Requisitos previos: enfoque FIFO (primero en entrar, primero en salir) en programación , enfoque FIFO vs LIFO en programación
LIFO es una abreviatura de último en entrar, primero en salir . Es un método para manejar estructuras de datos donde el primer elemento se procesa en último lugar y el último elemento se procesa en primer lugar.
Ejemplo de la vida real:
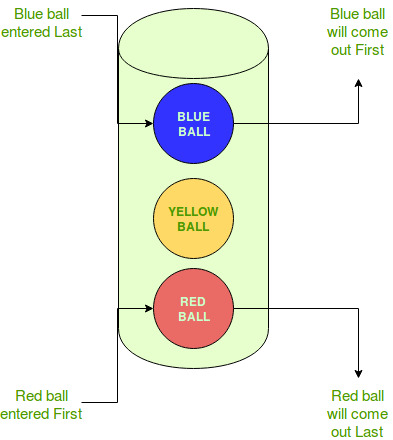
En este ejemplo, se deben considerar las siguientes cosas:
- Hay un balde que contiene pelotas.
- Se introducen diferentes tipos de bolas en el cubo.
- La bola que entre en último lugar en la cubeta se sacará primero.
- La bola que entre en el balde la penúltima será sacada después de la bola de arriba (la más nueva).
- De esta forma, la pelota que entre primero en la cubeta saldrá de la cubeta en último lugar.
- Por lo tanto, la última bola (azul) que ingresa al balde se retira primero y la primera bola (roja) que ingresa al balde se retira en último lugar.
Esto se conoce como enfoque de último en entrar, primero en salir o LIFO.
Dónde se usa LIFO:
- Estructuras de datos:
ciertas estructuras de datos como Stacks y otras variantes de Stacks utilizan el enfoque LIFO para procesar datos.
- Extracción de la información más reciente: a
veces, las computadoras usan LIFO cuando los datos se extraen de una array o un búfer de datos. Cuando se requiere ingresar la información más reciente, se utiliza el enfoque LIFO.
Ejemplos de programas para LIFO:
uso de la estructura de datos Stack:
C++
// C++ program to demonstrate
// working of LIFO
// using stack in C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Pushing element on the top of the stack
stack<int> stack_push(stack<int> stack)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
stack.push(i);
}
return stack;
}
// Popping element from the top of the stack
stack<int> stack_pop(stack<int> stack)
{
cout << "Pop :";
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
int y = (int)stack.top();
stack.pop();
cout << (y) << endl;
}
return stack;
}
// Displaying element on the top of the stack
void stack_peek(stack<int> stack)
{
int element = (int)stack.top();
cout << "Element on stack top : " << element << endl;
}
// Searching element in the stack
void stack_search(stack<int> stack, int element)
{
int pos = -1,co = 0;
while(stack.size() > 0)
{
co++;
if(stack.top() == element)
{
pos = co;
break;
}
stack.pop();
}
if (pos == -1)
cout << "Element not found" << endl;
else
cout << "Element is found at position " << pos << endl;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
stack<int> stack ;
stack = stack_push(stack);
stack = stack_pop(stack);
stack = stack_push(stack);
stack_peek(stack);
stack_search(stack, 2);
stack_search(stack, 6);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu
Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// working of LIFO
// using Stack in Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Pushing element on the top of the stack
static void stack_push(Stack<Integer> stack)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
stack.push(i);
}
}
// Popping element from the top of the stack
static void stack_pop(Stack<Integer> stack)
{
System.out.println("Pop :");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Integer y = (Integer)stack.pop();
System.out.println(y);
}
}
// Displaying element on the top of the stack
static void stack_peek(Stack<Integer> stack)
{
Integer element = (Integer)stack.peek();
System.out.println("Element on stack top : " + element);
}
// Searching element in the stack
static void stack_search(Stack<Integer> stack, int element)
{
Integer pos = (Integer)stack.search(element);
if (pos == -1)
System.out.println("Element not found");
else
System.out.println("Element is found at position " + pos);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
stack_push(stack);
stack_pop(stack);
stack_push(stack);
stack_peek(stack);
stack_search(stack, 2);
stack_search(stack, 6);
}
}
Python3
# Python3 program to demonstrate working of LIFO
# Pushing element on the top of the stack
def stack_push(stack):
for i in range(5):
stack.append(i)
return stack
# Popping element from the top of the stack
def stack_pop(stack):
print("Pop :")
for i in range(5):
y = stack[-1]
stack.pop()
print(y)
return stack
# Displaying element on the top of the stack
def stack_peek(stack):
element = stack[-1]
print("Element on stack top :", element)
# Searching element in the stack
def stack_search(stack, element):
pos = -1
co = 0
while(len(stack) > 0):
co+=1
if(stack[-1] == element):
pos = co
break
stack.pop()
if (pos == -1):
print( "Element not found")
else:
print("Element is found at position", pos)
stack = []
stack_push(stack)
stack_pop(stack)
stack_push(stack)
stack_peek(stack)
stack_search(stack, 2)
stack_search(stack, 6)
# This code is contributed by rameshtravel07.
C#
// C# program to demonstrate
// working of LIFO
// using Stack in C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// Pushing element on the top of the stack
static void stack_push(Stack<int> stack)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
stack.Push(i);
}
}
// Popping element from the top of the stack
static void stack_pop(Stack<int> stack)
{
Console.WriteLine("Pop :");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
int y = (int)stack.Pop();
Console.WriteLine(y);
}
}
// Displaying element on the top of the stack
static void stack_peek(Stack<int> stack)
{
int element = (int)stack.Peek();
Console.WriteLine("Element on stack top : " + element);
}
// Searching element in the stack
static void stack_search(Stack<int> stack, int element)
{
bool pos = stack.Contains(element);
if (pos == false)
Console.WriteLine("Element not found");
else
Console.WriteLine("Element is found at position " + pos);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Stack<int> stack = new Stack<int>();
stack_push(stack);
stack_pop(stack);
stack_push(stack);
stack_peek(stack);
stack_search(stack, 2);
stack_search(stack, 6);
}
}
// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program to demonstrate
// working of LIFO
// Pushing element on the top of the stack
function stack_push(stack)
{
for (var i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
stack.push(i);
}
return stack;
}
// Popping element from the top of the stack
function stack_pop(stack)
{
document.write( "Pop :<br>");
for (var i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
var y = parseInt(stack[stack.length-1]);
stack.pop();
document.write( y + "<br>");
}
return stack;
}
// Displaying element on the top of the stack
function stack_peek(stack)
{
var element = parseInt(stack[stack.length-1]);
document.write( "Element on stack top : " + element +
"<br>");
}
// Searching element in the stack
function stack_search( stack, element)
{
var pos = -1,co = 0;
while(stack.length > 0)
{
co++;
if(stack[stack.length-1] == element)
{
pos = co;
break;
}
stack.pop();
}
if (pos == -1)
document.write( "Element not found" + "<br>");
else
document.write("Element is found at position "
+ pos + "<br>");
}
stack=[] ;
stack = stack_push(stack);
stack = stack_pop(stack);
stack = stack_push(stack);
stack_peek(stack);
stack_search(stack, 2);
stack_search(stack, 6);
// This code is contributed by SoumikMondal
</script>
Producción:
Pop: 4 3 2 1 0 Element on stack top : 4 Element is found at position 3 Element not found
Complejidad de tiempo: O(n)
Espacio Auxiliar: O(n)