FIFO es la abreviatura de primero en entrar, primero en salir . Es un método para manejar estructuras de datos donde el primer elemento se procesa primero y el elemento más nuevo se procesa al final.
Ejemplo de la vida real:
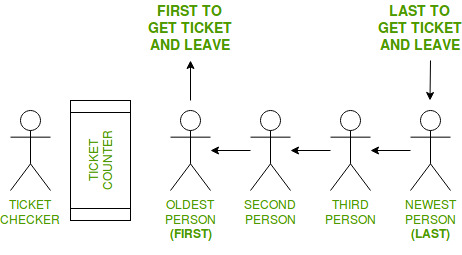
En este ejemplo, se deben considerar las siguientes cosas:
- Hay un mostrador de boletos donde la gente entra, toma boletos y se va.
- Las personas ingresan a una fila (cola) para llegar al Ticket Counter de manera organizada.
- La persona que ingrese primero a la fila, obtendrá el boleto primero y saldrá de la fila.
- La siguiente persona que ingrese a la fila obtendrá el boleto después de la persona que está frente a él.
- De esta forma, la persona que entre en último lugar en la cola tendrá las últimas entradas.
- Por lo tanto, la primera persona en ingresar a la fila obtiene el boleto primero y la última persona en ingresar a la fila obtiene el boleto en último lugar.
Esto se conoce como enfoque de primero en entrar, primero en salir o FIFO.
Dónde se usa FIFO:
- Estructuras de
datos Ciertas estructuras de datos como Queue y otras variantes de Queue utilizan el enfoque FIFO para procesar datos.
- Programación de
disco Los controladores de disco pueden usar el FIFO como un algoritmo de programación de disco para determinar el orden en el que atender las requests de E/S de disco.
- Comunicaciones y redes
Los puentes, conmutadores y enrutadores de las redes de comunicaciones que se utilizan en las redes informáticas utilizan FIFO para contener los paquetes de datos en ruta hacia su próximo destino.
Ejemplos de programa para FIFO
Programa 1: Cola
C++
// C++ program to demonstrate
// working of FIFO
// using Queue interface in C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// print the elements of queue
void print_queue(queue<int> q)
{
while (!q.empty())
{
cout << q.front() << " ";
q.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
queue<int> q ;
// Adds elements {0, 1, 2, 3, 4} to queue
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
q.push(i);
// Display contents of the queue.
cout << "Elements of queue-";
print_queue(q);
// To remove the head of queue.
// In this the oldest element '0' will be removed
int removedele = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << "removed element-" << removedele << endl;
print_queue(q);
// To view the head of queue
int head = q.front();
cout << "head of queue-" << head << endl;
// Rest all methods of collection interface,
// Like size and contains can be used with this
// implementation.
int size = q.size();
cout << "Size of queue-" << size;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu
Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// working of FIFO
// using Queue interface in Java
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class QueueExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
// Adds elements {0, 1, 2, 3, 4} to queue
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
q.add(i);
// Display contents of the queue.
System.out.println("Elements of queue-" + q);
// To remove the head of queue.
// In this the oldest element '0' will be removed
int removedele = q.remove();
System.out.println("removed element-" + removedele);
System.out.println(q);
// To view the head of queue
int head = q.peek();
System.out.println("head of queue-" + head);
// Rest all methods of collection interface,
// Like size and contains can be used with this
// implementation.
int size = q.size();
System.out.println("Size of queue-" + size);
}
}
Python3
# Python program to demonstrate
# working of FIFO
# using Queue interface in Java
q = []
# Adds elements {0, 1, 2, 3, 4} to queue
for i in range(5):
q.append(i)
# Display contents of the queue.
print("Elements of queue-" , q)
# To remove the head of queue.
# In this the oldest element '0' will be removed
removedele = q.pop(0)
print("removed element-" , removedele)
print(q)
# To view the head of queue
head = q[0]
print("head of queue-" , head)
# Rest all methods of collection interface,
# Like size and contains can be used with this
# implementation.
size = len(q)
print("Size of queue-" , size)
# This code is contributed by patel2127.
C#
// C# program to demonstrate
// working of FIFO
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class QueueExample
{
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Queue<int> q = new Queue<int>();
// Adds elements {0, 1, 2, 3, 4} to queue
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
q.Enqueue(i);
// Display contents of the queue.
Console.Write("Elements of queue-");
foreach(int s in q)
Console.Write(s + " ");
// To remove the head of queue.
// In this the oldest element '0' will be removed
int removedele = q.Dequeue();
Console.Write("\nremoved element-" + removedele + "\n");
foreach(int s in q)
Console.Write(s + " ");
// To view the head of queue
int head = q.Peek();
Console.Write("\nhead of queue-" + head);
// Rest all methods of collection interface,
// Like size and contains can be used with this
// implementation.
int size = q.Count;
Console.WriteLine("\nSize of queue-" + size);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program to demonstrate
// working of FIFO
// using Queue interface in Java
let q = [];
// Adds elements {0, 1, 2, 3, 4} to queue
for (let i = 0; i < 5; i++)
q.push(i);
// Display contents of the queue.
document.write("Elements of queue-[" + q.join(", ")+"]<br>");
// To remove the head of queue.
// In this the oldest element '0' will be removed
let removedele = q.shift();
document.write("removed element-" + removedele+"<br>");
document.write("["+q.join(", ")+"]<br>");
// To view the head of queue
let head = q[0];
document.write("head of queue-" + head+"<br>");
// Rest all methods of collection interface,
// Like size and contains can be used with this
// implementation.
let size = q.length;
document.write("Size of queue-" + size+"<br>");
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
</script>
Producción:
Elements of queue-[0, 1, 2, 3, 4] removed element-0 [1, 2, 3, 4] head of queue-1 Size of queue-4
Complejidad temporal: O(N)
Complejidad espacial: O(N)