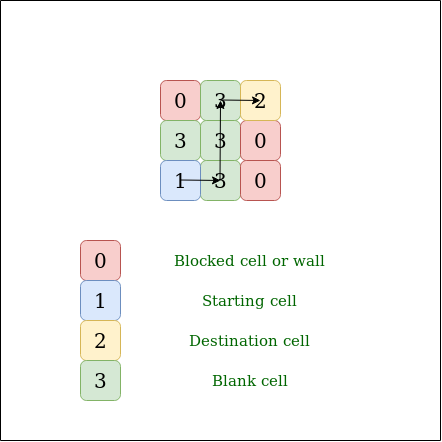
Dada la array NXN llena con 1, 0, 2, 3. Averigüe si hay un camino posible desde el origen hasta el destino, atravesando solo celdas en blanco. Puede desplazarse hacia arriba, abajo, derecha e izquierda.
- Un valor de la celda 1 significa Fuente.
- Un valor de la celda 2 significa Destino.
- Un valor de celda 3 significa celda en blanco.
- Un valor de celda 0 significa Muro en blanco.
Nota: hay una sola fuente y un solo destino (sumidero).
Ejemplos:
Entrada:
M[3][3] = {{ 0, 3, 2 },
{ 3, 3, 0 },
{ 1, 3, 0 }};
Salida: Sí
Explicación:
Entrada:
M[4][4] = {{ 0, 3, 1, 0 },
{ 3, 0, 3, 3 },
{ 2, 3, 0, 3 },
{ 0, 3, 3, 3 } };
Salida: Sí
Explicación:
Preguntado en: Entrevista de Adobe
Solución simple: recursividad.
Enfoque: Encuentre el índice de origen de la celda en cada array y luego busque recursivamente una ruta desde el índice de origen hasta el destino en la array. El algoritmo implica encontrar recursivamente todos los caminos hasta que se encuentra un camino final hacia el destino.
Algoritmo:
- Atraviese la array y encuentre el índice inicial de la array.
- Cree una función recursiva que tome el índice y la array visitada.
- Marque la celda actual y verifique si la celda actual es un destino o no. Si la celda actual es el destino, devuelve verdadero.
- Llame a la función de recursión para todas las celdas adyacentes vacías y no visitadas.
- Si alguna de las funciones recursivas devuelve verdadero, desmarque la celda y devuelva verdadero; de lo contrario, desmarque la celda y devuelva falso.
C++
// C++ program to find path between two
// cell in matrix
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define N 4
// Method for checking boundaries
bool isSafe(int i, int j, int matrix[][N])
{
if (i >= 0 && i < N && j >= 0 && j < N)
return true;
return false;
}
// Returns true if there is a
// path from a source (a
// cell with value 1) to a
// destination (a cell with
// value 2)
bool isPath(int matrix[][N], int i, int j,
bool visited[][N])
{
// Checking the boundaries, walls and
// whether the cell is unvisited
if (isSafe(i, j, matrix) && matrix[i][j] != 0
&& !visited[i][j])
{
// Make the cell visited
visited[i][j] = true;
// if the cell is the required
// destination then return true
if (matrix[i][j] == 2)
return true;
// traverse up
bool up = isPath(matrix, i - 1, j, visited);
// if path is found in up
// direction return true
if (up)
return true;
// traverse left
bool left = isPath(matrix, i, j - 1, visited);
// if path is found in left
// direction return true
if (left)
return true;
// traverse down
bool down = isPath(matrix, i + 1, j, visited);
// if path is found in down
// direction return true
if (down)
return true;
// traverse right
bool right = isPath(matrix, i, j + 1, visited);
// if path is found in right
// direction return true
if (right)
return true;
}
// no path has been found
return false;
}
// Method for finding and printing
// whether the path exists or not
void isPath(int matrix[][N])
{
// Defining visited array to keep
// track of already visited indexes
bool visited[N][N];
// Flag to indicate whether the
// path exists or not
bool flag = false;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
// if matrix[i][j] is source
// and it is not visited
if (matrix[i][j] == 1 && !visited[i][j])
// Starting from i, j and
// then finding the path
if (isPath(matrix, i, j, visited))
{
// if path exists
flag = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (flag)
cout << "YES";
else
cout << "NO";
}
// Driver program to
// check above function
int main()
{
int matrix[N][N] = { { 0, 3, 0, 1 },
{ 3, 0, 3, 3 },
{ 2, 3, 3, 3 },
{ 0, 3, 3, 3 } };
// calling isPath method
isPath(matrix);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by sudhanshugupta2019a.
Java
// Java program to find path between two
// cell in matrix
class Path {
// Method for finding and printing
// whether the path exists or not
public static void isPath(
int matrix[][], int n)
{
// Defining visited array to keep
// track of already visited indexes
boolean visited[][]
= new boolean[n][n];
// Flag to indicate whether the
// path exists or not
boolean flag = false;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// if matrix[i][j] is source
// and it is not visited
if (
matrix[i][j] == 1
&& !visited[i][j])
// Starting from i, j and
// then finding the path
if (isPath(
matrix, i, j, visited)) {
// if path exists
flag = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (flag)
System.out.println("YES");
else
System.out.println("NO");
}
// Method for checking boundaries
public static boolean isSafe(
int i, int j,
int matrix[][])
{
if (
i >= 0 && i < matrix.length
&& j >= 0
&& j < matrix[0].length)
return true;
return false;
}
// Returns true if there is a
// path from a source (a
// cell with value 1) to a
// destination (a cell with
// value 2)
public static boolean isPath(
int matrix[][],
int i, int j,
boolean visited[][])
{
// Checking the boundaries, walls and
// whether the cell is unvisited
if (
isSafe(i, j, matrix)
&& matrix[i][j] != 0
&& !visited[i][j]) {
// Make the cell visited
visited[i][j] = true;
// if the cell is the required
// destination then return true
if (matrix[i][j] == 2)
return true;
// traverse up
boolean up = isPath(
matrix, i - 1,
j, visited);
// if path is found in up
// direction return true
if (up)
return true;
// traverse left
boolean left
= isPath(
matrix, i, j - 1, visited);
// if path is found in left
// direction return true
if (left)
return true;
// traverse down
boolean down = isPath(
matrix, i + 1, j, visited);
// if path is found in down
// direction return true
if (down)
return true;
// traverse right
boolean right
= isPath(
matrix, i, j + 1,
visited);
// if path is found in right
// direction return true
if (right)
return true;
}
// no path has been found
return false;
}
// driver program to
// check above function
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int matrix[][] = { { 0, 3, 0, 1 },
{ 3, 0, 3, 3 },
{ 2, 3, 3, 3 },
{ 0, 3, 3, 3 } };
// calling isPath method
isPath(matrix, 4);
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Madhu Priya */
Python3
# Python3 program to find
# path between two cell in matrix
# Method for finding and printing
# whether the path exists or not
def isPath(matrix, n):
# Defining visited array to keep
# track of already visited indexes
visited = [[False for x in range (n)]
for y in range (n)]
# Flag to indicate whether the
# path exists or not
flag = False
for i in range (n):
for j in range (n):
# If matrix[i][j] is source
# and it is not visited
if (matrix[i][j] == 1 and not
visited[i][j]):
# Starting from i, j and
# then finding the path
if (checkPath(matrix, i,
j, visited)):
# If path exists
flag = True
break
if (flag):
print("YES")
else:
print("NO")
# Method for checking boundaries
def isSafe(i, j, matrix):
if (i >= 0 and i < len(matrix) and
j >= 0 and j < len(matrix[0])):
return True
return False
# Returns true if there is a
# path from a source(a
# cell with value 1) to a
# destination(a cell with
# value 2)
def checkPath(matrix, i, j,
visited):
# Checking the boundaries, walls and
# whether the cell is unvisited
if (isSafe(i, j, matrix) and
matrix[i][j] != 0 and not
visited[i][j]):
# Make the cell visited
visited[i][j] = True
# If the cell is the required
# destination then return true
if (matrix[i][j] == 2):
return True
# traverse up
up = checkPath(matrix, i - 1,
j, visited)
# If path is found in up
# direction return true
if (up):
return True
# Traverse left
left = checkPath(matrix, i,
j - 1, visited)
# If path is found in left
# direction return true
if (left):
return True
# Traverse down
down = checkPath(matrix, i + 1,
j, visited)
# If path is found in down
# direction return true
if (down):
return True
# Traverse right
right = checkPath(matrix, i,
j + 1, visited)
# If path is found in right
# direction return true
if (right):
return True
# No path has been found
return False
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
matrix = [[0, 3, 0, 1],
[3, 0, 3, 3],
[2, 3, 3, 3],
[0, 3, 3, 3]]
# calling isPath method
isPath(matrix, 4)
# This code is contributed by Chitranayal
C#
// C# program to find path between two
// cell in matrix
using System;
class GFG{
// Method for finding and printing
// whether the path exists or not
static void isPath(int[,] matrix, int n)
{
// Defining visited array to keep
// track of already visited indexes
bool[,] visited = new bool[n, n];
// Flag to indicate whether the
// path exists or not
bool flag = false;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
// If matrix[i][j] is source
// and it is not visited
if (matrix[i, j] == 1 &&
!visited[i, j])
// Starting from i, j and
// then finding the path
if (isPath(matrix, i, j,
visited))
{
// If path exists
flag = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (flag)
Console.WriteLine("YES");
else
Console.WriteLine("NO");
}
// Method for checking boundaries
public static bool isSafe(int i, int j,
int[,] matrix)
{
if (i >= 0 && i < matrix.GetLength(0) &&
j >= 0 && j < matrix.GetLength(1))
return true;
return false;
}
// Returns true if there is a path from
// a source (a cell with value 1) to a
// destination (a cell with value 2)
public static bool isPath(int[,] matrix, int i,
int j, bool[,] visited)
{
// Checking the boundaries, walls and
// whether the cell is unvisited
if (isSafe(i, j, matrix) &&
matrix[i, j] != 0 &&
!visited[i, j])
{
// Make the cell visited
visited[i, j] = true;
// If the cell is the required
// destination then return true
if (matrix[i, j] == 2)
return true;
// Traverse up
bool up = isPath(matrix, i - 1,
j, visited);
// If path is found in up
// direction return true
if (up)
return true;
// Traverse left
bool left = isPath(matrix, i,
j - 1, visited);
// If path is found in left
// direction return true
if (left)
return true;
// Traverse down
bool down = isPath(matrix, i + 1,
j, visited);
// If path is found in down
// direction return true
if (down)
return true;
// Traverse right
bool right = isPath(matrix, i, j + 1,
visited);
// If path is found in right
// direction return true
if (right)
return true;
}
// No path has been found
return false;
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
int[,] matrix = { { 0, 3, 0, 1 },
{ 3, 0, 3, 3 },
{ 2, 3, 3, 3 },
{ 0, 3, 3, 3 } };
// Calling isPath method
isPath(matrix, 4);
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program to find path between two
// cell in matrix
// Method for finding and printing
// whether the path exists or not
function isPath(matrix,n)
{
// Defining visited array to keep
// track of already visited indexes
let visited = new Array(n);
for(let i=0;i<n;i++)
{
visited[i]=new Array(n);
for(let j=0;j<n;j++)
{
visited[i][j]=false;
}
}
// Flag to indicate whether the
// path exists or not
let flag = false;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// if matrix[i][j] is source
// and it is not visited
if (
matrix[i][j] == 1
&& !visited[i][j])
// Starting from i, j and
// then finding the path
if (checkPath(
matrix, i, j, visited)) {
// if path exists
flag = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (flag)
document.write("YES<br>");
else
document.write("NO<br>");
}
// Method for checking boundaries
function isSafe(i,j,matrix)
{
if (
i >= 0 && i < matrix.length
&& j >= 0
&& j < matrix[0].length)
return true;
return false;
}
// Returns true if there is a
// path from a source (a
// cell with value 1) to a
// destination (a cell with
// value 2)
function checkPath(matrix,i,j,visited)
{
// Checking the boundaries, walls and
// whether the cell is unvisited
if (
isSafe(i, j, matrix)
&& matrix[i][j] != 0
&& !visited[i][j]) {
// Make the cell visited
visited[i][j] = true;
// if the cell is the required
// destination then return true
if (matrix[i][j] == 2)
return true;
// traverse up
let up = checkPath(
matrix, i - 1,
j, visited);
// if path is found in up
// direction return true
if (up)
return true;
// traverse left
let left
= checkPath(
matrix, i, j - 1, visited);
// if path is found in left
// direction return true
if (left)
return true;
// traverse down
let down = checkPath(
matrix, i + 1, j, visited);
// if path is found in down
// direction return true
if (down)
return true;
// traverse right
let right
= checkPath(
matrix, i, j + 1,
visited);
// if path is found in right
// direction return true
if (right)
return true;
}
// no path has been found
return false;
}
// driver program to
// check above function
let matrix= [[ 0, 3, 0, 1 ],
[ 3, 0, 3, 3 ],
[ 2, 3, 3, 3 ],
[ 0, 3, 3, 3 ]];
// calling isPath method
isPath(matrix, 4);
// This code is contributed by ab2127
</script>
YES
Análisis de Complejidad:
- Complejidad de Tiempo: O(n*m), En el peor de los casos, tenemos que visitar cada celda solo una vez porque mantenemos la array visitada para no visitar la celda ya visitada.
- Complejidad espacial: O(n*m), se requiere espacio para almacenar la array visitada.
Solución eficiente: Gráfica.
Enfoque: La idea es utilizar la búsqueda en amplitud . Considere cada celda como un Node y cada límite entre dos celdas adyacentes como un borde. por lo que el número total de Nodes es N * N.
Entonces, la idea es hacer una búsqueda en amplitud desde la celda inicial hasta que se encuentre la celda final.
Algoritmo:
- Cree un gráfico vacío que tenga N * N Node (vértice), inserte todos los Nodes en un gráfico y anote el vértice fuente y receptor.
- Ahora aplique BFS en el gráfico, cree una cola e inserte el Node de origen en la cola
- Ejecute un bucle hasta que el tamaño de la cola sea mayor que 0
- Elimine el Node frontal de la cola y verifique si el Node es el destino si el destino devuelve verdadero. marcar el Node
- Marque todas las celdas adyacentes si no están visitadas y en blanco, insértelas en la cola.
- Si no se alcanza el destino, devuelve verdadero.
C++
// C++ program to find path
// between two cell in matrix
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 4
class Graph {
int V;
list<int>* adj;
public:
Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list<int>[V];
}
void addEdge(int s, int d);
bool BFS(int s, int d);
};
// add edge to graph
void Graph::addEdge(int s, int d)
{
adj[s].push_back(d);
}
// BFS function to find path
// from source to sink
bool Graph::BFS(int s, int d)
{
// Base case
if (s == d)
return true;
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
bool* visited = new bool[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Create a queue for BFS
list<int> queue;
// Mark the current node as visited and
// enqueue it
visited[s] = true;
queue.push_back(s);
// it will be used to get all adjacent
// vertices of a vertex
list<int>::iterator i;
while (!queue.empty()) {
// Dequeue a vertex from queue
s = queue.front();
queue.pop_front();
// Get all adjacent vertices of the
// dequeued vertex s. If a adjacent has
// not been visited, then mark it visited
// and enqueue it
for (
i = adj[s].begin(); i != adj[s].end(); ++i) {
// If this adjacent node is the
// destination node, then return true
if (*i == d)
return true;
// Else, continue to do BFS
if (!visited[*i]) {
visited[*i] = true;
queue.push_back(*i);
}
}
}
// If BFS is complete without visiting d
return false;
}
bool isSafe(int i, int j, int M[][N])
{
if (
(i < 0 || i >= N)
|| (j < 0 || j >= N)
|| M[i][j] == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
// Returns true if there is
// a path from a source (a
// cell with value 1) to a
// destination (a cell with
// value 2)
bool findPath(int M[][N])
{
// source and destination
int s, d;
int V = N * N + 2;
Graph g(V);
// create graph with n*n node
// each cell consider as node
// Number of current vertex
int k = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (M[i][j] != 0) {
// connect all 4 adjacent
// cell to current cell
if (isSafe(i, j + 1, M))
g.addEdge(k, k + 1);
if (isSafe(i, j - 1, M))
g.addEdge(k, k - 1);
if (i < N - 1 && isSafe(i + 1, j, M))
g.addEdge(k, k + N);
if (i > 0 && isSafe(i - 1, j, M))
g.addEdge(k, k - N);
}
// Source index
if (M[i][j] == 1)
s = k;
// Destination index
if (M[i][j] == 2)
d = k;
k++;
}
}
// find path Using BFS
return g.BFS(s, d);
}
// driver program to check
// above function
int main()
{
int M[N][N] = { { 0, 3, 0, 1 },
{ 3, 0, 3, 3 },
{ 2, 3, 3, 3 },
{ 0, 3, 3, 3 } };
(findPath(M) == true) ? cout << "Yes" : cout << "No" << endl;
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to find path between two
// cell in matrix
import java.util.*;
class Graph {
int V;
List<List<Integer> > adj;
Graph(int V)
{
this.V = V;
adj = new ArrayList<>(V);
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
adj.add(i, new ArrayList<>());
}
}
// add edge to graph
void addEdge(int s, int d)
{
adj.get(s).add(d);
}
// BFS function to find path
// from source to sink
boolean BFS(int s, int d)
{
// Base case
if (s == d)
return true;
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
boolean[] visited = new boolean[V];
// Create a queue for BFS
Queue<Integer> queue
= new LinkedList<>();
// Mark the current node as visited and
// enqueue it
visited[s] = true;
queue.offer(s);
// it will be used to get all adjacent
// vertices of a vertex
List<Integer> edges;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
// Dequeue a vertex from queue
s = queue.poll();
// Get all adjacent vertices of the
// dequeued vertex s. If a adjacent has
// not been visited, then mark it visited
// and enqueue it
edges = adj.get(s);
for (int curr : edges) {
// If this adjacent node is the
// destination node, then return true
if (curr == d)
return true;
// Else, continue to do BFS
if (!visited[curr]) {
visited[curr] = true;
queue.offer(curr);
}
}
}
// If BFS is complete without visiting d
return false;
}
static boolean isSafe(
int i, int j, int[][] M)
{
int N = M.length;
if (
(i < 0 || i >= N)
|| (j < 0 || j >= N)
|| M[i][j] == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
// Returns true if there is a
// path from a source (a
// cell with value 1) to a
// destination (a cell with
// value 2)
static boolean findPath(int[][] M)
{
// Source and destination
int s = -1, d = -1;
int N = M.length;
int V = N * N + 2;
Graph g = new Graph(V);
// Create graph with n*n node
// each cell consider as node
int k = 1; // Number of current vertex
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (M[i][j] != 0) {
// connect all 4 adjacent
// cell to current cell
if (isSafe(i, j + 1, M))
g.addEdge(k, k + 1);
if (isSafe(i, j - 1, M))
g.addEdge(k, k - 1);
if (i < N - 1
&& isSafe(i + 1, j, M))
g.addEdge(k, k + N);
if (i > 0 && isSafe(i - 1, j, M))
g.addEdge(k, k - N);
}
// source index
if (M[i][j] == 1)
s = k;
// destination index
if (M[i][j] == 2)
d = k;
k++;
}
}
// find path Using BFS
return g.BFS(s, d);
}
// Driver program to check above function
public static void main(
String[] args) throws Exception
{
int[][] M = { { 0, 3, 0, 1 },
{ 3, 0, 3, 3 },
{ 2, 3, 3, 3 },
{ 0, 3, 3, 3 } };
System.out.println(
((findPath(M)) ? "Yes" : "No"));
}
}
// This code is contributed by abhay379201
Python3
# Python3 program to find path between two
# cell in matrix
from collections import defaultdict
class Graph:
def __init__(self):
self.graph = defaultdict(list)
# add edge to graph
def addEdge(self, u, v):
self.graph[u].append(v)
# BFS function to find path from source to sink
def BFS(self, s, d):
# Base case
if s == d:
return True
# Mark all the vertices as not visited
visited = [False]*(len(self.graph) + 1)
# Create a queue for BFS
queue = []
queue.append(s)
# Mark the current node as visited and
# enqueue it
visited[s] = True
while(queue):
# Dequeue a vertex from queue
s = queue.pop(0)
# Get all adjacent vertices of the
# dequeued vertex s. If a adjacent has
# not been visited, then mark it visited
# and enqueue it
for i in self.graph[s]:
# If this adjacent node is the destination
# node, then return true
if i == d:
return True
# Else, continue to do BFS
if visited[i] == False:
queue.append(i)
visited[i] = True
# If BFS is complete without visiting d
return False
def isSafe(i, j, matrix):
if i >= 0 and i <= len(matrix) and j >= 0 and j <= len(matrix[0]):
return True
else:
return False
# Returns true if there is a path from a source (a
# cell with value 1) to a destination (a cell with
# value 2)
def findPath(M):
s, d = None, None # source and destination
N = len(M)
g = Graph()
# create graph with n * n node
# each cell consider as node
k = 1 # Number of current vertex
for i in range(N):
for j in range(N):
if (M[i][j] != 0):
# connect all 4 adjacent cell to
# current cell
if (isSafe(i, j + 1, M)):
g.addEdge(k, k + 1)
if (isSafe(i, j - 1, M)):
g.addEdge(k, k - 1)
if (isSafe(i + 1, j, M)):
g.addEdge(k, k + N)
if (isSafe(i - 1, j, M)):
g.addEdge(k, k - N)
if (M[i][j] == 1):
s = k
# destination index
if (M[i][j] == 2):
d = k
k += 1
# find path Using BFS
return g.BFS(s, d)
# Driver code
if __name__=='__main__':
M =[[0, 3, 0, 1], [3, 0, 3, 3], [2, 3, 3, 3], [0, 3, 3, 3]]
if findPath(M):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
# This Code is Contributed by Vikash Kumar 37
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program to find path between two
// cell in matrix
let V;
let adj=[];
function Graph(v)
{
V=v;
for (let i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
adj.push([]);
}
}
// add edge to graph
function addEdge(s,d)
{
adj[s].push(d);
}
// BFS function to find path
// from source to sink
function BFS(s,d)
{
// Base case
if (s == d)
return true;
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
let visited = new Array(V);
for(let i=0;i<V;i++)
{
visited[i]=false;
}
// Create a queue for BFS
let queue=[];
// Mark the current node as visited and
// enqueue it
visited[s] = true;
queue.push(s);
// it will be used to get all adjacent
// vertices of a vertex
let edges;
while (queue.length!=0) {
// Dequeue a vertex from queue
s = queue.shift();
// Get all adjacent vertices of the
// dequeued vertex s. If a adjacent has
// not been visited, then mark it visited
// and enqueue it
edges = adj[s];
for (let curr=0;curr< edges.length;curr++) {
// If this adjacent node is the
// destination node, then return true
if (edges[curr] == d)
return true;
// Else, continue to do BFS
if (!visited[edges[curr]]) {
visited[edges[curr]] = true;
queue.push(edges[curr]);
}
}
}
// If BFS is complete without visiting d
return false;
}
function isSafe(i,j,M)
{
let N = M.length;
if (
(i < 0 || i >= N)
|| (j < 0 || j >= N)
|| M[i][j] == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
// Returns true if there is a
// path from a source (a
// cell with value 1) to a
// destination (a cell with
// value 2)
function findPath(M)
{
// Source and destination
let s = -1, d = -1;
let N = M.length;
let V = N * N + 2;
Graph(V);
// Create graph with n*n node
// each cell consider as node
let k = 1; // Number of current vertex
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (M[i][j] != 0) {
// connect all 4 adjacent
// cell to current cell
if (isSafe(i, j + 1, M))
addEdge(k, k + 1);
if (isSafe(i, j - 1, M))
addEdge(k, k - 1);
if (i < N - 1
&& isSafe(i + 1, j, M))
addEdge(k, k + N);
if (i > 0 && isSafe(i - 1, j, M))
addEdge(k, k - N);
}
// source index
if (M[i][j] == 1)
s = k;
// destination index
if (M[i][j] == 2)
d = k;
k++;
}
}
// find path Using BFS
return BFS(s, d);
}
// Driver program to check above function
let M = [[ 0, 3, 0, 1 ],
[ 3, 0, 3, 3 ],
[ 2, 3, 3, 3 ],
[ 0, 3, 3, 3 ]];
document.write(((findPath(M)) ? "Yes" : "No"));
// This code is contributed by patel2127
</script>
Yes
Análisis de Complejidad:
- Complejidad temporal: O(n*m).
Cada celda de la array se visita una sola vez, por lo que la complejidad temporal es O(n*m). - Complejidad espacial: O(n*m).
Se requiere espacio para almacenar la array visitada y para crear la cola.
Solución simple y eficiente : el gráfico es la array en sí mismo.
Enfoque : La idea es utilizar Breadth-First Search en la propia array.
Considere una celda = (i, j) como un vértice v en la cola BFS. Un nuevo vértice u se coloca en la cola BFS si u=(i+1,j) o u=(i-1,j) o u=(i,j+1) o u=(i,j-1) . Comenzando el algoritmo BFS desde la celda = (i,j) tal que M[i][j] es 1 y deteniéndose si hubiera un vértice alcanzable u=(i,j) tal que M[i][j] sea 2 y devolver verdadero o cada celda estaba cubierta y no había tal celda y devolver falso.
Algoritmo :
1) Crear cola BFS q
2) escanee la array, si existe una celda en la array tal que su valor sea 1, luego empújela a q
3) ejecutar el algoritmo BFS con q, omitiendo las celdas que no son válidas. es decir: son muros (el valor es 0) o están fuera de los límites de la array y los marcan como muros después de una visita exitosa.
3.1) si en el proceso del algoritmo BFS hubiera un vértice x=(i,j) tal que M[i][j] es 2 detener y devolver verdadero
4) El algoritmo BFS terminó sin devolver verdadero, entonces no había ningún elemento M[i][j] que es 2, luego devolvió falso
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
#define R 4
#define C 4
// Structure to define a vertex u=(i,j)
typedef struct BFSElement {
BFSElement(int i, int j)
{
this->i = i;
this->j = j;
}
int i;
int j;
} BFSElement;
bool findPath(int M[R][C])
{
// 1) Create BFS queue q
queue<BFSElement> q;
// 2)scan the matrix
for (int i = 0; i < R; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < C; ++j) {
// if there exists a cell in the matrix such
// that its value is 1 then push it to q
if (M[i][j] == 1) {
q.push(BFSElement(i, j));
break;
}
}
}
// 3) run BFS algorithm with q.
while (!q.empty()) {
BFSElement x = q.front();
q.pop();
int i = x.i;
int j = x.j;
// skipping cells which are not valid.
// if outside the matrix bounds
if (i < 0 || i > R || j < 0 || j > C)
continue;
// if they are walls (value is 0).
if (M[i][j] == 0)
continue;
// 3.1) if in the BFS algorithm process there was a
// vertex x=(i,j) such that M[i][j] is 2 stop and
// return true
if (M[i][j] == 2)
return true;
// marking as wall upon successful visitation
M[i][j] = 0;
// pushing to queue u=(i,j+1),u=(i,j-1)
// u=(i+1,j),u=(i-1,j)
for (int k = -1; k <= 1; k += 2) {
q.push(BFSElement(i + k, j));
q.push(BFSElement(i, j + k));
}
}
// BFS algorithm terminated without returning true
// then there was no element M[i][j] which is 2, then
// return false
return false;
}
// Main Driver code
int main()
{
int M[R][C] = { { 0, 3, 0, 1 },
{ 3, 0, 3, 3 },
{ 2, 3, 3, 3 },
{ 0, 3, 3, 3 } };
(findPath(M) == true) ? cout << "Yes"
: cout << "No" << endl;
return 0;
}
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class BFSElement
{
int i, j;
BFSElement(int i, int j)
{
this.i = i;
this.j = j;
}
}
class GFG {
static int R = 4, C = 4;
BFSElement b;
static boolean findPath(int M[][])
{
// 1) Create BFS queue q
Queue<BFSElement> q = new LinkedList<>();
// 2)scan the matrix
for (int i = 0; i < R; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < C; ++j)
{
// if there exists a cell in the matrix such
// that its value is 1 then push it to q
if (M[i][j] == 1) {
q.add(new BFSElement(i, j));
break;
}
}
}
// 3) run BFS algorithm with q.
while (q.size() != 0)
{
BFSElement x = q.peek();
q.remove();
int i = x.i;
int j = x.j;
// skipping cells which are not valid.
// if outside the matrix bounds
if (i < 0 || i >= R || j < 0 || j >= C)
continue;
// if they are walls (value is 0).
if (M[i][j] == 0)
continue;
// 3.1) if in the BFS algorithm process there was a
// vertex x=(i,j) such that M[i][j] is 2 stop and
// return true
if (M[i][j] == 2)
return true;
// marking as wall upon successful visitation
M[i][j] = 0;
// pushing to queue u=(i,j+1),u=(i,j-1)
// u=(i+1,j),u=(i-1,j)
for (int k = -1; k <= 1; k += 2)
{
q.add(new BFSElement(i + k, j));
q.add(new BFSElement(i, j + k));
}
}
// BFS algorithm terminated without returning true
// then there was no element M[i][j] which is 2, then
// return false
return false;
}
// Main Driver code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int M[][] = { { 0, 3, 0, 1 },
{ 3, 0, 3, 3 },
{ 2, 3, 3, 3 },
{ 0, 3, 3, 3 } };
if(findPath(M) == true)
System.out.println("Yes");
else
System.out.println("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
Python3
class BFSElement:
def __init__(self, i, j):
self.i = i
self.j = j
R,C = 4,4
def findPath(M):
# 1) Create BFS queue q
q = []
# 2)scan the matrix
for i in range(R):
for j in range(C):
# if there exists a cell in the matrix such
# that its value is 1 then append it to q
if (M[i][j] == 1):
q.append(BFSElement(i, j))
break
# 3) run BFS algorithm with q.
while (len(q) != 0):
x = q[0]
q = q[1:]
i = x.i
j = x.j
# skipping cells which are not valid.
# if outside the matrix bounds
if (i < 0 or i >= R or j < 0 or j >= C):
continue
# if they are walls (value is 0).
if (M[i][j] == 0):
continue
# 3.1) if in the BFS algorithm process there was a
# vertex x=(i,j) such that M[i][j] is 2 stop and
# return True
if (M[i][j] == 2):
return True
# marking as wall upon successful visitation
M[i][j] = 0
# appending to queue u=(i,j+1),u=(i,j-1)
# u=(i+1,j),u=(i-1,j)
for k in range(-1, 2, 2):
q.append(BFSElement(i + k, j))
q.append(BFSElement(i, j + k))
# BFS algorithm terminated without returning True
# then there was no element M[i][j] which is 2, then
# return false
return False
# Main Driver code
M = [[ 0, 3, 0, 1 ],
[ 3, 0, 3, 3 ],
[ 2, 3, 3, 3 ],
[ 0, 3, 3, 3 ]]
if(findPath(M) == True):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
# This code is contributed by shinjanpatra
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class BFSElement
{
public int i, j;
public BFSElement(int i, int j)
{
this.i = i;
this.j = j;
}
}
public class GFG
{
static int R = 4, C = 4;
static bool findPath(int[,] M)
{
// 1) Create BFS queue q
Queue<BFSElement> q = new Queue<BFSElement>();
// 2)scan the matrix
for (int i = 0; i < R; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < C; ++j)
{
// if there exists a cell in the matrix such
// that its value is 1 then push it to q
if (M[i, j] == 1) {
q.Enqueue(new BFSElement(i, j));
break;
}
}
}
// 3) run BFS algorithm with q.
while (q.Count != 0)
{
BFSElement x = q.Peek();
q.Dequeue();
int i = x.i;
int j = x.j;
// skipping cells which are not valid.
// if outside the matrix bounds
if (i < 0 || i >= R || j < 0 || j >= C)
continue;
// if they are walls (value is 0).
if (M[i, j] == 0)
continue;
// 3.1) if in the BFS algorithm process there was a
// vertex x=(i,j) such that M[i][j] is 2 stop and
// return true
if (M[i, j] == 2)
return true;
// marking as wall upon successful visitation
M[i, j] = 0;
// pushing to queue u=(i,j+1),u=(i,j-1)
// u=(i+1,j),u=(i-1,j)
for (int k = -1; k <= 1; k += 2)
{
q.Enqueue(new BFSElement(i + k, j));
q.Enqueue(new BFSElement(i, j + k));
}
}
// BFS algorithm terminated without returning true
// then there was no element M[i][j] which is 2, then
// return false
return false;
}
// Main Driver code
static public void Main (){
int[,] M = { { 0, 3, 0, 1 },
{ 3, 0, 3, 3 },
{ 2, 3, 3, 3 },
{ 0, 3, 3, 3 } };
if(findPath(M) == true)
Console.WriteLine("Yes");
else
Console.WriteLine("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by rag2127
Javascript
<script>
class BFSElement
{
constructor(i,j)
{
this.i=i;
this.j=j;
}
}
let R = 4, C = 4;
let b;
function findPath(M)
{
// 1) Create BFS queue q
let q = [];
// 2)scan the matrix
for (let i = 0; i < R; ++i)
{
for (let j = 0; j < C; ++j)
{
// if there exists a cell in the matrix such
// that its value is 1 then push it to q
if (M[i][j] == 1) {
q.push(new BFSElement(i, j));
break;
}
}
}
// 3) run BFS algorithm with q.
while (q.length != 0)
{
let x = q.shift();
let i = x.i;
let j = x.j;
// skipping cells which are not valid.
// if outside the matrix bounds
if (i < 0 || i >= R || j < 0 || j >= C)
continue;
// if they are walls (value is 0).
if (M[i][j] == 0)
continue;
// 3.1) if in the BFS algorithm process there was a
// vertex x=(i,j) such that M[i][j] is 2 stop and
// return true
if (M[i][j] == 2)
return true;
// marking as wall upon successful visitation
M[i][j] = 0;
// pushing to queue u=(i,j+1),u=(i,j-1)
// u=(i+1,j),u=(i-1,j)
for (let k = -1; k <= 1; k += 2)
{
q.push(new BFSElement(i + k, j));
q.push(new BFSElement(i, j + k));
}
}
// BFS algorithm terminated without returning true
// then there was no element M[i][j] which is 2, then
// return false
return false;
}
// Main Driver code
let M=[[ 0, 3, 0, 1 ],
[ 3, 0, 3, 3 ],
[ 2, 3, 3, 3 ],
[ 0, 3, 3, 3 ]];
if(findPath(M) == true)
document.write("Yes");
else
document.write("No");
// This code is contributed by unknown2108
</script>
Yes
Complejidad temporal : O(n*m).
Complejidad espacial : O(n*m).
La mejora es aportada por Ephi F.
Este artículo es una contribución de Nishant Singh . Si te gusta GeeksforGeeks y te gustaría contribuir, también puedes escribir un artículo usando write.geeksforgeeks.org o enviar tu artículo por correo a review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA