En este artículo, aprenderemos cómo desechar datos en el tráfico de red usando Python.
Módulos necesarios
- selenium : Selenium es un marco portátil para controlar el navegador web.
- tiempo: Este módulo proporciona varias funciones relacionadas con el tiempo.
- json : este módulo es necesario para trabajar con datos JSON.
- browsermobproxy: este módulo nos ayuda a obtener el archivo HAR del tráfico de red.
Hay dos formas en las que podemos desechar los datos de tráfico de la red.
Método 1: Usar el método get_log() de Selenium
Para comenzar, descargue y extraiga el controlador web de Chrome de aquí de acuerdo con la versión de su navegador Chrome y copie la ruta del ejecutable.
Acercarse:
- Importe DesiredCapabilities desde el módulo de selenium y habilite el registro de rendimiento.
- Inicie el controlador web de Chrome con la ruta ejecutable y las opciones predeterminadas de Chrome o agregue algunos argumentos y las capacidades deseadas modificadas .
- Envíe una solicitud GET al sitio web usando driver.get() y espere unos segundos para cargar la página.
Sintaxis:
conductor.get(url)
- Obtenga los registros de rendimiento utilizando driver.get_log() y almacénelos en una variable.
Sintaxis:
controlador.get_log(“rendimiento”)
- Repita cada registro y analícelo usando json.loads() para filtrar todos los registros relacionados con la red.
- Escriba los registros filtrados en un archivo JSON convirtiéndolos a una string JSON usando json.dumps().
Ejemplo:
Python3
# Import the required modules
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.desired_capabilities import DesiredCapabilities
import time
import json
# Main Function
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Enable Performance Logging of Chrome.
desired_capabilities = DesiredCapabilities.CHROME
desired_capabilities["goog:loggingPrefs"] = {"performance": "ALL"}
# Create the webdriver object and pass the arguments
options = webdriver.ChromeOptions()
# Chrome will start in Headless mode
options.add_argument('headless')
# Ignores any certificate errors if there is any
options.add_argument("--ignore-certificate-errors")
# Startup the chrome webdriver with executable path and
# pass the chrome options and desired capabilities as
# parameters.
driver = webdriver.Chrome(executable_path="C:/chromedriver.exe",
chrome_options=options,
desired_capabilities=desired_capabilities)
# Send a request to the website and let it load
driver.get("https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/")
# Sleeps for 10 seconds
time.sleep(10)
# Gets all the logs from performance in Chrome
logs = driver.get_log("performance")
# Opens a writable JSON file and writes the logs in it
with open("network_log.json", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write("[")
# Iterates every logs and parses it using JSON
for log in logs:
network_log = json.loads(log["message"])["message"]
# Checks if the current 'method' key has any
# Network related value.
if("Network.response" in network_log["method"]
or "Network.request" in network_log["method"]
or "Network.webSocket" in network_log["method"]):
# Writes the network log to a JSON file by
# converting the dictionary to a JSON string
# using json.dumps().
f.write(json.dumps(network_log)+",")
f.write("{}]")
print("Quitting Selenium WebDriver")
driver.quit()
# Read the JSON File and parse it using
# json.loads() to find the urls containing images.
json_file_path = "network_log.json"
with open(json_file_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
logs = json.loads(f.read())
# Iterate the logs
for log in logs:
# Except block will be accessed if any of the
# following keys are missing.
try:
# URL is present inside the following keys
url = log["params"]["request"]["url"]
# Checks if the extension is .png or .jpg
if url[len(url)-4:] == ".png" or url[len(url)-4:] == ".jpg":
print(url, end='\n\n')
except Exception as e:
pass
Producción:
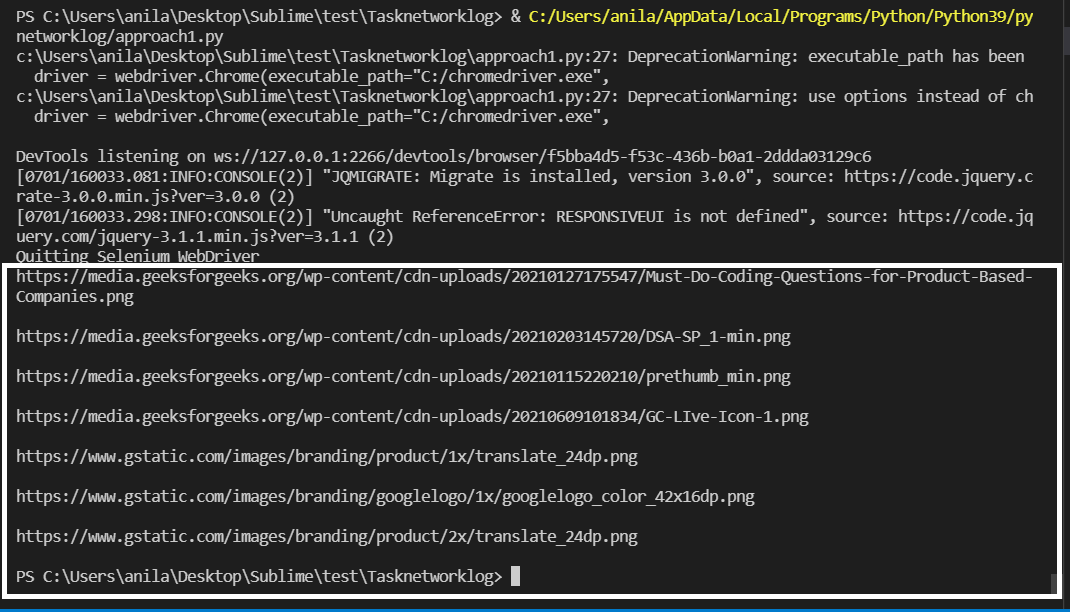
Las URL de la imagen están resaltadas arriba.
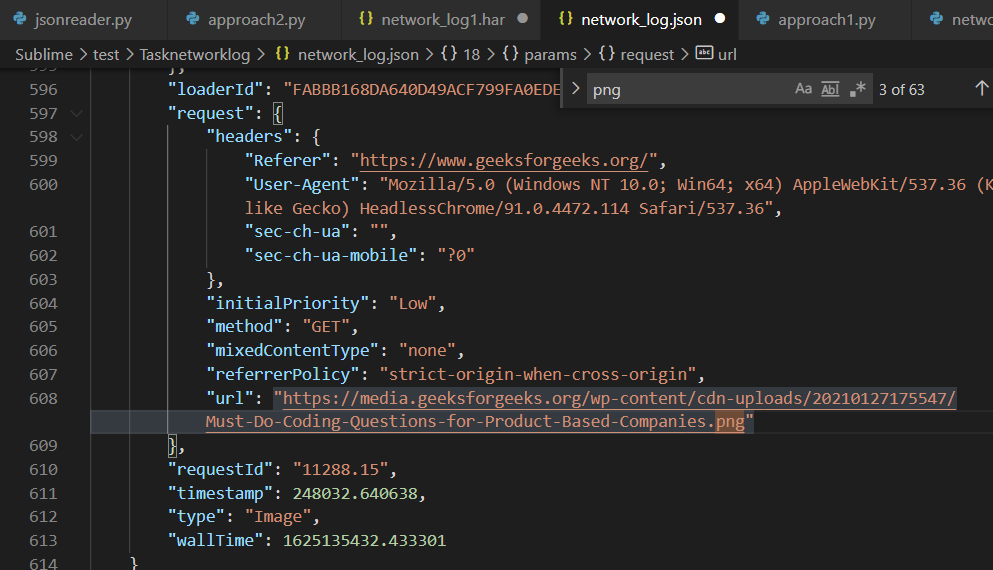
network_log.json que contiene la URL de la imagen
Método 2: usar browsermobproxy para capturar el archivo HAR desde la pestaña de red del navegador
Para ello, se deben cumplir los siguientes requisitos.
- Descargue e instale Java v8 desde aquí
- Descargue y extraiga browsermobproxy desde aquí y copie la ruta de la carpeta bin.
- Instale browsermob-proxy usando pip usando el comando en la terminal:
pip instalar navegador mob-proxy
- Descargue y extraiga el controlador web de Chrome desde aquí, según la versión de su navegador Chrome y copie la ruta del ejecutable.
Acercarse:
- Importe el módulo del servidor desde browsermobproxy e inicie el servidor con la ruta de la carpeta bin copiada y configure el puerto como 8090 .
- Llame al método create_proxy para crear el objeto proxy desde el servidor y establezca el parámetro «trustAllServers» como verdadero .
- Inicie Chrome webdriver con executable_path y chrome -options discutidos en el código a continuación.
- Ahora, cree un nuevo archivo HAR usando el objeto proxy con el dominio del sitio web.
- Envíe una solicitud GET usando driver.get() y espere unos segundos para cargarlo correctamente.
Sintaxis:
conductor.get(url)
- Escriba el archivo HAR del tráfico de red del objeto proxy en un archivo HAR convirtiéndolo en una string JSON mediante json.dumps() .
Ejemplo:
Python3
# Import the required modules
from selenium import webdriver
from browsermobproxy import Server
import time
import json
# Main Function
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Enter the path of bin folder by
# extracting browsermob-proxy-2.1.4-bin
path_to_browsermobproxy = "C:\\browsermob-proxy-2.1.4\\bin\\"
# Start the server with the path and port 8090
server = Server(path_to_browsermobproxy
+ "browsermob-proxy", options={'port': 8090})
server.start()
# Create the proxy with following parameter as true
proxy = server.create_proxy(params={"trustAllServers": "true"})
# Create the webdriver object and pass the arguments
options = webdriver.ChromeOptions()
# Chrome will start in Headless mode
options.add_argument('headless')
# Ignores any certificate errors if there is any
options.add_argument("--ignore-certificate-errors")
# Setting up Proxy for chrome
options.add_argument("--proxy-server={0}".format(proxy.proxy))
# Startup the chrome webdriver with executable path and
# the chrome options as parameters.
driver = webdriver.Chrome(executable_path="C:/chromedriver.exe",
chrome_options=options)
# Create a new HAR file of the following domain
# using the proxy.
proxy.new_har("geeksforgeeks.org/")
# Send a request to the website and let it load
driver.get("https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/")
# Sleeps for 10 seconds
time.sleep(10)
# Write it to a HAR file.
with open("network_log1.har", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(json.dumps(proxy.har))
print("Quitting Selenium WebDriver")
driver.quit()
# Read HAR File and parse it using JSON
# to find the urls containing images.
har_file_path = "network_log1.har"
with open(har_file_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
logs = json.loads(f.read())
# Store the network logs from 'entries' key and
# iterate them
network_logs = logs['log']['entries']
for log in network_logs:
# Except block will be accessed if any of the
# following keys are missing
try:
# URL is present inside the following keys
url = log['request']['url']
# Checks if the extension is .png or .jpg
if url[len(url)-4:] == '.png' or url[len(url)-4:] == '.jpg':
print(url, end="\n\n")
except Exception as e:
# print(e)
pass
Producción:
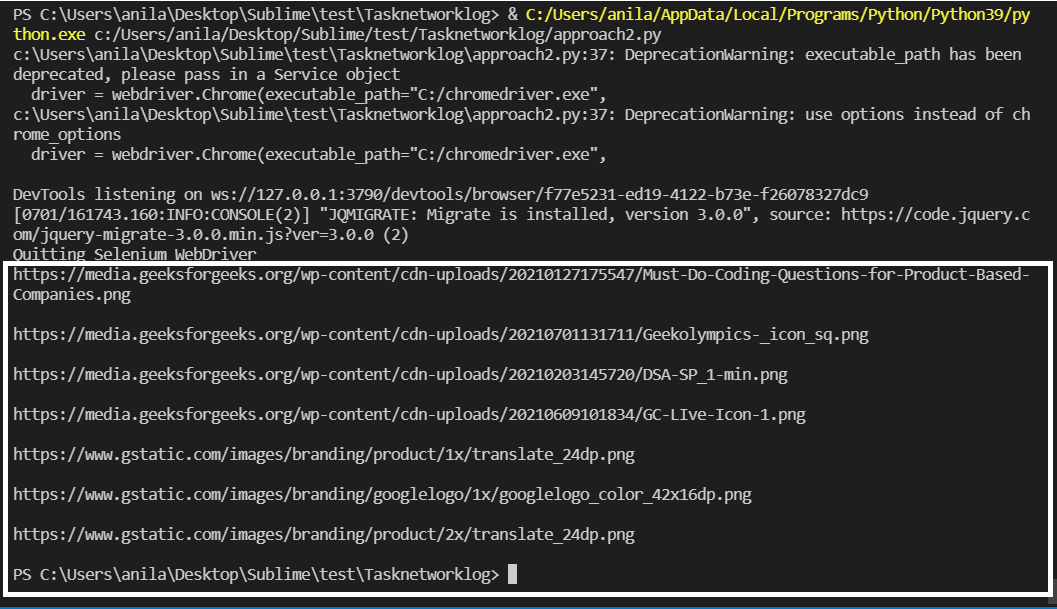
Las URL de la imagen están resaltadas arriba.
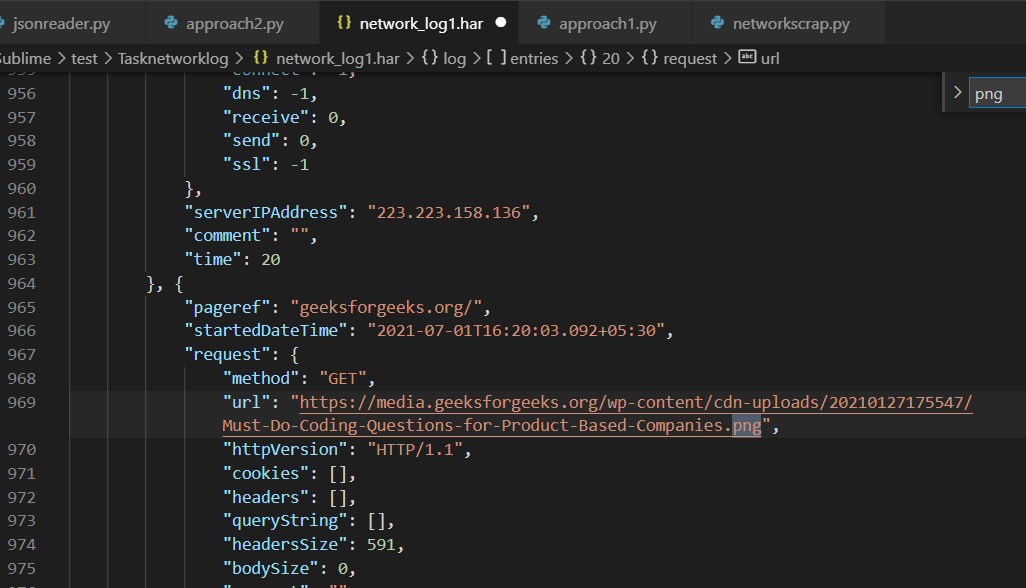
network_log1.har que contiene la URL de la imagen
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por anilabhadatta y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA