Hay dos listas enlazadas individualmente en un sistema. Por algún error de programación, el Node final de una de las listas vinculadas se vinculó a la segunda lista, formando una lista en forma de Y invertida. Escriba un programa para obtener el punto donde se fusionan dos listas enlazadas.
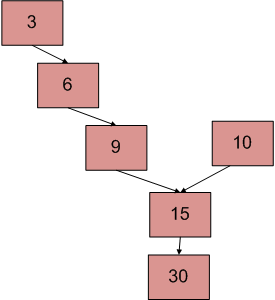
El diagrama anterior muestra un ejemplo con dos listas enlazadas que tienen 15 como punto de intersección.
Enfoque: Se puede observar que el número de Nodes al atravesar la primera lista enlazada y luego desde la cabeza de la segunda lista enlazada hasta el punto de intersección es igual al número de Nodes involucrados en atravesar la segunda lista enlazada y luego desde la cabeza de la primera lista hasta el punto de intersección. Teniendo en cuenta el ejemplo anterior, comience a recorrer las dos listas vinculadas con dos punteros curr1 y curr2 apuntando a los encabezados de las listas vinculadas dadas, respectivamente.
- Si curr1 != null , actualícelo para que apunte al siguiente Node; de lo contrario, se actualiza para que apunte al primer Node de la segunda lista.
- Si curr2 != null , actualícelo para que apunte al siguiente Node; de lo contrario, se actualizará para que apunte al primer Node de la primera lista.
- Repita los pasos anteriores mientras curr1 no sea igual a curr2 .
Los dos punteros curr1 y curr2 apuntarán ahora al mismo Node, es decir, al punto de fusión.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Link list node
struct Node {
int data;
Node* next;
};
// Function to get the intersection point
// of the given linked lists
int getIntersectionNode(Node* head1, Node* head2)
{
Node *curr1 = head1, *curr2 = head2;
// While both the pointers are not equal
while (curr1 != curr2) {
// If the first pointer is null then
// set it to point to the head of
// the second linked list
if (curr1 == NULL) {
curr1 = head2;
}
// Else point it to the next node
else {
curr1 = curr1->next;
}
// If the second pointer is null then
// set it to point to the head of
// the first linked list
if (curr2 == NULL) {
curr2 = head1;
}
// Else point it to the next node
else {
curr2 = curr2->next;
}
}
// Return the intersection node
return curr1->data;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
/*
Create two linked lists
1st Linked list is 3->6->9->15->30
2nd Linked list is 10->15->30
15 is the intersection point
*/
Node* newNode;
Node* head1 = new Node();
head1->data = 10;
Node* head2 = new Node();
head2->data = 3;
newNode = new Node();
newNode->data = 6;
head2->next = newNode;
newNode = new Node();
newNode->data = 9;
head2->next->next = newNode;
newNode = new Node();
newNode->data = 15;
head1->next = newNode;
head2->next->next->next = newNode;
newNode = new Node();
newNode->data = 30;
head1->next->next = newNode;
head1->next->next->next = NULL;
// Print the intersection node
cout << getIntersectionNode(head1, head2);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation of the approach
class GFG
{
// Link list node
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
};
// Function to get the intersection point
// of the given linked lists
static int getIntersectionNode(Node head1, Node head2)
{
Node curr1 = head1, curr2 = head2;
// While both the pointers are not equal
while (curr1 != curr2)
{
// If the first pointer is null then
// set it to point to the head of
// the second linked list
if (curr1 == null)
{
curr1 = head2;
}
// Else point it to the next node
else
{
curr1 = curr1.next;
}
// If the second pointer is null then
// set it to point to the head of
// the first linked list
if (curr2 == null)
{
curr2 = head1;
}
// Else point it to the next node
else
{
curr2 = curr2.next;
}
}
// Return the intersection node
return curr1.data;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/*
Create two linked lists
1st Linked list is 3.6.9.15.30
2nd Linked list is 10.15.30
15 is the intersection point
*/
Node newNode;
Node head1 = new Node();
head1.data = 10;
Node head2 = new Node();
head2.data = 3;
newNode = new Node();
newNode.data = 6;
head2.next = newNode;
newNode = new Node();
newNode.data = 9;
head2.next.next = newNode;
newNode = new Node();
newNode.data = 15;
head1.next = newNode;
head2.next.next.next = newNode;
newNode = new Node();
newNode.data = 30;
head1.next.next = newNode;
head1.next.next.next = null;
// Print the intersection node
System.out.print(getIntersectionNode(head1, head2));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach # Link list node class Node: def __init__(self): self.data = 0 self.next = None # Function to get the intersection point # of the given linked lists def getIntersectionNode( head1, head2): curr1 = head1 curr2 = head2 # While both the pointers are not equal while (curr1 != curr2): # If the first pointer is None then # set it to point to the head of # the second linked list if (curr1 == None) : curr1 = head2 # Else point it to the next node else: curr1 = curr1.next # If the second pointer is None then # set it to point to the head of # the first linked list if (curr2 == None): curr2 = head1 # Else point it to the next node else: curr2 = curr2.next # Return the intersection node return curr1.data # Driver code # Create two linked lists # 1st Linked list is 3.6.9.15.30 # 2nd Linked list is 10.15.30 # 15 is the intersection point newNode = None head1 = Node() head1.data = 10 head2 = Node() head2.data = 3 newNode = Node() newNode.data = 6 head2.next = newNode newNode = Node() newNode.data = 9 head2.next.next = newNode newNode = Node() newNode.data = 15 head1.next = newNode head2.next.next.next = newNode newNode = Node() newNode.data = 30 head1.next.next = newNode head1.next.next.next = None # Print the intersection node print( getIntersectionNode(head1, head2)) # This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu
C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// Link list node
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
};
// Function to get the intersection point
// of the given linked lists
static int getIntersectionNode(Node head1,
Node head2)
{
Node curr1 = head1, curr2 = head2;
// While both the pointers are not equal
while (curr1 != curr2)
{
// If the first pointer is null then
// set it to point to the head of
// the second linked list
if (curr1 == null)
{
curr1 = head2;
}
// Else point it to the next node
else
{
curr1 = curr1.next;
}
// If the second pointer is null then
// set it to point to the head of
// the first linked list
if (curr2 == null)
{
curr2 = head1;
}
// Else point it to the next node
else
{
curr2 = curr2.next;
}
}
// Return the intersection node
return curr1.data;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
/*
Create two linked lists
1st Linked list is 3.6.9.15.30
2nd Linked list is 10.15.30
15 is the intersection point
*/
Node newNode;
Node head1 = new Node();
head1.data = 10;
Node head2 = new Node();
head2.data = 3;
newNode = new Node();
newNode.data = 6;
head2.next = newNode;
newNode = new Node();
newNode.data = 9;
head2.next.next = newNode;
newNode = new Node();
newNode.data = 15;
head1.next = newNode;
head2.next.next.next = newNode;
newNode = new Node();
newNode.data = 30;
head1.next.next = newNode;
head1.next.next.next = null;
// Print the intersection node
Console.Write(getIntersectionNode(head1, head2));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript implementation of the approach
// Link list node
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
// Function to get the intersection point
// of the given linked lists
function getIntersectionNode(head1, head2)
{
var curr1 = head1, curr2 = head2;
// While both the pointers are not equal
while (curr1 != curr2)
{
// If the first pointer is null then
// set it to point to the head of
// the second linked list
if (curr1 == null)
{
curr1 = head2;
}
// Else point it to the next node
else
{
curr1 = curr1.next;
}
// If the second pointer is null then
// set it to point to the head of
// the first linked list
if (curr2 == null)
{
curr2 = head1;
}
// Else point it to the next node
else
{
curr2 = curr2.next;
}
}
// Return the intersection node
return curr1.data;
}
// Driver Code
/*
Create two linked lists
1st Linked list is 3.6.9.15.30
2nd Linked list is 10.15.30
15 is the intersection point
*/
var newNode;
var head1 = new Node();
head1.data = 10;
var head2 = new Node();
head2.data = 3;
newNode = new Node();
newNode.data = 6;
head2.next = newNode;
newNode = new Node();
newNode.data = 9;
head2.next.next = newNode;
newNode = new Node();
newNode.data = 15;
head1.next = newNode;
head2.next.next.next = newNode;
newNode = new Node();
newNode.data = 30;
head1.next.next = newNode;
head1.next.next.next = null;
// Print the intersection node
document.write(getIntersectionNode(head1, head2));
// This code is contributed by jana_sayantan.
</script>
15
Complejidad temporal : O(N + M).
Espacio Auxiliar : O(1).
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por codingbuff y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA