Dadas dos arrays de enteros, encuentre un par de valores (un valor de cada array) que pueda intercambiar para dar a las dos arrays la misma suma.
Ejemplos:
Entrada : A[] = {4, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2}, B[] = (3, 6, 3, 3)
Salida : {1, 3}
Suma de elementos en A[] = 11
Suma de elementos en B[] = 15
Para obtener la misma suma de ambas arrays, podemos
intercambiar los siguientes valores:
1 de A[] y 3 de B[]
Entrada : A[] = {5, 7, 4, 6}, B [] = {1, 2, 3, 8}
Salida : 6 2
Método 1 (Implementación ingenua) :
iterar a través de las arrays y verificar todos los pares de valores. Compara nuevas sumas o busca un par con esa diferencia.
C++
// CPP code naive solution to find a pair swapping// which makes sum of arrays sum.#include <iostream>usingnamespacestd;// Function to calculate sum of elements of arrayintgetSum(intX[],intn){intsum = 0;for(inti = 0; i < n; i++)sum += X[i];returnsum;}voidfindSwapValues(intA[],intn,intB[],intm){// Calculation of sums from both arraysintsum1 = getSum(A, n);intsum2 = getSum(B, m);// Look for val1 and val2, such that// sumA - val1 + val2 = sumB - val2 + val1intnewsum1, newsum2, val1, val2;for(inti = 0; i < n; i++) {for(intj = 0; j < m; j++) {newsum1 = sum1 - A[i] + B[j];newsum2 = sum2 - B[j] + A[i];if(newsum1 == newsum2) {val1 = A[i];val2 = B[j];}}}cout << val1 <<" "<< val2;}// Driver codeintmain(){intA[] = { 4, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2 };intn =sizeof(A) /sizeof(A[0]);intB[] = { 3, 6, 3, 3 };intm =sizeof(B) /sizeof(B[0]);// Call to functionfindSwapValues(A, n, B, m);return0;}Java
// Java program to find a pair swapping// which makes sum of arrays sumimportjava.io.*;classGFG{// Function to calculate sum of elements of arraystaticintgetSum(intX[],intn){intsum =0;for(inti =0; i < n; i++)sum += X[i];returnsum;}// Function to prints elements to be swappedstaticvoidfindSwapValues(intA[],intn,intB[],intm){// Calculation of sums from both arraysintsum1 = getSum(A, n);intsum2 = getSum(B, m);// Look for val1 and val2, such that// sumA - val1 + val2 = sumB - val2 + val1intnewsum1, newsum2, val1 =0, val2 =0;for(inti =0; i < n; i++){for(intj =0; j < m; j++){newsum1 = sum1 - A[i] + B[j];newsum2 = sum2 - B[j] + A[i];if(newsum1 == newsum2){val1 = A[i];val2 = B[j];}}}System.out.println(val1+" "+val2);}// driver programpublicstaticvoidmain (String[] args){intA[] = {4,1,2,1,1,2};intn = A.length;intB[] = {3,6,3,3};intm = B.length;// Call to functionfindSwapValues(A, n, B, m);}}// Contributed by Pramod KumarPython3
# Python code naive solution to find a pair swapping# which makes sum of lists sum.# Function to calculate sum of elements of listdefgetSum(X):sum=0foriinX:sum+=ireturnsum# Function to prints elements to be swappeddeffindSwapValues(A,B):# Calculation if sums from both listssum1=getSum(A)sum2=getSum(B)# Boolean variable used to reduce further iterations# after the pair is foundk=False# Lool for val1 and val2, such that# sumA - val1 + val2 = sumB -val2 + val1val1,val2=0,0foriinA:forjinB:newsum1=sum1-i+jnewsum2=sum2-j+iifnewsum1==newsum2:val1=ival2=j# Set to True when pair is foundk=Truebreak# If k is True, it means pair is found.# So, no further iterations.ifk==True:break(val1,val2)return# Driver codeA=[4,1,2,1,1,2]B=[3,6,3,3]# Call to functionfindSwapValues(A,B)# code contributed by sachin bishtC#
// C# program to find a pair swapping// which makes sum of arrays sumusingSystem;classGFG{// Function to calculate sum// of elements of arraystaticintgetSum(int[] X,intn){intsum = 0;for(inti = 0; i < n; i++)sum += X[i];returnsum;}// Function to prints elements// to be swappedstaticvoidfindSwapValues(int[] A,intn,int[] B,intm){// Calculation of sums from// both arraysintsum1 = getSum(A, n);intsum2 = getSum(B, m);// Look for val1 and val2, such that// sumA - val1 + val2 = sumB - val2 + val1intnewsum1, newsum2,val1 = 0, val2 = 0;for(inti = 0; i < n; i++){for(intj = 0; j < m; j++){newsum1 = sum1 - A[i] + B[j];newsum2 = sum2 - B[j] + A[i];if(newsum1 == newsum2){val1 = A[i];val2 = B[j];}}}Console.Write(val1 +" "+ val2);}// Driver CodepublicstaticvoidMain(){int[] A = { 4, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2 };intn = A.Length;int[] B = { 3, 6, 3, 3 };intm = B.Length;// Call to functionfindSwapValues(A, n, B, m);}}// This code is contributed// by ChitraNayalPHP
<?php// PHP code naive solution to find// a pair swapping which makes sum// of arrays sum.// Function to calculate sum of// elements of arrayfunctiongetSum($X,$n){$sum= 0;for($i= 0;$i<$n;$i++)$sum+=$X[$i];return$sum;}functionfindSwapValues($A,$n,$B,$m){// Calculation of sums from both arrays$sum1= getSum($A,$n);$sum2= getSum($B,$m);// Look for val1 and val2, such that// sumA - val1 + val2 = sumB - val2 + val1for($i= 0;$i<$n;$i++){for($j= 0;$j<$m;$j++){$newsum1=$sum1-$A[$i] +$B[$j];$newsum2=$sum2-$B[$j] +$A[$i];if($newsum1==$newsum2){$val1=$A[$i];$val2=$B[$j];}}}echo$val1." ".$val2;}// Driver code$A=array(4, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2 );$n= sizeof($A);$B=array(3, 6, 3, 3 );$m= sizeof($B);// Call to functionfindSwapValues($A,$n,$B,$m);// This code is contributed// by Akanksha Rai?>JavaScript
<script>// Javascript program to find a pair swapping// which makes sum of arrays sum// Function to calculate sum of elements of arrayfunctiongetSum(X,n){let sum = 0;for(let i = 0; i < n; i++)sum += X[i];returnsum;}// Function to prints elements to be swappedfunctionfindSwapValues(A,n,B,m){// Calculation of sums from both arrayslet sum1 = getSum(A, n);let sum2 = getSum(B, m);// Look for val1 and val2, such that// sumA - val1 + val2 = sumB - val2 + val1let newsum1, newsum2, val1 = 0, val2 = 0;for(let i = 0; i < n; i++){for(let j = 0; j < m; j++){newsum1 = sum1 - A[i] + B[j];newsum2 = sum2 - B[j] + A[i];if(newsum1 == newsum2){val1 = A[i];val2 = B[j];}}}document.write(val1+" "+val2);}// driver programlet A=[4, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2];let n = A.length;let B=[3, 6, 3, 3 ];let m = B.length;// Call to functionfindSwapValues(A, n, B, m);//This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155</script>Producción1 3Complejidad de tiempo :- O(n*m)
Complejidad de espacio : O(1)Método 2 -> Otra implementación Naive
We are looking for two values, a and b, such that: sumA - a + b = sumB - b + a 2a - 2b = sumA - sumB a - b = (sumA - sumB) / 2Por lo tanto, buscamos dos valores que tengan una diferencia objetivo específica: (sumA – sumB) / 2 .
C++
// CPP code for naive implementation#include <iostream>usingnamespacestd;// Function to calculate sum of elements of arrayintgetSum(intX[],intn){intsum = 0;for(inti = 0; i < n; i++)sum += X[i];returnsum;}// Function to calculate : a - b = (sumA - sumB) / 2intgetTarget(intA[],intn,intB[],intm){// Calculation of sums from both arraysintsum1 = getSum(A, n);intsum2 = getSum(B, m);// because that the target must be an integerif((sum1 - sum2) % 2 != 0)return0;return((sum1 - sum2) / 2);}voidfindSwapValues(intA[],intn,intB[],intm){inttarget = getTarget(A, n, B, m);if(target == 0)return;// Look for val1 and val2, such that// val1 - val2 = (sumA - sumB) / 2intval1, val2;for(inti = 0; i < n; i++) {for(intj = 0; j < m; j++) {if(A[i] - B[j] == target) {val1 = A[i];val2 = B[j];}}}cout << val1 <<" "<< val2;}// Driver codeintmain(){intA[] = { 4, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2 };intn =sizeof(A) /sizeof(A[0]);intB[] = { 3, 6, 3, 3 };intm =sizeof(B) /sizeof(B[0]);// Call to functionfindSwapValues(A, n, B, m);return0;}Java
// Java program to find a pair swapping// which makes sum of arrays sumimportjava.io.*;classGFG{// Function to calculate sum of elements of arraystaticintgetSum(intX[],intn){intsum =0;for(inti =0; i < n; i++)sum += X[i];returnsum;}// Function to calculate : a - b = (sumA - sumB) / 2staticintgetTarget(intA[],intn,intB[],intm){// Calculation of sums from both arraysintsum1 = getSum(A, n);intsum2 = getSum(B, m);// because that the target must be an integerif((sum1 - sum2) %2!=0)return0;return((sum1 - sum2) /2);}// Function to prints elements to be swappedstaticvoidfindSwapValues(intA[],intn,intB[],intm){inttarget = getTarget(A, n, B, m);if(target ==0)return;// Look for val1 and val2, such that// val1 - val2 = (sumA - sumB) / 2intval1 =0, val2 =0;for(inti =0; i < n; i++){for(intj =0; j < m; j++){if(A[i] - B[j] == target){val1 = A[i];val2 = B[j];}}}System.out.println(val1+" "+val2);}// driver programpublicstaticvoidmain (String[] args){intA[] = {4,1,2,1,1,2};intn = A.length;intB[] = {3,6,3,3};intm = B.length;// Call to functionfindSwapValues(A, n, B, m);}}// Contributed by Pramod KumarPython3
# Python Code for naive implementation# Function to calculate sum of elements of listdefgetSum(X):sum=0foriinX:sum+=ireturnsum# Function to calculate : a-b = (sumA - sumB) / 2defgetTarget(A,B):#Calculations of sums from both listssum1=getSum(A)sum2=getSum(B)# Because the target must be an integerif( (sum1-sum2)%2!=0):return0return(sum1-sum2)//2deffindSwapValues(A,B):target=getTarget(A,B)iftarget==0:return# Boolean variable used to reduce further iterations# after the pair is foundflag=False# Look for val1 and val2, such that# val1 - val2 = (sumA -sumB) /2val1,val2=0,0foriinA:forjinB:ifi-j==target:val1=ival2=j# Set to True when pair is foundflag=Truebreakifflag==True:break(val1,val2)return# Driver codeA=[4,1,2,1,1,2]B=[3,6,3,3]# Call to functionfindSwapValues(A,B)# code contributed by sachin bishtC#
// C# program to find a pair swapping// which makes sum of arrays sumusingSystem;classGFG{// Function to calculate sum of elements of arraystaticintgetSum(int[]X,intn){intsum = 0;for(inti = 0; i < n; i++)sum += X[i];returnsum;}// Function to calculate : a - b = (sumA - sumB) / 2staticintgetTarget(int[]A,intn,int[]B,intm){// Calculation of sums from both arraysintsum1 = getSum(A, n);intsum2 = getSum(B, m);// because that the target must be an integerif((sum1 - sum2) % 2 != 0)return0;return((sum1 - sum2) / 2);}// Function to prints elements to be swappedstaticvoidfindSwapValues(int[]A,intn,int[]B,intm){inttarget = getTarget(A, n, B, m);if(target == 0)return;// Look for val1 and val2, such that// val1 - val2 = (sumA - sumB) / 2intval1 = 0, val2 = 0;for(inti = 0; i < n; i++){for(intj = 0; j < m; j++){if(A[i] - B[j] == target){val1 = A[i];val2 = B[j];}}}Console.Write(val1+" "+val2);}// Driver codepublicstaticvoidMain(){int[]A = { 4, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2 };intn = A.Length;int[]B = { 3, 6, 3, 3 };intm = B.Length;// Call to functionfindSwapValues(A, n, B, m);}}/*This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar*/PHP
<?php// PHP code for naive implementation// Function to calculate sum// of elements of arrayfunctiongetSum($X,$n){$sum= 0;for($i= 0;$i<$n;$i++)$sum+=$X[$i];return$sum;}// Function to calculate :// a - b = (sumA - sumB) / 2functiongetTarget($A,$n,$B,$m){// Calculation of sums from// both arrays$sum1= getSum($A,$n);$sum2= getSum($B,$m);// because that the target// must be an integerif(($sum1-$sum2) % 2 != 0)return0;return(($sum1-$sum2) / 2);}functionfindSwapValues($A,$n,$B,$m){$target= getTarget($A,$n,$B,$m);if($target== 0)return;// Look for val1 and val2, such that// val1 - val2 = (sumA - sumB) / 2for($i= 0;$i<$n;$i++){for($j= 0;$j<$m;$j++){if($A[$i] -$B[$j] ==$target){$val1=$A[$i];$val2=$B[$j];}}}echo$val1." ".$val2;}// Driver code$A=array(4, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2);$n= sizeof($A);$B=array(3, 6, 3, 3);$m= sizeof($B);// Call to functionfindSwapValues($A,$n,$B,$m);// This code is contributed// by Akanksha Rai?>JavaScript
<script>// Javascript program to find a pair swapping// which makes sum of arrays sum// Function to calculate sum of elements of arrayfunctiongetSum(X,n){let sum = 0;for(let i = 0; i < n; i++)sum += X[i];returnsum;}// Function to calculate : a - b = (sumA - sumB) / 2functiongetTarget(A,n,B,m){// Calculation of sums from both arrayslet sum1 = getSum(A, n);let sum2 = getSum(B, m);// because that the target must be an integerif((sum1 - sum2) % 2 != 0)return0;return((sum1 - sum2) / 2);}// Function to prints elements to be swappedfunctionfindSwapValues(A,n,B,m){let target = getTarget(A, n, B, m);if(target == 0)return;// Look for val1 and val2, such that// val1 - val2 = (sumA - sumB) / 2let val1 = 0, val2 = 0;for(let i = 0; i < n; i++){for(let j = 0; j < m; j++){if(A[i] - B[j] == target){val1 = A[i];val2 = B[j];}}}document.write(val1+" "+val2+"<br>");}// driver programlet A=[4, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2];let n = A.length;let B=[3, 6, 3, 3 ];let m = B.length;// Call to functionfindSwapValues(A, n, B, m);// This code is contributed by ab2127</script>Producción1 3Complejidad de tiempo :- O(n*m)
Complejidad de espacio :- O(1)Método 3 -> Solución optimizada: –
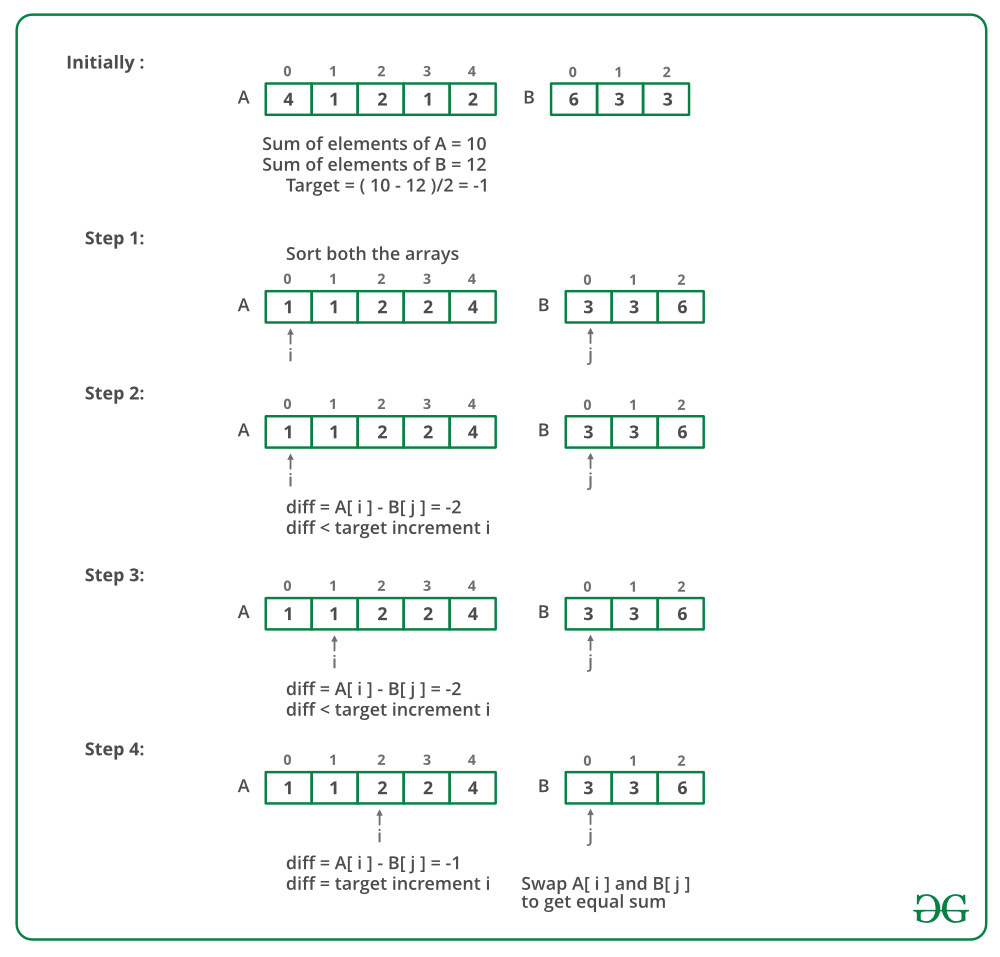
- Ordenar las arrays.
- Atraviese ambas arrays simultáneamente y haga lo siguiente para cada par.
- Si la diferencia es demasiado pequeña, hágala más grande moviendo ‘a’ a un valor más grande.
- Si es demasiado grande, hazlo más pequeño moviendo b a un valor mayor.
- Si es correcto, devuelva este par.
La imagen de abajo es una ejecución en seco del enfoque anterior:
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// CPP code for optimized implementation#include <bits/stdc++.h>usingnamespacestd;// Returns sum of elements in X[]intgetSum(intX[],intn){intsum = 0;for(inti = 0; i < n; i++)sum += X[i];returnsum;}// Finds value of// a - b = (sumA - sumB) / 2intgetTarget(intA[],intn,intB[],intm){// Calculation of sums from both arraysintsum1 = getSum(A, n);intsum2 = getSum(B, m);// because that the target must be an integerif((sum1 - sum2) % 2 != 0)return0;return((sum1 - sum2) / 2);}// Prints elements to be swappedvoidfindSwapValues(intA[],intn,intB[],intm){// Call for sorting the arrayssort(A, A + n);sort(B, B + m);// Note that target can be negativeinttarget = getTarget(A, n, B, m);// target 0 means, answer is not possibleif(target == 0)return;inti = 0, j = 0;while(i < n && j < m) {intdiff = A[i] - B[j];if(diff == target) {cout << A[i] <<" "<< B[j];return;}// Look for a greater value in A[]elseif(diff < target)i++;// Look for a greater value in B[]elsej++;}}// Driver codeintmain(){intA[] = { 4, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2 };intn =sizeof(A) /sizeof(A[0]);intB[] = { 1, 6, 3, 3 };intm =sizeof(B) /sizeof(B[0]);findSwapValues(A, n, B, m);return0;}Java
// Java code for optimized implementationimportjava.io.*;importjava.util.*;classGFG{// Function to calculate sum of elements of arraystaticintgetSum(intX[],intn){intsum =0;for(inti =0; i < n; i++)sum += X[i];returnsum;}// Function to calculate : a - b = (sumA - sumB) / 2staticintgetTarget(intA[],intn,intB[],intm){// Calculation of sums from both arraysintsum1 = getSum(A, n);intsum2 = getSum(B, m);// because that the target must be an integerif((sum1 - sum2) %2!=0)return0;return((sum1 - sum2) /2);}// Function to prints elements to be swappedstaticvoidfindSwapValues(intA[],intn,intB[],intm){// Call for sorting the arraysArrays.sort(A);Arrays.sort(B);// Note that target can be negativeinttarget = getTarget(A, n, B, m);// target 0 means, answer is not possibleif(target ==0)return;inti =0, j =0;while(i < n && j < m){intdiff = A[i] - B[j];if(diff == target){System.out.println(A[i]+" "+B[i]);return;}// Look for a greater value in A[]elseif(diff < target)i++;// Look for a greater value in B[]elsej++;}}// driver programpublicstaticvoidmain (String[] args){intA[] = {4,1,2,1,1,2};intn = A.length;intB[] = {3,6,3,3};intm = B.length;// Call to functionfindSwapValues(A, n, B, m);}}// Contributed by Pramod KumarPython3
# Python code for optimized implementation#Returns sum of elements in listdefgetSum(X):sum=0foriinX:sum+=ireturnsum# Finds value of# a - b = (sumA - sumB) / 2defgetTarget(A,B):# Calculations of sumd from both listssum1=getSum(A)sum2=getSum(B)# Because that target must be an integerif( (sum1-sum2)%2!=0):return0return(sum1-sum2)//2# Prints elements to be swappeddeffindSwapValues(A,B):# Call for sorting the listsA.sort()B.sort()#Note that target can be negativetarget=getTarget(A,B)# target 0 means, answer is not possibleif(target==0):returni,j=0,0while(i<len(A)andj<len(B)):diff=A[i]-B[j]ifdiff==target:(A[i],B[j])return# Look for a greater value in list Aelifdiff <target:i+=1# Look for a greater value in list Belse:j+=1A=[4,1,2,1,1,2]B=[3,6,3,3]findSwapValues(A,B)#code contributed by sachin bishtC#
// C# code for optimized implementationusingSystem;classGFG{// Function to calculate sum of elements of arraystaticintgetSum(int[]X,intn){intsum = 0;for(inti = 0; i < n; i++)sum += X[i];returnsum;}// Function to calculate : a - b = (sumA - sumB) / 2staticintgetTarget(int[]A,intn,int[]B,intm){// Calculation of sums from both arraysintsum1 = getSum(A, n);intsum2 = getSum(B, m);// because that the target must be an integerif((sum1 - sum2) % 2 != 0)return0;return((sum1 - sum2) / 2);}// Function to prints elements to be swappedstaticvoidfindSwapValues(int[]A,intn,int[]B,intm){// Call for sorting the arraysArray.Sort(A);Array.Sort(B);// Note that target can be negativeinttarget = getTarget(A, n, B, m);// target 0 means, answer is not possibleif(target == 0)return;inti = 0, j = 0;while(i < n && j < m){intdiff = A[i] - B[j];if(diff == target){Console.WriteLine(A[i]+" "+B[i]);return;}// Look for a greater value in A[]elseif(diff < target)i++;// Look for a greater value in B[]elsej++;}}// Driver codepublicstaticvoidMain (String[] args){int[]A = { 4, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2 };intn = A.Length;int[]B = { 3, 6, 3, 3 };intm = B.Length;// Call to functionfindSwapValues(A, n, B, m);}}// This code has been contributed by 29AjayKumarJavaScript
<script>// Javascript code for optimized implementation// Function to calculate sum of elements of arrayfunctiongetSum(X,n){let sum = 0;for(let i = 0; i < n; i++)sum += X[i];returnsum;}// Function to calculate : a - b = (sumA - sumB) / 2functiongetTarget(A,n,B,m){// Calculation of sums from both arrayslet sum1 = getSum(A, n);let sum2 = getSum(B, m);// because that the target must be an integerif((sum1 - sum2) % 2 != 0)return0;return((sum1 - sum2) / 2);}// Function to prints elements to be swappedfunctionfindSwapValues(A,n,B,m){// Call for sorting the arraysA.sort(function(a,b){returna-b;});B.sort(function(a,b){returna-b;});// Note that target can be negativelet target = getTarget(A, n, B, m);// target 0 means, answer is not possibleif(target == 0)return;let i = 0, j = 0;while(i < n && j < m){let diff = A[i] - B[j];if(diff == target){document.write(A[i]+" "+B[j]);return;}// Look for a greater value in A[]elseif(diff < target)i++;// Look for a greater value in B[]elsej++;}}// driver programlet A=[4, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2 ];let n = A.length;let B=[3, 6, 3, 3 ];let m = B.length;// Call to functionfindSwapValues(A, n, B, m);// This code is contributed by unknown2108</script>Producción2 3Complejidad de tiempo: –
Si las arrays están ordenadas: O (n + m)
Si las arrays no están ordenadas: O (nlog (n) + mlog (m))Complejidad espacial: O(1)
Método 4 (Hashing)
Podemos resolver este problema en O(m+n) tiempo y O(m) espacio auxiliar. A continuación se muestran los pasos algorítmicos.
// assume array1 is small i.e. (m < n) // where m is array1.length and n is array2.length 1. Find sum1(sum of small array elements) ans sum2 (sum of larger array elements). // time O(m+n) 2. Make a hashset for small array(here array1). 3. Calculate diff as (sum1-sum2)/2. 4. Run a loop for array2 for (int i equal to 0 to n-1) if (hashset contains (array2[i]+diff)) print array2[i]+diff and array2[i] set flag and break; 5. If flag is unset then there is no such kind of pair.Gracias a nicky khan por sugerir el método 4.
Este artículo es una contribución de Sakshi Tiwari . Si le gusta GeeksforGeeks (¡sabemos que le gusta!) y le gustaría contribuir, también puede escribir un artículo usando contribuya.geeksforgeeks.org o envíe su artículo por correo a contribuya@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Otro enfoque:
También podemos resolver este problema en tiempo lineal usando hashing . Supongamos que la suma de los elementos del primer arreglo a[] es s1, y del segundo arreglo b[] es s2. Suponga también que un par a intercambiar es (p, q), donde p pertenece a a[] y q pertenece a b[]. Por lo tanto, tenemos la ecuación s1 – p + q = s2 – q + p, es decir, 2q = s2 – s1 + 2p . Dado que tanto 2p como 2q son números enteros pares, la diferencia s2 – s1 también debe ser un número entero par . Entonces, dado cualquier p, nuestro objetivo es encontrar un q apropiado que satisfaga las condiciones anteriores.
A continuación se muestra una implementación de dicho enfoque:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>usingnamespacestd;voidfindSwapValues(inta[],intm,intb[],intn);intmain(){inta[] = { 4, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2 }, b[] = { 1, 6, 3, 3 };intm, n;m =sizeof(a) /sizeof(int),n =sizeof(b) /sizeof(int);findSwapValues(a, m, b, n);return0;}voidfindSwapValues(inta[],intm,intb[],intn){unordered_set<int> x,y;/* Unordered sets (and unordered maps) areimplemented internally using hash tables; theysupport dictionary operations (i.e. search,insert, delete) in O(1) time on an average. */unordered_set<int>::iterator p, q;ints1, s2;inti;s1 = 0;for(i = 0; i < m;i++)/* Determining sum s1 of the elements of arraya[], and simultaneously inserting the arrayelements in the unordered set. */s1 += a[i], x.insert(a[i]);s2 = 0;for(i = 0; i < n; i++)s2 += b[i], y.insert(b[i]);if((s1 - s2) % 2)/* Checking if difference between thetwo array sumsis even or not. */{printf("No such values exist.\n");return;}for(p = x.begin(); p != x.end(); p++) {q = y.find(((s2 - s1) + 2 * *p)/ 2);// Finding q for a given p in O(1) time.if(q != y.end()) {printf("%d %d\n", *p, *q);return;}}printf("No such values exist.\n");}Producción2 3La complejidad temporal del código anterior es O(m + n) , donde m y n representan respectivamente los tamaños de las dos arrays de entrada, y la complejidad espacial O(s + t) , donde s y t representan respectivamente el número de elementos distintos presentes en las dos arrays de entrada.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA