Para eliminar un árbol, debemos recorrer todos los Nodes del árbol y eliminarlos uno por uno. Entonces, ¿qué recorrido deberíamos usar: transversal en orden, transversal en preorden o transversal en postorden? La respuesta es simple. Deberíamos usar la transversal de orden posterior porque antes de eliminar el Node principal, primero debemos eliminar sus Nodes secundarios.
Podemos eliminar el árbol con otros recorridos también con complejidad de espacio adicional, pero ¿por qué deberíamos optar por los otros recorridos si tenemos disponible el postorder que hace el trabajo sin almacenar nada en la misma complejidad de tiempo?
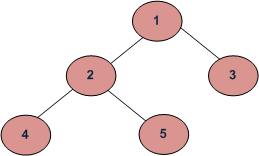
Para el siguiente árbol, los Nodes se eliminan en el orden: 4, 5, 2, 3, 1.
C++
// C++ program to Delete a Tree
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data,
pointer to left child and
a pointer to right child */
class node
{
public:
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
/* Constructor that allocates
a new node with the given data
and NULL left and right pointers. */
node(int data)
{
this->data = data;
this->left = NULL;
this->right = NULL;
}
};
/* This function traverses tree
in post order to delete each
and every node of the tree */
void deleteTree(node* node)
{
if (node == NULL) return;
/* first delete both subtrees */
deleteTree(node->left);
deleteTree(node->right);
/* then delete the node */
cout << "\n Deleting node: " << node->data;
delete node;
}
/* Driver code*/
int main()
{
node *root = new node(1);
root->left = new node(2);
root->right = new node(3);
root->left->left = new node(4);
root->left->right = new node(5);
deleteTree(root);
root = NULL;
cout << "\n Tree deleted ";
return 0;
}
//This code is contributed by rathbhupendra
C
// C program to Delete a Tree
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct node
{
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node = (struct node*)
malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return(node);
}
/* This function traverses tree in post order to
to delete each and every node of the tree */
void deleteTree(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL) return;
/* first delete both subtrees */
deleteTree(node->left);
deleteTree(node->right);
/* then delete the node */
printf("\n Deleting node: %d", node->data);
free(node);
}
/* Driver program to test deleteTree function*/
int main()
{
struct node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
deleteTree(root);
root = NULL;
printf("\n Tree deleted ");
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to delete a tree
// A binary tree node
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
/* This function traverses tree in post order to
to delete each and every node of the tree */
void deleteTree(Node node)
{
// In Java automatic garbage collection
// happens, so we can simply make root
// null to delete the tree
root = null;
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
/* Print all root-to-leaf paths of the input tree */
tree.deleteTree(tree.root);
tree.root = null;
System.out.println("Tree deleted");
}
}
Python3
""" program to Delete a Tree """
# Helper function that allocates a new
# node with the given data and None
# left and right pointers.
class newNode:
# Construct to create a new node
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
""" This function traverses tree in post order to
to delete each and every node of the tree """
def deleteTree( node) :
if node != None:
deleteTree(node.left)
deleteTree(node.right)
del node
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = newNode(1)
root.left = newNode(2)
root.right = newNode(3)
root.left.left = newNode(4)
root.left.right = newNode(5)
deleteTree(root)
root = None
print("Tree deleted ")
# This code is contributed by
# Shubham Prashar(shubhamprashar)
C#
using System;
// C# program to delete a tree
// A binary tree node
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
public Node root;
/* This function traverses tree in post order to
to delete each and every node of the tree */
public virtual void deleteTree(Node node)
{
// In Java automatic garbage collection
// happens, so we can simply make root
// null to delete the tree
root = null;
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
/* Print all root-to-leaf paths of the input tree */
tree.deleteTree(tree.root);
tree.root = null;
Console.WriteLine("Tree deleted");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13
Javascript
<script>
// javascript program to delete a tree
// A binary tree node
class Node {
constructor(item) {
this.data = item;
this.left = this.right = null;
}
}
var root;
/*
* This function traverses tree in post order to to delete each and every node
* of the tree
*/
function deleteTree(node) {
// In javascript automatic garbage collection
// happens, so we can simply make root
// null to delete the tree
root = null;
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
/* Print all root-to-leaf paths of the input tree */
deleteTree(root);
root = null;
document.write("Tree deleted");
// This code contributed by gauravrajput1
</script>
C++
// CPP program to Delete a Tree
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
class node
{
public:
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
};
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
node* newNode(int data)
{
node* Node = new node();
Node->data = data;
Node->left = NULL;
Node->right = NULL;
return(Node);
}
/* This function is same as deleteTree()
in the previous program */
void _deleteTree(node* node)
{
if (node == NULL) return;
/* first delete both subtrees */
_deleteTree(node->left);
_deleteTree(node->right);
/* then delete the node */
cout << "Deleting node: " << node->data << endl;
delete node;
}
/* Deletes a tree and sets the root as NULL */
void deleteTree(node** node_ref)
{
_deleteTree(*node_ref);
*node_ref = NULL;
}
/* Driver code*/
int main()
{
node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
// Note that we pass the address of root here
deleteTree(&root);
cout << "Tree deleted ";
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra
C
// C program to Delete a Tree
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct node
{
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node = (struct node*)
malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return(node);
}
/* This function is same as deleteTree() in the previous program */
void _deleteTree(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL) return;
/* first delete both subtrees */
_deleteTree(node->left);
_deleteTree(node->right);
/* then delete the node */
printf("\n Deleting node: %d", node->data);
free(node);
}
/* Deletes a tree and sets the root as NULL */
void deleteTree(struct node** node_ref)
{
_deleteTree(*node_ref);
*node_ref = NULL;
}
/* Driver program to test deleteTree function*/
int main()
{
struct node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
// Note that we pass the address of root here
deleteTree(&root);
printf("\n Tree deleted ");
getchar();
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to delete a tree
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and pointer to right child */
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree
{
static Node root;
/* This function is same as deleteTree() in the previous program */
void deleteTree(Node node)
{
// In Java automatic garbage collection
// happens, so we can simply make root
// null to delete the tree
root = null;
}
/* Wrapper function that deletes the tree and
sets root node as null */
void deleteTreeRef(Node nodeRef)
{
deleteTree(nodeRef);
nodeRef=null;
}
/* Driver program to test deleteTree function */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
/* Note that we pass root node here */
tree.deleteTreeRef(root);
System.out.println("Tree deleted");
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal(mayank_24)
Python3
# Python3 program to count all nodes
# having k leaves in subtree rooted with them
# A binary tree node has data, pointer to
# left child and a pointer to right child
# Helper function that allocates a new node
# with the given data and None left and
# right pointers
class newNode:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
''' This function is same as deleteTree()
in the previous program '''
def _deleteTree(node):
if (node == None):
return
# first delete both subtrees
_deleteTree(node.left)
_deleteTree(node.right)
# then delete the node
print("Deleting node: ",
node.data)
node = None
# Deletes a tree and sets the root as NULL
def deleteTree(node_ref):
_deleteTree(node_ref[0])
node_ref[0] = None
# Driver code
root = [0]
root[0] = newNode(1)
root[0].left = newNode(2)
root[0].right = newNode(3)
root[0].left.left = newNode(4)
root[0].left.right = newNode(5)
# Note that we pass the address
# of root here
deleteTree(root)
print("Tree deleted ")
# This code is contributed by SHUBHAMSINGH10
C#
using System;
// C# program to delete a tree
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and pointer to right child */
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
public static Node root;
/* This function is same as deleteTree() in the previous program */
public virtual void deleteTree(Node node)
{
// In Java automatic garbage collection
// happens, so we can simply make root
// null to delete the tree
root = null;
}
/* Wrapper function that deletes the tree and
sets root node as null */
public virtual void deleteTreeRef(Node nodeRef)
{
deleteTree(nodeRef);
nodeRef = null;
}
/* Driver program to test deleteTree function */
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
BinaryTree.root = new Node(1);
BinaryTree.root.left = new Node(2);
BinaryTree.root.right = new Node(3);
BinaryTree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
BinaryTree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
/* Note that we pass root node here */
tree.deleteTreeRef(root);
Console.WriteLine("Tree deleted");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program to delete a tree
class Node
{
constructor(data) {
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
this.data = data;
}
}
let root;
/* This function is same as deleteTree()
in the previous program */
function deleteTree(node)
{
if (node == null) return;
/* first delete both subtrees */
deleteTree(node.left);
deleteTree(node.right);
/* then delete the node */
document.write("Deleting node: " + node.data + "</br>");
}
/* Wrapper function that deletes the tree and
sets root node as null */
function deleteTreeRef(nodeRef)
{
deleteTree(nodeRef);
nodeRef=null;
}
root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
/* Note that we pass root node here */
deleteTreeRef(root);
document.write("Tree deleted");
</script>
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA