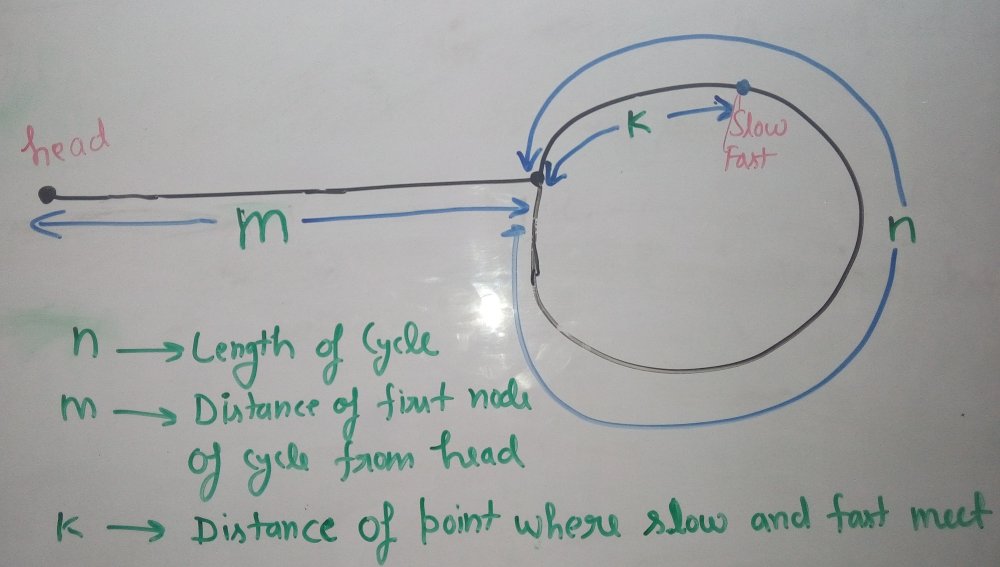
Podemos concluir a continuación del diagrama anterior
Distance traveled by fast pointer = 2 * (Distance traveled
by slow pointer)
(m + n*x + k) = 2*(m + n*y + k)
Note that before meeting the point shown above, fast
was moving at twice speed.
x --> Number of complete cyclic rounds made by
fast pointer before they meet first time
y --> Number of complete cyclic rounds made by
slow pointer before they meet first time
De la ecuación anterior, podemos concluir a continuación
m + k = (x-2y)*n Which means m+k is a multiple of n.
Entonces, si comenzamos a mover ambos punteros nuevamente a la misma velocidad , de modo que un puntero (digamos lento) comience desde el Node principal de la lista vinculada y otros punteros (digamos rápido) comiencen desde el punto de encuentro. Cuando el puntero lento llega al comienzo del bucle (ha dado m pasos), el puntero rápido también habrá movido m pasos, ya que ahora se están moviendo al mismo ritmo. Dado que m+k es un múltiplo de n y rápido comienza desde k, se encontrarían al principio. ¿Se pueden encontrar antes también? No, porque el puntero lento entra en el ciclo por primera vez después de m pasos.
Método 2:
en este método, se crea un Node temporal. El siguiente puntero de cada Node que se atraviesa apunta a este Node temporal. De esta forma estamos usando el siguiente puntero de un Node como bandera para indicar si el Node ha sido atravesado o no. Cada Node se comprueba para ver si el siguiente apunta a un Node temporal o no. En el caso del primer Node del bucle, la segunda vez que lo recorremos esta condición será verdadera, por lo que devolvemos ese Node.
El código se ejecuta en una complejidad de tiempo O(n) y utiliza un espacio de memoria constante.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program to return first node of loop
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node* next;
};
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
void printList(Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
cout << head->key << " ";
head = head->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
Node* detectLoop(Node* head)
{
// Create a temporary node
Node* temp = new Node;
while (head != NULL) {
// This condition is for the case
// when there is no loop
if (head->next == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
// Check if next is already
// pointing to temp
if (head->next == temp) {
break;
}
// Store the pointer to the next node
// in order to get to it in the next step
Node* nex = head->next;
// Make next point to temp
head->next = temp;
// Get to the next node in the list
head = nex;
}
return head;
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
Node* head = newNode(50);
head->next = newNode(20);
head->next->next = newNode(15);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head->next->next;
Node* res = detectLoop(head);
if (res == NULL)
cout << "Loop does not exist";
else
cout << "Loop starting node is " << res->key;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Aditya Kumar (adityakumar129)
C
// C program to return first node of loop
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct Node {
int key;
struct Node* next;
} Node;
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
temp->key = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
void printList(Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
printf("%d ", head->key);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
Node* detectLoop(Node* head)
{
// Create a temporary node
Node* temp = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
while (head != NULL) {
// This condition is for the case when there is no
// loop
if (head->next == NULL)
return NULL;
// Check if next is already pointing to temp
if (head->next == temp)
break;
// Store the pointer to the next node
// in order to get to it in the next step
Node* nex = head->next;
// Make next point to temp
head->next = temp;
// Get to the next node in the list
head = nex;
}
return head;
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
Node* head = newNode(50);
head->next = newNode(20);
head->next->next = newNode(15);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head->next->next;
Node* res = detectLoop(head);
if (res == NULL)
printf("Loop does not exist");
else
printf("Loop starting node is %d ", res->key);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Aditya Kumar (adityakumar129)
Java
// Java program to return first node of loop
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static class Node
{
int key;
Node next;
};
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.next = null;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
static void printList(Node head)
{
while (head != null)
{
System.out.print(head.key + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
static Node detectLoop(Node head)
{
// Create a temporary node
Node temp = new Node();
while (head != null)
{
// This condition is for the case
// when there is no loop
if (head.next == null)
{
return null;
}
// Check if next is already
// pointing to temp
if (head.next == temp)
{
break;
}
// Store the pointer to the next node
// in order to get to it in the next step
Node nex = head.next;
// Make next point to temp
head.next = temp;
// Get to the next node in the list
head = nex;
}
return head;
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node head = newNode(50);
head.next = newNode(20);
head.next.next = newNode(15);
head.next.next.next = newNode(4);
head.next.next.next.next = newNode(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
Node res = detectLoop(head);
if (res == null)
System.out.print("Loop does not exist");
else
System.out.print("Loop starting node is " +
res.key);
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
Python3
# Python3 program to return first node of loop
class Node:
def __init__(self, x):
self.key = x
self.next = None
# A utility function to print a linked list
def printList(head):
while (head != None):
print(head.key, end = " ")
head = head.next
# Function to detect first node of loop
# in a linked list that may contain loop
def detectLoop(head):
# Create a temporary node
temp = Node(-1)
while (head != None):
# This condition is for the case
# when there is no loop
if (head.next == None):
return None
# Check if next is already
# pointing to temp
if (head.next == temp):
break
# Store the pointer to the next node
# in order to get to it in the next step
nex = head.next
# Make next point to temp
head.next = temp
# Get to the next node in the list
head = nex
return head
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
head = Node(50)
head.next = Node(20)
head.next.next = Node(15)
head.next.next.next = Node(4)
head.next.next.next.next = Node(10)
# Create a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next
res = detectLoop(head)
if (res == None):
print("Loop does not exist")
else:
print("Loop starting node is ", res.key)
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29
C#
// C# program to return first node of loop
using System;
class GFG{
class Node
{
public int key;
public Node next;
};
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.next = null;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
static void printList(Node head)
{
while (head != null)
{
Console.Write(head.key + " ");
head = head.next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
static Node detectLoop(Node head)
{
// Create a temporary node
Node temp = new Node();
while (head != null)
{
// This condition is for the case
// when there is no loop
if (head.next == null)
{
return null;
}
// Check if next is already
// pointing to temp
if (head.next == temp)
{
break;
}
// Store the pointer to the next node
// in order to get to it in the next step
Node nex = head.next;
// Make next point to temp
head.next = temp;
// Get to the next node in the list
head = nex;
}
return head;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node head = newNode(50);
head.next = newNode(20);
head.next.next = newNode(15);
head.next.next.next = newNode(4);
head.next.next.next.next = newNode(10);
// Create a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
Node res = detectLoop(head);
if (res == null)
Console.Write("Loop does not exist");
else
Console.Write("Loop starting node is " +
res.key);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar
Javascript
<script>
// javascript program to return first node of loop
class Node {
constructor() {
this.key = 0;
this.next = null;
}
}
function newNode(key) {
temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.next = null;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
function printList( head) {
while (head != null) {
document.write(head.key + " ");
head = head.next;
}
document.write("<br/>");
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
function detectLoop( head) {
// Create a temporary node
temp = new Node();
while (head != null) {
// This condition is for the case
// when there is no loop
if (head.next == null) {
return null;
}
// Check if next is already
// pointing to temp
if (head.next == temp) {
break;
}
// Store the pointer to the next node
// in order to get to it in the next step
nex = head.next;
// Make next point to temp
head.next = temp;
// Get to the next node in the list
head = nex;
}
return head;
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
head = newNode(50);
head.next = newNode(20);
head.next.next = newNode(15);
head.next.next.next = newNode(4);
head.next.next.next.next = newNode(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
res = detectLoop(head);
if (res == null)
document.write("Loop does not exist");
else
document.write("Loop starting node is " + res.key);
// This code contributed by gauravrajput1
</script>
Loop starting node is 15
Método 3:
También podemos usar el concepto de hashing para detectar el primer Node del bucle. La idea es simple, simplemente itere sobre toda la lista vinculada y almacene las direcciones de Node en un conjunto ( C++ STL ) una por una, mientras agrega la dirección de Node en el conjunto, verifique si ya contiene esa dirección de Node en particular, de lo contrario, agregue la dirección de Node a set si ya está presente en el conjunto, entonces el Node actual es el primer Node del ciclo.
C++14
// The below function take head of Linked List as
// input and return Address of first node in
// the loop if present else return NULL.
/* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };*/
ListNode* detectCycle(ListNode* A)
{
// declaring map to store node address
unordered_set<ListNode*> uset;
ListNode *ptr = A;
// Default consider that no cycle is present
while (ptr != NULL) {
// checking if address is already present in map
if (uset.find(ptr) != uset.end())
return ptr;
// if address not present then insert into the set
else
uset.insert(ptr);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
return NULL;
}
// This code is contributed by Pankaj_Joshi
Java
// The below function take head of Linked List as
// input and return Address of first node in
// the loop if present else return NULL.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static Node detectCycle(Node A)
{
// declaring map to store node address
Set<Node> uset = new HashSet<Node>();
Node = A;
// Default consider that no cycle is present
while (ptr != NULL)
{
// checking if address is already present in map
if(uset.contains(ptr))
{
return ptr;
}
// if address not present then insert into the set
else
{
uset.add(ptr);
}
ptr = ptr.next;
}
return null;
}
}
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
Python3
# The below function take head of Linked List as # input and return Address of first node in # the loop if present else return NULL. ''' Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode: * def __init__(self, x): * self.val=x * self.next=None * ''' def detectCycle(A): # Declaring map to store node # address uset = set() ptr = A # Default consider that no cycle # is present while (ptr != None): # Checking if address is already # present in map if (ptr in uset): return ptr # If address not present then # insert into the set else: uset.add(ptr) ptr = ptr.next return None # This code is contributed by pratham76
C#
// The below function take head of Linked List as
// input and return Address of first node in
// the loop if present else return NULL.
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG
{
class Node
{
public int key;
public Node next;
};
static Node detectCycle(Node A)
{
// declaring map to store node address
HashSet<Node> uset = new HashSet<Node>();
Node ptr = A;
// Default consider that no cycle is present
while (ptr != null)
{
// checking if address is already present in map
if(uset.Contains(ptr))
{
return ptr;
}
// if address not present then insert into the set
else
{
uset.Add(ptr);
}
ptr = ptr.next;
}
return null;
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
<script>
// The below function take head of Linked List as
// input and return Address of first node in
// the loop if present else return NULL.
function detectCycle(A)
{
// declaring map to store node address
let uset = new Set();
let ptr = A;
// Default consider that no cycle is present
while (ptr != NULL)
{
// checking if address is already present in map
if(uset.has(ptr))
{
return ptr;
}
// if address not present then insert into the set
else
{
uset.add(ptr);
}
ptr = ptr.next;
}
return null;
}
// This code is contributed by patel2127
</script>
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por TanyaSethi y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA
