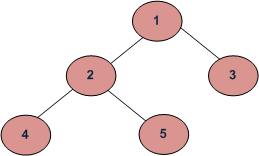
Dado un árbol binario, encuentra su altura. La altura del árbol vacío es -1, la altura del árbol con un Node es 0 y la altura del árbol inferior es 2.
C++
// C++ program to find height of tree
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
class node
{
public:
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
};
/* Compute the "maxDepth" of a tree -- the number of
nodes along the longest path from the root node
down to the farthest leaf node.*/
int maxDepth(node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return -1;
else
{
/* compute the depth of each subtree */
int lDepth = maxDepth(node->left);
int rDepth = maxDepth(node->right);
/* use the larger one */
if (lDepth > rDepth)
return(lDepth + 1);
else return(rDepth + 1);
}
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
node* newNode(int data)
{
node* Node = new node();
Node->data = data;
Node->left = NULL;
Node->right = NULL;
return(Node);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
cout << "Height of tree is " << maxDepth(root);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Srivastav
C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct node {
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
/* Compute the "maxDepth" of a tree -- the number of
nodes along the longest path from the root node
down to the farthest leaf node.*/
int maxDepth(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return -1;
else {
/* compute the depth of each subtree */
int lDepth = maxDepth(node->left);
int rDepth = maxDepth(node->right);
/* use the larger one */
if (lDepth > rDepth)
return (lDepth + 1);
else
return (rDepth + 1);
}
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node
= (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
int main()
{
struct node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
printf("Height of tree is %d", maxDepth(root));
getchar();
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to find height of tree
// A binary tree node
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
/* Compute the "maxDepth" of a tree -- the number of
nodes along the longest path from the root node
down to the farthest leaf node.*/
int maxDepth(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return -1;
else
{
/* compute the depth of each subtree */
int lDepth = maxDepth(node.left);
int rDepth = maxDepth(node.right);
/* use the larger one */
if (lDepth > rDepth)
return (lDepth + 1);
else
return (rDepth + 1);
}
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
System.out.println("Height of tree is : " +
tree.maxDepth(tree.root));
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Amit Srivastav
Python3
# Python3 program to find the maximum depth of tree
# A binary tree node
class Node:
# Constructor to create a new node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Compute the "maxDepth" of a tree -- the number of nodes
# along the longest path from the root node down to the
# farthest leaf node
def maxDepth(node):
if node is None:
return -1 ;
else :
# Compute the depth of each subtree
lDepth = maxDepth(node.left)
rDepth = maxDepth(node.right)
# Use the larger one
if (lDepth > rDepth):
return lDepth+1
else:
return rDepth+1
# Driver program to test above function
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
print ("Height of tree is %d" %(maxDepth(root)))
# This code is contributed by Amit Srivastav
C#
// C# program to find height of tree
using System;
// A binary tree node
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
/* Compute the "maxDepth" of a tree -- the number of
nodes along the longest path from the root node
down to the farthest leaf node.*/
int maxDepth(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return -1;
else
{
/* compute the depth of each subtree */
int lDepth = maxDepth(node.left);
int rDepth = maxDepth(node.right);
/* use the larger one */
if (lDepth > rDepth)
return (lDepth + 1);
else
return (rDepth + 1);
}
}
/* Driver code */
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
Console.WriteLine("Height of tree is : " +
tree.maxDepth(tree.root));
}
}
// This code has been contributed by
// Correction done by Amit Srivastav
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program to find height of tree
// A binary tree node
class Node
{
constructor(item)
{
this.data=item;
this.left=this.right=null;
}
}
let root;
/* Compute the "maxDepth" of a tree -- the number of
nodes along the longest path from the root node
down to the farthest leaf node.*/
function maxDepth(node)
{
if (node == null)
return -1;
else
{
/* compute the depth of each subtree */
let lDepth = maxDepth(node.left);
let rDepth = maxDepth(node.right);
/* use the larger one */
if (lDepth > rDepth)
return (lDepth + 1);
else
return (rDepth + 1);
}
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
document.write("Height of tree is : " +
maxDepth(root));
// This code is contributed by rag2127
//Correction done by Amit Srivastav
</script>
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// A Tree node
struct Node
{
int key;
struct Node* left, *right;
};
// Utility function to create a new node
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return (temp);
}
/*Function to find the height(depth) of the tree*/
int height(struct Node* root){
//Initialising a variable to count the
//height of tree
int depth = 0;
queue<Node*>q;
//Pushing first level element along with NULL
q.push(root);
q.push(NULL);
while(!q.empty()){
Node* temp = q.front();
q.pop();
//When NULL encountered, increment the value
if(temp == NULL){
depth++;
}
//If NULL not encountered, keep moving
if(temp != NULL){
if(temp->left){
q.push(temp->left);
}
if(temp->right){
q.push(temp->right);
}
}
//If queue still have elements left,
//push NULL again to the queue.
else if(!q.empty()){
q.push(NULL);
}
}
return depth;
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
// Let us create Binary Tree shown in above example
Node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(12);
root->right = newNode(13);
root->right->left = newNode(14);
root->right->right = newNode(15);
root->right->left->left = newNode(21);
root->right->left->right = newNode(22);
root->right->right->left = newNode(23);
root->right->right->right = newNode(24);
cout<<"Height(Depth) of tree is: "<<height(root);
}
Java
// Java program for above approach
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class GFG {
// A tree node structure
static class Node {
int key;
Node left;
Node right;
}
// Utility function to create
// a new node
static Node newNode(int key) {
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
/*Function to find the height(depth) of the tree*/
public static int height( Node root){
//Initialising a variable to count the
//height of tree
int depth = 0;
Queue<Node> q=new LinkedList<>();
//Pushing first level element along with null
q.add(root);
q.add(null);
while(!q.isEmpty()){
Node temp = q.peek();
q.remove();
//When null encountered, increment the value
if(temp == null){
depth++;
}
//If null not encountered, keep moving
if(temp != null){
if(temp.left!=null){
q.add(temp.left);
}
if(temp.right!=null){
q.add(temp.right);
}
}
//If queue still have elements left,
//push null again to the queue.
else if(!q.isEmpty()){
q.add(null);
}
}
return depth;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[]) {
Node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(12);
root.right = newNode(13);
root.right.left = newNode(14);
root.right.right = newNode(15);
root.right.left.left = newNode(21);
root.right.left.right = newNode(22);
root.right.right.left = newNode(23);
root.right.right.right = newNode(24);
System.out.println("Height(Depth) of tree is: "+height(root));
}
}
// This code is contributed by jana_sayantan.
Python3
# Python code to implement the approach
# A Tree node
class Node:
def __init__(self):
self.key = 0
self.left,self.right = None,None
# Utility function to create a new node
def newNode(key):
temp = Node()
temp.key = key
temp.left,temp.right = None,None
return temp
# Function to find the height(depth) of the tree
def height(root):
#Initialising a variable to count the
#height of tree
depth = 0
q = []
#appending first level element along with None
q.append(root)
q.append(None)
while(len(q)>0):
temp = q[0]
q = q[1:]
#When None encountered, increment the value
if(temp == None):
depth += 1
#If None not encountered, keep moving
if(temp != None):
if(temp.left):
q.append(temp.left)
if(temp.right):
q.append(temp.right)
#If queue still have elements left,
#append None again to the queue.
elif(len(q)>0):
q.append(None)
return depth
# Driver program
# Let us create Binary Tree shown in above example
root = newNode(1)
root.left = newNode(12)
root.right = newNode(13)
root.right.left = newNode(14)
root.right.right = newNode(15)
root.right.left.left = newNode(21)
root.right.left.right = newNode(22)
root.right.right.left = newNode(23)
root.right.right.right = newNode(24)
print(f"Height(Depth) of tree is: {height(root)}")
# This code is contributed by shinjanpatra
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript code to implement the approach
// A Tree node
class Node{
constructor(){
this.key = 0
this.left = null
this.right = null
}
}
// Utility function to create a new node
function newNode(key){
let temp = new Node()
temp.key = key
temp.left = null
temp.right = null
return temp
}
// Function to find the height(depth) of the tree
function height(root){
// Initialising a variable to count the
// height of tree
let depth = 0
let q = []
// pushing first level element along with null
q.push(root)
q.push(null)
while(q.length>0){
let temp = q.shift()
// When null encountered, increment the value
if(temp == null)
depth += 1
// If null not encountered, keep moving
if(temp != null){
if(temp.left)
q.push(temp.left)
if(temp.right)
q.push(temp.right)
}
// If queue still have elements left,
// push null again to the queue.
else if(q.length>0)
q.push(null)
}
return depth
}
// Driver program
// Let us create Binary Tree shown in above example
let root = newNode(1)
root.left = newNode(12)
root.right = newNode(13)
root.right.left = newNode(14)
root.right.right = newNode(15)
root.right.left.left = newNode(21)
root.right.left.right = newNode(22)
root.right.right.left = newNode(23)
root.right.right.right = newNode(24)
document.write(`Height(Depth) of tree is: ${height(root)}`,"</br>")
// This code is contributed by shinjanpatra
</script>
Java
// Java program for above approach
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class GFG {
// A tree node structure
static class Node {
int key;
Node left;
Node right;
}
// Utility function to create
// a new node
static Node newNode(int key) {
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
/*Function to find the height(depth) of the tree*/
public static int height( Node root){
//Initialising a variable to count the
//height of tree
Queue<Node>q=new LinkedList<Node>();
q.add(root);
int height=0;
while(!q.isEmpty()){
int size=q.size();
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
Node temp=q.poll();
if(temp.left!=null){
q.add(temp.left);
}
if(temp.right!=null){
q.add(temp.right);
}
}
height++;
}
return height;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[]) {
Node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(12);
root.right = newNode(13);
root.right.left = newNode(14);
root.right.right = newNode(15);
root.right.left.left = newNode(21);
root.right.left.right = newNode(22);
root.right.right.left = newNode(23);
root.right.right.right = newNode(24);
System.out.println("Height(Depth) of tree is: "+height(root));
}
}
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA