Dado un árbol de búsqueda binario equilibrado y una suma objetivo, escriba una función que devuelva verdadero si hay un par con una suma igual a la suma objetivo; de lo contrario, devuelva falso. La complejidad de tiempo esperada es O(n) y solo se puede usar el espacio adicional O(Logn). No se permite ninguna modificación al árbol de búsqueda binaria. Tenga en cuenta que la altura de un BST equilibrado siempre es O (Iniciar sesión).
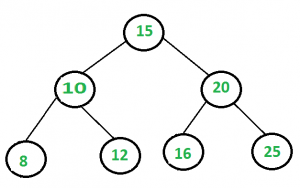
Este problema es principalmente una extensión de la publicación anterior . Aquí no se nos permite modificar el BST.
La solución de fuerza bruta es considerar cada par en BST y verificar si la suma es igual a X. La complejidad temporal de esta solución será O (n ^ 2).
Una mejor solución es crear una array auxiliar y almacenar el recorrido en orden de BST en la array. La array se ordenará como el recorrido en orden de BST siempre produce datos ordenados. Una vez que tenemos el recorrido Inorder, podemos emparejar en tiempo O(n) (Ver esto para más detalles). Esta solución funciona en tiempo O(n) pero requiere espacio auxiliar O(n).
Implementación:
C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node{
public:
int data;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node(int d)
{
data=d;
left=NULL;
right=NULL;
}
};
class BinarySearchTree {
// Root of BST
public:
Node *root;
// Constructor
BinarySearchTree()
{
root = NULL;
}
// Utility function for inorder traversal of the tree
void inorderUtil(Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
inorderUtil(node->left);
cout << node->data << " ";
inorderUtil(node->right);
}
// Inorder traversal of the tree
void inorder()
{
inorderUtil(this->root);
}
/* A recursive function to insert a new key in BST */
Node* insertRec(Node* root, int data)
{
/* If the tree is empty, return a new node */
if (root == NULL) {
root = new Node(data);
return root;
}
/* Otherwise, recur down the tree */
if (data < root->data)
root->left = insertRec(root->left, data);
else if (data > root->data)
root->right = insertRec(root->right, data);
return root;
}
// This method mainly calls insertRec()
void insert(int key)
{
root = insertRec(root, key);
}
// Method that adds values of given BST into vector
// and hence returns the vector
vector<int> treeToList(Node* node, vector<int>& list)
{
// Base Case
if (node == NULL)
return list;
treeToList(node->left, list);
list.push_back(node->data);
treeToList(node->right, list);
return list;
}
// method that checks if there is a pair present
bool isPairPresent(Node* node, int target)
{
// This list a1 is passed as an argument
// in treeToList method
// which is later on filled by the values of BST
vector<int> a1;
// a2 list contains all the values of BST
// returned by treeToList method
vector<int> a2 = treeToList(node, a1);
int start = 0; // Starting index of a2
int end = (int)a2.size() - 1; // Ending index of a2
while (start < end) {
if (a2[start] + a2[end] == target) // Target Found!
{
cout << "Pair Found: " << a2[start] << " + " << a2[end] << " = " << target << '\n';
return true;
}
if (a2[start] + a2[end] > target) // decrements end
{
end--;
}
if (a2[start] + a2[end] < target) // increments start
{
start++;
}
}
cout << "No such values are found!\n";
return false;
}
};
// Driver function
int main()
{
BinarySearchTree *tree = new BinarySearchTree();
/*
15
/ \
10 20
/ \ / \
8 12 16 25 */
tree->insert(15);
tree->insert(10);
tree->insert(20);
tree->insert(8);
tree->insert(12);
tree->insert(16);
tree->insert(25);
tree->isPairPresent(tree->root, 33);
}
Java
// Java code to find a pair with given sum
// in a Balanced BST
import java.util.ArrayList;
// A binary tree node
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinarySearchTree {
// Root of BST
Node root;
// Constructor
BinarySearchTree()
{
root = null;
}
// Inorder traversal of the tree
void inorder()
{
inorderUtil(this.root);
}
// Utility function for inorder traversal of the tree
void inorderUtil(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
inorderUtil(node.left);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
inorderUtil(node.right);
}
// This method mainly calls insertRec()
void insert(int key)
{
root = insertRec(root, key);
}
/* A recursive function to insert a new key in BST */
Node insertRec(Node root, int data)
{
/* If the tree is empty, return a new node */
if (root == null) {
root = new Node(data);
return root;
}
/* Otherwise, recur down the tree */
if (data < root.data)
root.left = insertRec(root.left, data);
else if (data > root.data)
root.right = insertRec(root.right, data);
return root;
}
// Method that adds values of given BST into ArrayList
// and hence returns the ArrayList
ArrayList<Integer> treeToList(Node node, ArrayList<Integer>
list)
{
// Base Case
if (node == null)
return list;
treeToList(node.left, list);
list.add(node.data);
treeToList(node.right, list);
return list;
}
// method that checks if there is a pair present
boolean isPairPresent(Node node, int target)
{
// This list a1 is passed as an argument
// in treeToList method
// which is later on filled by the values of BST
ArrayList<Integer> a1 = new ArrayList<>();
// a2 list contains all the values of BST
// returned by treeToList method
ArrayList<Integer> a2 = treeToList(node, a1);
int start = 0; // Starting index of a2
int end = a2.size() - 1; // Ending index of a2
while (start < end) {
if (a2.get(start) + a2.get(end) == target) // Target Found!
{
System.out.println("Pair Found: " + a2.get(start) + " + " + a2.get(end) + " "
+ "= " + target);
return true;
}
if (a2.get(start) + a2.get(end) > target) // decrements end
{
end--;
}
if (a2.get(start) + a2.get(end) < target) // increments start
{
start++;
}
}
System.out.println("No such values are found!");
return false;
}
// Driver function
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BinarySearchTree tree = new BinarySearchTree();
/*
15
/ \
10 20
/ \ / \
8 12 16 25 */
tree.insert(15);
tree.insert(10);
tree.insert(20);
tree.insert(8);
tree.insert(12);
tree.insert(16);
tree.insert(25);
tree.isPairPresent(tree.root, 33);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Kamal Rawal
Python3
# Python3 code to find a pair with given sum
# in a Balanced BST
class Node:
# Construct to create a new Node
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.left = self.right = None
# A utility function to insert a new
# Node with given key in BST
def insert(root: Node, key: int):
# If the tree is empty, return a new Node
if root is None:
return Node(key)
# Otherwise, recur down the tree
if root.data > key:
root.left = insert(root.left, key)
elif root.data < key:
root.right = insert(root.right, key)
# return the (unchanged) Node pointer
return root
# Function that adds values of given BST into
# ArrayList and hence returns the ArrayList
def tree_to_list(root: Node, arr: list):
if not root:
return arr
tree_to_list(root.left, arr)
arr.append(root.data)
tree_to_list(root.right, arr)
return arr
# Function that checks if there is a pair present
def isPairPresent(root: Node, target: int) -> bool:
# This list a1 is passed as an argument
# in treeToList method which is later
# on filled by the values of BST
arr1 = []
# a2 list contains all the values of BST
# returned by treeToList method
arr2 = tree_to_list(root, arr1)
# Starting index of a2
start = 0
# Ending index of a2
end = len(arr2) - 1
while start < end:
# If target found
if arr2[start] + arr2[end] == target:
print(f"Pair Found: {arr2[start]} + {arr2[end]} = {target}")
return True
# Decrements end
if arr2[start] + arr2[end] > target:
end -= 1
# Increments start
if arr2[start] + arr2[end] < target:
start += 1
print("No such values are found!")
return False
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = None
root = insert(root, 15)
root = insert(root, 10)
root = insert(root, 20)
root = insert(root, 8)
root = insert(root, 12)
root = insert(root, 16)
root = insert(root, 25)
isPairPresent(root, 33)
# This code is contributed by shindesharad71
C#
// C# code to find a pair with given sum
// in a Balanced BST
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// A binary tree node
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinarySearchTree {
// Root of BST
Node root;
// Constructor
BinarySearchTree()
{
root = null;
}
// Inorder traversal of the tree
void inorder()
{
inorderUtil(this.root);
}
// Utility function for inorder traversal of the tree
void inorderUtil(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
inorderUtil(node.left);
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
inorderUtil(node.right);
}
// This method mainly calls insertRec()
void insert(int key)
{
root = insertRec(root, key);
}
/* A recursive function to insert a new key in BST */
Node insertRec(Node root, int data)
{
/* If the tree is empty, return a new node */
if (root == null) {
root = new Node(data);
return root;
}
/* Otherwise, recur down the tree */
if (data < root.data)
root.left = insertRec(root.left, data);
else if (data > root.data)
root.right = insertRec(root.right, data);
return root;
}
// Method that adds values of given BST into ArrayList
// and hence returns the ArrayList
List<int> treeToList(Node node, List<int> list)
{
// Base Case
if (node == null)
return list;
treeToList(node.left, list);
list.Add(node.data);
treeToList(node.right, list);
return list;
}
// method that checks if there is a pair present
bool isPairPresent(Node node, int target)
{
// This list a1 is passed as an argument
// in treeToList method
// which is later on filled by the values of BST
List<int> a1 = new List<int>();
// a2 list contains all the values of BST
// returned by treeToList method
List<int> a2 = treeToList(node, a1);
int start = 0; // Starting index of a2
int end = a2.Count - 1; // Ending index of a2
while (start < end) {
if (a2[start] + a2[end] == target) // Target Found!
{
Console.WriteLine("Pair Found: " + a2[start] + " + " + a2[end] + " "
+ "= " + target);
return true;
}
if (a2[start] + a2[end] > target) // decrements end
{
end--;
}
if (a2[start] + a2[end] < target) // increments start
{
start++;
}
}
Console.WriteLine("No such values are found!");
return false;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
BinarySearchTree tree = new BinarySearchTree();
/*
15
/ \
10 20
/ \ / \
8 12 16 25 */
tree.insert(15);
tree.insert(10);
tree.insert(20);
tree.insert(8);
tree.insert(12);
tree.insert(16);
tree.insert(25);
tree.isPairPresent(tree.root, 33);
}
}
// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript code to find a pair with given sum
// in a Balanced BST
// A binary tree node
class Node {
constructor(d) {
this.data = d;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
class BinarySearchTree {
// Constructor
constructor() {
this.root = null;
}
// Inorder traversal of the tree
inorder() {
this.inorderUtil(this.root);
}
// Utility function for inorder traversal of the tree
inorderUtil(node) {
if (node == null) return;
this.inorderUtil(node.left);
document.write(node.data + " ");
this.inorderUtil(node.right);
}
// This method mainly calls insertRec()
insert(key) {
this.root = this.insertRec(this.root, key);
}
/* A recursive function to insert a new key in BST */
insertRec(root, data) {
/* If the tree is empty, return a new node */
if (root == null) {
root = new Node(data);
return root;
}
/* Otherwise, recur down the tree */
if (data < root.data)
root.left = this.insertRec(root.left, data);
else if (data > root.data)
root.right = this.insertRec(root.right, data);
return root;
}
// Method that adds values of given BST into ArrayList
// and hence returns the ArrayList
treeToList(node, list) {
// Base Case
if (node == null) return list;
this.treeToList(node.left, list);
list.push(node.data);
this.treeToList(node.right, list);
return list;
}
// method that checks if there is a pair present
isPairPresent(node, target) {
// This list a1 is passed as an argument
// in treeToList method
// which is later on filled by the values of BST
var a1 = [];
// a2 list contains all the values of BST
// returned by treeToList method
var a2 = this.treeToList(node, a1);
var start = 0; // Starting index of a2
var end = a2.length - 1; // Ending index of a2
while (start < end) {
if (a2[start] + a2[end] == target) {
// Target Found!
document.write(
"Pair Found: " +
a2[start] +
" + " +
a2[end] +
" " +
"= " +
target +
"<br>"
);
return true;
}
if (a2[start] + a2[end] > target) {
// decrements end
end--;
}
if (a2[start] + a2[end] < target) {
// increments start
start++;
}
}
document.write("No such values are found!");
return false;
}
}
// Driver code
var tree = new BinarySearchTree();
/*
15
/ \
10 20
/ \ / \
8 12 16 25 */
tree.insert(15);
tree.insert(10);
tree.insert(20);
tree.insert(8);
tree.insert(12);
tree.insert(16);
tree.insert(25);
tree.isPairPresent(tree.root, 33);
</script>
Pair Found: 8 + 25 = 33
Análisis de Complejidad:
- Complejidad temporal: O(n).
Inorder Traversal de BST toma un tiempo lineal. - Espacio Auxiliar: O(n).
Uso de array para almacenar Inorder Traversal.
Una solución optimizada para el espacio se analiza en una publicación anterior . La idea era convertir primero en el lugar BST a Lista doblemente enlazada (DLL), luego encontrar el par en DLL ordenado en tiempo O (n). Esta solución toma O(n) tiempo y O(Logn) espacio extra, pero modifica el BST dado.
La solución discutida a continuación toma el tiempo O(n), el espacio O(Logn) y no modifica BST . La idea es la misma que encontrar el par en una array ordenada (consulte el método 1 de esto para obtener más detalles). Atravesamos BST en orden normal e inverso simultáneamente. En orden inverso, comenzamos desde el Node más a la derecha que es el Node de valor máximo. En orden normal, comenzamos desde el Node más a la izquierda, que es el Node de valor mínimo. Agregamos la suma de los Nodes actuales en ambos recorridos y comparamos esta suma con la suma objetivo dada. Si la suma es la misma que la suma objetivo, devolvemos verdadero. Si la suma es mayor que la suma objetivo, nos movemos al siguiente Node en un recorrido en orden inverso; de lo contrario, nos movemos al siguiente Node en un recorrido en orden normal. Si alguno de los recorridos se termina sin encontrar un par, devolvemos falso.
A continuación se muestra la implementación de este enfoque.
C++
/* In a balanced binary search tree
isPairPresent two element which sums to
a given value time O(n) space O(logn) */
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_SIZE 100
// A BST node
class node {
public:
int val;
node *left, *right;
};
// Stack type
class Stack {
public:
int size;
int top;
node** array;
};
// A utility function to create a stack of given size
Stack* createStack(int size)
{
Stack* stack = new Stack();
stack->size = size;
stack->top = -1;
stack->array = new node*[(stack->size * sizeof(node*))];
return stack;
}
// BASIC OPERATIONS OF STACK
int isFull(Stack* stack)
{
return stack->top - 1 == stack->size;
}
int isEmpty(Stack* stack)
{
return stack->top == -1;
}
void push(Stack* stack, node* node)
{
if (isFull(stack))
return;
stack->array[++stack->top] = node;
}
node* pop(Stack* stack)
{
if (isEmpty(stack))
return NULL;
return stack->array[stack->top--];
}
// Returns true if a pair with target
// sum exists in BST, otherwise false
bool isPairPresent(node* root, int target)
{
// Create two stacks. s1 is used for
// normal inorder traversal and s2 is
// used for reverse inorder traversal
Stack* s1 = createStack(MAX_SIZE);
Stack* s2 = createStack(MAX_SIZE);
// Note the sizes of stacks is MAX_SIZE,
// we can find the tree size and fix stack size
// as O(Logn) for balanced trees like AVL and Red Black
// tree. We have used MAX_SIZE to keep the code simple
// done1, val1 and curr1 are used for
// normal inorder traversal using s1
// done2, val2 and curr2 are used for
// reverse inorder traversal using s2
bool done1 = false, done2 = false;
int val1 = 0, val2 = 0;
node *curr1 = root, *curr2 = root;
// The loop will break when we either find a pair or one of the two
// traversals is complete
while (1) {
// Find next node in normal Inorder
// traversal. See following post
// https:// www.geeksforgeeks.org/inorder-tree-traversal-without-recursion/
while (done1 == false) {
if (curr1 != NULL) {
push(s1, curr1);
curr1 = curr1->left;
}
else {
if (isEmpty(s1))
done1 = 1;
else {
curr1 = pop(s1);
val1 = curr1->val;
curr1 = curr1->right;
done1 = 1;
}
}
}
// Find next node in REVERSE Inorder traversal. The only
// difference between above and below loop is, in below loop
// right subtree is traversed before left subtree
while (done2 == false) {
if (curr2 != NULL) {
push(s2, curr2);
curr2 = curr2->right;
}
else {
if (isEmpty(s2))
done2 = 1;
else {
curr2 = pop(s2);
val2 = curr2->val;
curr2 = curr2->left;
done2 = 1;
}
}
}
// If we find a pair, then print the pair and return. The first
// condition makes sure that two same values are not added
if ((val1 != val2) && (val1 + val2) == target) {
cout << "Pair Found: " << val1 << "+ " << val2 << " = " << target << endl;
return true;
}
// If sum of current values is smaller,
// then move to next node in
// normal inorder traversal
else if ((val1 + val2) < target)
done1 = false;
// If sum of current values is greater,
// then move to next node in
// reverse inorder traversal
else if ((val1 + val2) > target)
done2 = false;
// If any of the inorder traversals is
// over, then there is no pair
// so return false
if (val1 >= val2)
return false;
}
}
// A utility function to create BST node
node* NewNode(int val)
{
node* tmp = new node();
tmp->val = val;
tmp->right = tmp->left = NULL;
return tmp;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
/*
15
/ \
10 20
/ \ / \
8 12 16 25 */
node* root = NewNode(15);
root->left = NewNode(10);
root->right = NewNode(20);
root->left->left = NewNode(8);
root->left->right = NewNode(12);
root->right->left = NewNode(16);
root->right->right = NewNode(25);
int target = 33;
if (isPairPresent(root, target) == false)
cout << "\nNo such values are found\n";
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra
C
/* In a balanced binary search tree isPairPresent two element which sums to
a given value time O(n) space O(logn) */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 100
// A BST node
struct node {
int val;
struct node *left, *right;
};
// Stack type
struct Stack {
int size;
int top;
struct node** array;
};
// A utility function to create a stack of given size
struct Stack* createStack(int size)
{
struct Stack* stack = (struct Stack*)malloc(sizeof(struct Stack));
stack->size = size;
stack->top = -1;
stack->array = (struct node**)malloc(stack->size * sizeof(struct node*));
return stack;
}
// BASIC OPERATIONS OF STACK
int isFull(struct Stack* stack)
{
return stack->top - 1 == stack->size;
}
int isEmpty(struct Stack* stack)
{
return stack->top == -1;
}
void push(struct Stack* stack, struct node* node)
{
if (isFull(stack))
return;
stack->array[++stack->top] = node;
}
struct node* pop(struct Stack* stack)
{
if (isEmpty(stack))
return NULL;
return stack->array[stack->top--];
}
// Returns true if a pair with target sum exists in BST, otherwise false
bool isPairPresent(struct node* root, int target)
{
// Create two stacks. s1 is used for normal inorder traversal
// and s2 is used for reverse inorder traversal
struct Stack* s1 = createStack(MAX_SIZE);
struct Stack* s2 = createStack(MAX_SIZE);
// Note the sizes of stacks is MAX_SIZE, we can find the tree size and
// fix stack size as O(Logn) for balanced trees like AVL and Red Black
// tree. We have used MAX_SIZE to keep the code simple
// done1, val1 and curr1 are used for normal inorder traversal using s1
// done2, val2 and curr2 are used for reverse inorder traversal using s2
bool done1 = false, done2 = false;
int val1 = 0, val2 = 0;
struct node *curr1 = root, *curr2 = root;
// The loop will break when we either find a pair or one of the two
// traversals is complete
while (1) {
// Find next node in normal Inorder traversal. See following post
// https:// www.geeksforgeeks.org/inorder-tree-traversal-without-recursion/
while (done1 == false) {
if (curr1 != NULL) {
push(s1, curr1);
curr1 = curr1->left;
}
else {
if (isEmpty(s1))
done1 = 1;
else {
curr1 = pop(s1);
val1 = curr1->val;
curr1 = curr1->right;
done1 = 1;
}
}
}
// Find next node in REVERSE Inorder traversal. The only
// difference between above and below loop is, in below loop
// right subtree is traversed before left subtree
while (done2 == false) {
if (curr2 != NULL) {
push(s2, curr2);
curr2 = curr2->right;
}
else {
if (isEmpty(s2))
done2 = 1;
else {
curr2 = pop(s2);
val2 = curr2->val;
curr2 = curr2->left;
done2 = 1;
}
}
}
// If we find a pair, then print the pair and return. The first
// condition makes sure that two same values are not added
if ((val1 != val2) && (val1 + val2) == target) {
printf("\n Pair Found: %d + %d = %d\n", val1, val2, target);
return true;
}
// If sum of current values is smaller, then move to next node in
// normal inorder traversal
else if ((val1 + val2) < target)
done1 = false;
// If sum of current values is greater, then move to next node in
// reverse inorder traversal
else if ((val1 + val2) > target)
done2 = false;
// If any of the inorder traversals is over, then there is no pair
// so return false
if (val1 >= val2)
return false;
}
}
// A utility function to create BST node
struct node* NewNode(int val)
{
struct node* tmp = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
tmp->val = val;
tmp->right = tmp->left = NULL;
return tmp;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
/*
15
/ \
10 20
/ \ / \
8 12 16 25 */
struct node* root = NewNode(15);
root->left = NewNode(10);
root->right = NewNode(20);
root->left->left = NewNode(8);
root->left->right = NewNode(12);
root->right->left = NewNode(16);
root->right->right = NewNode(25);
int target = 33;
if (isPairPresent(root, target) == false)
printf("\n No such values are found\n");
getchar();
return 0;
}
Java
/* In a balanced binary search tree
isPairPresent two element which sums to
a given value time O(n) space O(logn) */
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static final int MAX_SIZE= 100;
// A BST node
static class node
{
int val;
node left, right;
};
// Stack type
static class Stack
{
int size;
int top;
node []array;
};
// A utility function to create a stack of given size
static Stack createStack(int size)
{
Stack stack = new Stack();
stack.size = size;
stack.top = -1;
stack.array = new node[stack.size];
return stack;
}
// BASIC OPERATIONS OF STACK
static int isFull(Stack stack)
{
return (stack.top - 1 == stack.size)?1:0 ;
}
static int isEmpty(Stack stack)
{
return stack.top == -1?1:0;
}
static void push(Stack stack, node node)
{
if (isFull(stack)==1)
return;
stack.array[++stack.top] = node;
}
static node pop(Stack stack)
{
if (isEmpty(stack) == 1)
return null;
return stack.array[stack.top--];
}
// Returns true if a pair with target
// sum exists in BST, otherwise false
static boolean isPairPresent(node root, int target)
{
// Create two stacks. s1 is used for
// normal inorder traversal and s2 is
// used for reverse inorder traversal
Stack s1 = createStack(MAX_SIZE);
Stack s2 = createStack(MAX_SIZE);
// Note the sizes of stacks is MAX_SIZE,
// we can find the tree size and fix stack size
// as O(Logn) for balanced trees like AVL and Red Black
// tree. We have used MAX_SIZE to keep the code simple
// done1, val1 and curr1 are used for
// normal inorder traversal using s1
// done2, val2 and curr2 are used for
// reverse inorder traversal using s2
boolean done1 = false, done2 = false;
int val1 = 0, val2 = 0;
node curr1 = root, curr2 = root;
// The loop will break when we either
// find a pair or one of the two
// traversals is complete
while (true)
{
// Find next node in normal Inorder
// traversal. See following post
// https:// www.geeksforgeeks.org/inorder-tree-traversal-without-recursion/
while (done1 == false)
{
if (curr1 != null)
{
push(s1, curr1);
curr1 = curr1.left;
}
else
{
if (isEmpty(s1) == 1)
done1 = true;
else
{
curr1 = pop(s1);
val1 = curr1.val;
curr1 = curr1.right;
done1 = true;
}
}
}
// Find next node in REVERSE Inorder traversal. The only
// difference between above and below loop is, in below loop
// right subtree is traversed before left subtree
while (done2 == false)
{
if (curr2 != null)
{
push(s2, curr2);
curr2 = curr2.right;
}
else {
if (isEmpty(s2) == 1)
done2 = true;
else {
curr2 = pop(s2);
val2 = curr2.val;
curr2 = curr2.left;
done2 = true;
}
}
}
// If we find a pair, then print the pair and return. The first
// condition makes sure that two same values are not added
if ((val1 != val2) && (val1 + val2) == target)
{
System.out.print("Pair Found: " +
val1+ "+ " +
val2+ " = " +
target +"\n");
return true;
}
// If sum of current values is smaller,
// then move to next node in
// normal inorder traversal
else if ((val1 + val2) < target)
done1 = false;
// If sum of current values is greater,
// then move to next node in
// reverse inorder traversal
else if ((val1 + val2) > target)
done2 = false;
// If any of the inorder traversals is
// over, then there is no pair
// so return false
if (val1 >= val2)
return false;
}
}
// A utility function to create BST node
static node NewNode(int val)
{
node tmp = new node();
tmp.val = val;
tmp.right = tmp.left = null;
return tmp;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/*
15
/ \
10 20
/ \ / \
8 12 16 25 */
node root = NewNode(15);
root.left = NewNode(10);
root.right = NewNode(20);
root.left.left = NewNode(8);
root.left.right = NewNode(12);
root.right.left = NewNode(16);
root.right.right = NewNode(25);
int target = 33;
if (isPairPresent(root, target) == false)
System.out.print("\nNo such values are found\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by aashish1995
Python3
# In a balanced binary search tree
# isPairPresent two element which sums to
# a given value time O(n) space O(logn)
MAX_SIZE= 100
# A BST node
class Node:
def __init__(self,val):
self.val = val
self.left = self.right = None
# Stack type
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.size = 0
self.top = 0
self.array = []
# A utility function to create a stack of given size
def createStack(size):
stack = Stack()
stack.size = size
stack.top = -1
stack.array = [0 for i in range(stack.size)]
return stack
# BASIC OPERATIONS OF STACK
def isFull(stack):
return 1 if(stack.top - 1 == stack.size) else 0
def isEmpty(stack):
return 1 if stack.top == -1 else 0
def push(stack,node):
if (isFull(stack)==1):
return
stack.array[stack.top+1] = node
stack.top += 1
def pop(stack):
if (isEmpty(stack) == 1):
return None
x = stack.array[stack.top]
stack.top -= 1
return x
# Returns true if a pair with target
# sum exists in BST, otherwise False
def isPairPresent(root,target):
# Create two stacks. s1 is used for
# normal inorder traversal and s2 is
# used for reverse inorder traversal
s1 = createStack(MAX_SIZE)
s2 = createStack(MAX_SIZE)
# Note the sizes of stacks is MAX_SIZE,
# we can find the tree size and fix stack size
# as O(Logn) for balanced trees like AVL and Red Black
# tree. We have used MAX_SIZE to keep the code simple
# done1, val1 and curr1 are used for
# normal inorder traversal using s1
# done2, val2 and curr2 are used for
# reverse inorder traversal using s2
done1,done2 = False,False
val1,val2 = 0,0
curr1,curr2 = root,root
# The loop will break when we either
# find a pair or one of the two
# traversals is complete
while (True):
# Find next node in normal Inorder
# traversal. See following post
# https:# www.geeksforgeeks.org/inorder-tree-traversal-without-recursion/
while (done1 == False):
if (curr1 != None):
push(s1, curr1)
curr1 = curr1.left
else:
if (isEmpty(s1) == 1):
done1 = True
else:
curr1 = pop(s1)
val1 = curr1.val
curr1 = curr1.right
done1 = True
# Find next node in REVERSE Inorder traversal. The only
# difference between above and below loop is, in below loop
# right subtree is traversed before left subtree
while (done2 == False):
if (curr2 != None):
push(s2, curr2)
curr2 = curr2.right
else:
if (isEmpty(s2) == 1):
done2 = True
else:
curr2 = pop(s2)
val2 = curr2.val
curr2 = curr2.left
done2 = True
# If we find a pair, then print the pair and return. The first
# condition makes sure that two same values are not added
if ((val1 != val2) and (val1 + val2) == target):
print("Pair Found: " +str(val1)+ " + " +str(val2)+ " = " +str(target))
return True
# If sum of current values is smaller,
# then move to next node in
# normal inorder traversal
elif ((val1 + val2) < target):
done1 = False
# If sum of current values is greater,
# then move to next node in
# reverse inorder traversal
elif ((val1 + val2) > target):
done2 = False
# If any of the inorder traversals is
# over, then there is no pair
# so return False
if (val1 >= val2):
return False
# Driver program to test above functions
# 15
# / \
# 10 20
# / \ / \
# 8 12 16 25
root = Node(15)
root.left = Node(10)
root.right = Node(20)
root.left.left = Node(8)
root.left.right = Node(12)
root.right.left = Node(16)
root.right.right = Node(25)
target = 33
if (isPairPresent(root, target) == False):
print("<br>No such values are found")
# This code is contributed by shinjanpatra
C#
/* In a balanced binary search tree
isPairPresent two element which sums to
a given value time O(n) space O(logn) */
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG
{
static readonly int MAX_SIZE= 100;
// A BST node
public
class node
{
public
int val;
public
node left, right;
};
// Stack type
public
class Stack
{
public
int size;
public
int top;
public
node []array;
};
// A utility function to create a stack of given size
static Stack createStack(int size)
{
Stack stack = new Stack();
stack.size = size;
stack.top = -1;
stack.array = new node[stack.size];
return stack;
}
// BASIC OPERATIONS OF STACK
static int isFull(Stack stack)
{
return (stack.top - 1 == stack.size) ? 1 : 0 ;
}
static int isEmpty(Stack stack)
{
return stack.top == -1?1:0;
}
static void push(Stack stack, node node)
{
if (isFull(stack)==1)
return;
stack.array[++stack.top] = node;
}
static node pop(Stack stack)
{
if (isEmpty(stack) == 1)
return null;
return stack.array[stack.top--];
}
// Returns true if a pair with target
// sum exists in BST, otherwise false
static bool isPairPresent(node root, int target)
{
// Create two stacks. s1 is used for
// normal inorder traversal and s2 is
// used for reverse inorder traversal
Stack s1 = createStack(MAX_SIZE);
Stack s2 = createStack(MAX_SIZE);
// Note the sizes of stacks is MAX_SIZE,
// we can find the tree size and fix stack size
// as O(Logn) for balanced trees like AVL and Red Black
// tree. We have used MAX_SIZE to keep the code simple
// done1, val1 and curr1 are used for
// normal inorder traversal using s1
// done2, val2 and curr2 are used for
// reverse inorder traversal using s2
bool done1 = false, done2 = false;
int val1 = 0, val2 = 0;
node curr1 = root, curr2 = root;
// The loop will break when we either
// find a pair or one of the two
// traversals is complete
while (true)
{
// Find next node in normal Inorder
// traversal. See following post
// https:// www.geeksforgeeks.org/inorder-tree-traversal-without-recursion/
while (done1 == false)
{
if (curr1 != null)
{
push(s1, curr1);
curr1 = curr1.left;
}
else
{
if (isEmpty(s1) == 1)
done1 = true;
else
{
curr1 = pop(s1);
val1 = curr1.val;
curr1 = curr1.right;
done1 = true;
}
}
}
// Find next node in REVERSE Inorder traversal. The only
// difference between above and below loop is, in below loop
// right subtree is traversed before left subtree
while (done2 == false)
{
if (curr2 != null)
{
push(s2, curr2);
curr2 = curr2.right;
}
else {
if (isEmpty(s2) == 1)
done2 = true;
else {
curr2 = pop(s2);
val2 = curr2.val;
curr2 = curr2.left;
done2 = true;
}
}
}
// If we find a pair, then print the pair and return. The first
// condition makes sure that two same values are not added
if ((val1 != val2) && (val1 + val2) == target)
{
Console.Write("Pair Found: " +
val1+ "+ " +
val2+ " = " +
target +"\n");
return true;
}
// If sum of current values is smaller,
// then move to next node in
// normal inorder traversal
else if ((val1 + val2) < target)
done1 = false;
// If sum of current values is greater,
// then move to next node in
// reverse inorder traversal
else if ((val1 + val2) > target)
done2 = false;
// If any of the inorder traversals is
// over, then there is no pair
// so return false
if (val1 >= val2)
return false;
}
}
// A utility function to create BST node
static node NewNode(int val)
{
node tmp = new node();
tmp.val = val;
tmp.right = tmp.left = null;
return tmp;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
/*
15
/ \
10 20
/ \ / \
8 12 16 25 */
node root = NewNode(15);
root.left = NewNode(10);
root.right = NewNode(20);
root.left.left = NewNode(8);
root.left.right = NewNode(12);
root.right.left = NewNode(16);
root.right.right = NewNode(25);
int target = 33;
if (isPairPresent(root, target) == false)
Console.Write("\nNo such values are found\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by aashish1995
Javascript
<script>
/* In a balanced binary search tree
isPairPresent two element which sums to
a given value time O(n) space O(logn) */
let MAX_SIZE= 100;
// A BST node
class Node
{
constructor(val)
{
this.val = val;
this.left = this.right = null;
}
}
// Stack type
class Stack
{
constructor()
{
this.size = 0;
this.top = 0;
this.array;
}
}
// A utility function to create a stack of given size
function createStack(size)
{
let stack = new Stack();
stack.size = size;
stack.top = -1;
stack.array = new Array(stack.size);
return stack;
}
// BASIC OPERATIONS OF STACK
function isFull(stack)
{
return (stack.top - 1 == stack.size)?1:0 ;
}
function isEmpty(stack)
{
return stack.top == -1?1:0;
}
function push(stack,node)
{
if (isFull(stack)==1)
return;
stack.array[++stack.top] = node;
}
function pop(stack)
{
if (isEmpty(stack) == 1)
return null;
return stack.array[stack.top--];
}
// Returns true if a pair with target
// sum exists in BST, otherwise false
function isPairPresent(root,target)
{
// Create two stacks. s1 is used for
// normal inorder traversal and s2 is
// used for reverse inorder traversal
let s1 = createStack(MAX_SIZE);
let s2 = createStack(MAX_SIZE);
// Note the sizes of stacks is MAX_SIZE,
// we can find the tree size and fix stack size
// as O(Logn) for balanced trees like AVL and Red Black
// tree. We have used MAX_SIZE to keep the code simple
// done1, val1 and curr1 are used for
// normal inorder traversal using s1
// done2, val2 and curr2 are used for
// reverse inorder traversal using s2
let done1 = false, done2 = false;
let val1 = 0, val2 = 0;
let curr1 = root, curr2 = root;
// The loop will break when we either
// find a pair or one of the two
// traversals is complete
while (true)
{
// Find next node in normal Inorder
// traversal. See following post
// https:// www.geeksforgeeks.org/inorder-tree-traversal-without-recursion/
while (done1 == false)
{
if (curr1 != null)
{
push(s1, curr1);
curr1 = curr1.left;
}
else
{
if (isEmpty(s1) == 1)
done1 = true;
else
{
curr1 = pop(s1);
val1 = curr1.val;
curr1 = curr1.right;
done1 = true;
}
}
}
// Find next node in REVERSE Inorder traversal. The only
// difference between above and below loop is, in below loop
// right subtree is traversed before left subtree
while (done2 == false)
{
if (curr2 != null)
{
push(s2, curr2);
curr2 = curr2.right;
}
else {
if (isEmpty(s2) == 1)
done2 = true;
else {
curr2 = pop(s2);
val2 = curr2.val;
curr2 = curr2.left;
done2 = true;
}
}
}
// If we find a pair, then print the pair and return. The first
// condition makes sure that two same values are not added
if ((val1 != val2) && (val1 + val2) == target)
{
document.write("Pair Found: " +
val1+ "+ " +
val2+ " = " +
target +"<br>");
return true;
}
// If sum of current values is smaller,
// then move to next node in
// normal inorder traversal
else if ((val1 + val2) < target)
done1 = false;
// If sum of current values is greater,
// then move to next node in
// reverse inorder traversal
else if ((val1 + val2) > target)
done2 = false;
// If any of the inorder traversals is
// over, then there is no pair
// so return false
if (val1 >= val2)
return false;
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
/*
15
/ \
10 20
/ \ / \
8 12 16 25 */
let root = new Node(15);
root.left = new Node(10);
root.right = new Node(20);
root.left.left = new Node(8);
root.left.right = new Node(12);
root.right.left = new Node(16);
root.right.right = new Node(25);
let target = 33;
if (isPairPresent(root, target) == false)
document.write("<br>No such values are found<br>");
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
</script>
Pair Found: 8+ 25 = 33
Análisis de Complejidad:
- Complejidad temporal: O(n).
Inorder Traversal de BST toma un tiempo lineal. - Espacio Auxiliar: O(logn).
La pila contiene valores de registro N como en un solo momento
https://youtube.com/watch?v=TvAFvAoS6s8%3Flist%3DPLqM7alHXFySHCXD7r1J0ky9Zg_GBB1dbk
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA