Dada una serie de strings, encuentre si las strings dadas se pueden enstringr para formar un círculo. Una string X se puede poner antes de otra string Y en un círculo si el último carácter de X es el mismo que el primer carácter de Y.
Ejemplos:
Input: arr[] = {"geek", "king"}
Output: Yes, the given strings can be chained.
Note that the last character of first string is same
as first character of second string and vice versa is
also true.
Input: arr[] = {"for", "geek", "rig", "kaf"}
Output: Yes, the given strings can be chained.
The strings can be chained as "for", "rig", "geek"
and "kaf"
Input: arr[] = {"aab", "bac", "aaa", "cda"}
Output: Yes, the given strings can be chained.
The strings can be chained as "aaa", "aab", "bac"
and "cda"
Input: arr[] = {"aaa", "bbb", "baa", "aab"};
Output: Yes, the given strings can be chained.
The strings can be chained as "aaa", "aab", "bbb"
and "baa"
Input: arr[] = {"aaa"};
Output: Yes
Input: arr[] = {"aaa", "bbb"};
Output: No
Input : arr[] = ["abc", "efg", "cde", "ghi", "ija"]
Output : Yes
These strings can be reordered as, “abc”, “cde”, “efg”,
“ghi”, “ija”
Input : arr[] = [“ijk”, “kji”, “abc”, “cba”]
Output : No
Le recomendamos encarecidamente que haga clic aquí y lo practique antes de pasar a la solución.
Hemos discutido un enfoque para este problema en la publicación a continuación.
Encuentra si una array de strings se puede enstringr para formar un círculo | Serie 1
En este post, se discute otro enfoque. Resolvemos este problema tratándolo como un problema gráfico, donde los vértices serán el primer y último carácter de las strings, y dibujaremos una arista entre dos vértices si son el primer y último carácter de la misma string, por lo que un número de los bordes en el gráfico serán los mismos que el número de strings en la array.
La representación gráfica de algunas arrays de strings se da en el siguiente diagrama,
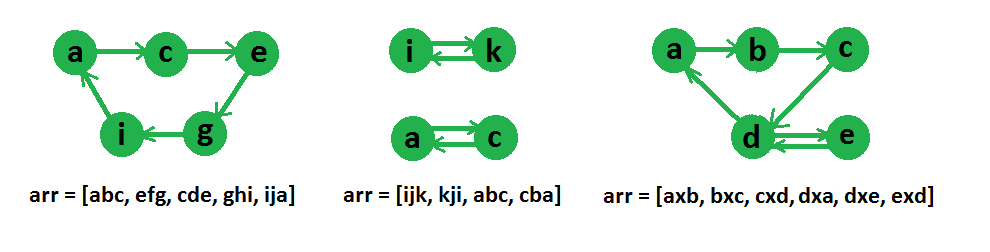
Ahora se puede ver claramente después de la representación del gráfico que si es posible un bucle entre los vértices del gráfico, entonces podemos reordenar las strings, de lo contrario no. Como en el ejemplo del diagrama anterior, se puede encontrar un bucle en la primera y tercera array de strings, pero no en la segunda array de strings. Ahora, para verificar si este gráfico puede tener un bucle que pase por todos los vértices , verificaremos dos condiciones,
- Los grados de entrada y salida de cada vértice deben ser iguales.
- El gráfico debe estar fuertemente conectado.
La primera condición se puede verificar fácilmente manteniendo dos arrays, dentro y fuera para cada carácter. Verificar si un gráfico tiene un bucle que pasa por todos los vértices es lo mismo que verificar si el gráfico dirigido completo está fuertemente conectado o no, porque si tiene un bucle que pasa por todos los vértices, entonces podemos llegar a cualquier vértice desde cualquier otro vértice que es decir, el gráfico estará fuertemente conectado y el mismo argumento también se puede dar para la declaración inversa.
Ahora, para verificar la segunda condición, solo ejecutaremos un DFS desde cualquier carácter y visitaremos todos los vértices accesibles desde esto, ahora si el gráfico tiene un bucle, luego de este DFS se deben visitar todos los vértices, si se visitan todos los vértices, entonces regresaremos verdadero, de lo contrario, falso, por lo que visitar todos los vértices en un solo DFS marca un posible orden entre las strings .
C++
// C++ code to check if cyclic order is possible among strings
// under given constraints
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define M 26
// Utility method for a depth first search among vertices
void dfs(vector<int> g[], int u, vector<bool> &visit)
{
visit[u] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < g[u].size(); ++i)
if(!visit[g[u][i]])
dfs(g, g[u][i], visit);
}
// Returns true if all vertices are strongly connected
// i.e. can be made as loop
bool isConnected(vector<int> g[], vector<bool> &mark, int s)
{
// Initialize all vertices as not visited
vector<bool> visit(M, false);
// perform a dfs from s
dfs(g, s, visit);
// now loop through all characters
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
/* I character is marked (i.e. it was first or last
character of some string) then it should be
visited in last dfs (as for looping, graph
should be strongly connected) */
if (mark[i] && !visit[i])
return false;
}
// If we reach that means graph is connected
return true;
}
// return true if an order among strings is possible
bool possibleOrderAmongString(string arr[], int N)
{
// Create an empty graph
vector<int> g[M];
// Initialize all vertices as not marked
vector<bool> mark(M, false);
// Initialize indegree and outdegree of every
// vertex as 0.
vector<int> in(M, 0), out(M, 0);
// Process all strings one by one
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
// Find first and last characters
int f = arr[i].front() - 'a';
int l = arr[i].back() - 'a';
// Mark the characters
mark[f] = mark[l] = true;
// increase indegree and outdegree count
in[l]++;
out[f]++;
// Add an edge in graph
g[f].push_back(l);
}
// If for any character indegree is not equal to
// outdegree then ordering is not possible
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
if (in[i] != out[i])
return false;
return isConnected(g, mark, arr[0].front() - 'a');
}
// Driver code to test above methods
int main()
{
// string arr[] = {"abc", "efg", "cde", "ghi", "ija"};
string arr[] = {"ab", "bc", "cd", "de", "ed", "da"};
int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
if (possibleOrderAmongString(arr, N) == false)
cout << "Ordering not possible\n";
else
cout << "Ordering is possible\n";
return 0;
}
Java
// Java code to check if cyclic order is
// possible among strings under given constraints
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Return true if an order among strings is possible
public static boolean possibleOrderAmongString(
String s[], int n)
{
int m = 26;
boolean mark[] = new boolean[m];
int in[] = new int[26];
int out[] = new int[26];
ArrayList<
ArrayList<Integer>> adj = new ArrayList<
ArrayList<Integer>>();
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
// Process all strings one by one
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Find first and last characters
int f = (int)(s[i].charAt(0) - 'a');
int l = (int)(s[i].charAt(
s[i].length() - 1) - 'a');
// Mark the characters
mark[f] = mark[l] = true;
// Increase indegree and outdegree count
in[l]++;
out[f]++;
// Add an edge in graph
adj.get(f).add(l);
}
// If for any character indegree is not equal to
// outdegree then ordering is not possible
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
if (in[i] != out[i])
return false;
}
return isConnected(adj, mark,
s[0].charAt(0) - 'a');
}
// Returns true if all vertices are strongly
// connected i.e. can be made as loop
public static boolean isConnected(
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj,
boolean mark[], int src)
{
boolean visited[] = new boolean[26];
// Perform a dfs from src
dfs(adj, visited, src);
for(int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
{
/* I character is marked (i.e. it was first or
last character of some string) then it should
be visited in last dfs (as for looping, graph
should be strongly connected) */
if (mark[i] && !visited[i])
return false;
}
// If we reach that means graph is connected
return true;
}
// Utility method for a depth first
// search among vertices
public static void dfs(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj,
boolean visited[], int src)
{
visited[src] = true;
for(int i = 0; i < adj.get(src).size(); i++)
if (!visited[adj.get(src).get(i)])
dfs(adj, visited, adj.get(src).get(i));
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String s[] = { "ab", "bc", "cd", "de", "ed", "da" };
int n = s.length;
if (possibleOrderAmongString(s, n))
System.out.println("Ordering is possible");
else
System.out.println("Ordering is not possible");
}
}
// This code is contributed by parascoding
Python3
# Python3 code to check if
# cyclic order is possible
# among strings under given
# constraints
M = 26
# Utility method for a depth
# first search among vertices
def dfs(g, u, visit):
visit[u] = True
for i in range(len(g[u])):
if(not visit[g[u][i]]):
dfs(g, g[u][i], visit)
# Returns true if all vertices
# are strongly connected i.e.
# can be made as loop
def isConnected(g, mark, s):
# Initialize all vertices
# as not visited
visit = [False for i in range(M)]
# Perform a dfs from s
dfs(g, s, visit)
# Now loop through
# all characters
for i in range(M):
# I character is marked
# (i.e. it was first or last
# character of some string)
# then it should be visited
# in last dfs (as for looping,
# graph should be strongly
# connected) */
if(mark[i] and (not visit[i])):
return False
# If we reach that means
# graph is connected
return True
# return true if an order among
# strings is possible
def possibleOrderAmongString(arr, N):
# Create an empty graph
g = {}
# Initialize all vertices
# as not marked
mark = [False for i in range(M)]
# Initialize indegree and
# outdegree of every
# vertex as 0.
In = [0 for i in range(M)]
out = [0 for i in range(M)]
# Process all strings
# one by one
for i in range(N):
# Find first and last
# characters
f = (ord(arr[i][0]) -
ord('a'))
l = (ord(arr[i][-1]) -
ord('a'))
# Mark the characters
mark[f] = True
mark[l] = True
# Increase indegree
# and outdegree count
In[l] += 1
out[f] += 1
if f not in g:
g[f] = []
# Add an edge in graph
g[f].append(l)
# If for any character
# indegree is not equal to
# outdegree then ordering
# is not possible
for i in range(M):
if(In[i] != out[i]):
return False
return isConnected(g, mark,
ord(arr[0][0]) -
ord('a'))
# Driver code
arr = ["ab", "bc",
"cd", "de",
"ed", "da"]
N = len(arr)
if(possibleOrderAmongString(arr, N) ==
False):
print("Ordering not possible")
else:
print("Ordering is possible")
# This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
C#
// C# code to check if cyclic order is
// possible among strings under given constraints
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
// Return true if an order among strings is possible
static bool possibleOrderAmongString(string[] s, int n)
{
int m = 26;
bool[] mark = new bool[m];
int[] In = new int[26];
int[] Out = new int[26];
List<List<int>> adj = new List<List<int>>();
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
adj.Add(new List<int>());
// Process all strings one by one
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Find first and last characters
int f = (int)(s[i][0] - 'a');
int l = (int)(s[i][s[i].Length - 1] - 'a');
// Mark the characters
mark[f] = mark[l] = true;
// Increase indegree and outdegree count
In[l]++;
Out[f]++;
// Add an edge in graph
adj[f].Add(l);
}
// If for any character indegree is not equal to
// outdegree then ordering is not possible
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
if (In[i] != Out[i])
return false;
}
return isConnected(adj, mark,
s[0][0] - 'a');
}
// Returns true if all vertices are strongly
// connected i.e. can be made as loop
public static bool isConnected(
List<List<int>> adj,
bool[] mark, int src)
{
bool[] visited = new bool[26];
// Perform a dfs from src
dfs(adj, visited, src);
for(int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
{
/* I character is marked (i.e. it was first or
last character of some string) then it should
be visited in last dfs (as for looping, graph
should be strongly connected) */
if (mark[i] && !visited[i])
return false;
}
// If we reach that means graph is connected
return true;
}
// Utility method for a depth first
// search among vertices
public static void dfs(List<List<int>> adj,
bool[] visited, int src)
{
visited[src] = true;
for(int i = 0; i < adj[src].Count; i++)
if (!visited[adj[src][i]])
dfs(adj, visited, adj[src][i]);
}
static void Main() {
string[] s = { "ab", "bc", "cd", "de", "ed", "da" };
int n = s.Length;
if (possibleOrderAmongString(s, n))
Console.Write("Ordering is possible");
else
Console.Write("Ordering is not possible");
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyesh072019.
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript code to check if cyclic order is
// possible among strings under given constraints
// Return true if an order among strings is possible
function possibleOrderAmongString(s, n)
{
let m = 26;
let mark = new Array(m);
mark.fill(false);
let In = new Array(26);
In.fill(0);
let Out = new Array(26);
Out.fill(0);
let adj = [];
for(let i = 0; i < m; i++)
adj.push([]);
// Process all strings one by one
for(let i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Find first and last characters
let f = (s[i][0].charCodeAt() - 'a'.charCodeAt());
let l = (s[i][s[i].length - 1].charCodeAt() - 'a'.charCodeAt());
// Mark the characters
mark[f] = mark[l] = true;
// Increase indegree and outdegree count
In[l]++;
Out[f]++;
// Add an edge in graph
adj[f].push(l);
}
// If for any character indegree is not equal to
// outdegree then ordering is not possible
for(let i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
if (In[i] != Out[i])
return false;
}
return isConnected(adj, mark, s[0][0].charCodeAt() - 'a'.charCodeAt());
}
// Returns true if all vertices are strongly
// connected i.e. can be made as loop
function isConnected(adj, mark, src)
{
let visited = new Array(26);
visited.fill(false);
// Perform a dfs from src
dfs(adj, visited, src);
for(let i = 0; i < 26; i++)
{
/* I character is marked (i.e. it was first or
last character of some string) then it should
be visited in last dfs (as for looping, graph
should be strongly connected) */
if (mark[i] && !visited[i])
return false;
}
// If we reach that means graph is connected
return true;
}
// Utility method for a depth first
// search among vertices
function dfs(adj, visited, src)
{
visited[src] = true;
for(let i = 0; i < adj[src].length; i++)
if (!visited[adj[src][i]])
dfs(adj, visited, adj[src][i]);
}
let s = [ "ab", "bc", "cd", "de", "ed", "da" ];
let n = s.length;
if (possibleOrderAmongString(s, n))
document.write("Ordering is possible");
else
document.write("Ordering is not possible");
// This code is contributed by decode2207.
</script>
Ordering is possible
Complejidad temporal: O(n)
Espacio auxiliar: O(n)
Este artículo es una contribución de Utkarsh Trivedi . Si te gusta GeeksforGeeks y te gustaría contribuir, también puedes escribir un artículo usando write.geeksforgeeks.org o enviar tu artículo por correo a review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA