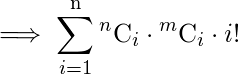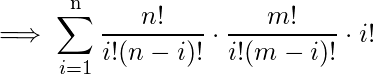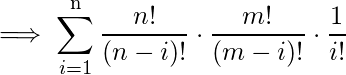Dados dos números positivos ‘n’ y ‘m’ (n <= m) que representan el número total de elementos del primer y segundo tipo de conjuntos, respectivamente. Encuentre el número total de formas de seleccionar al menos un par seleccionando un artículo del primer tipo (I) y otro artículo del segundo tipo (II). En cualquier arreglo, un artículo no debe ser común entre dos pares.
Nota: Dado que la respuesta puede ser grande, envíela en módulo 1000000007 .
Input: 2 2 Output: 6 Explanation Let's denote the items of I type as a, b and II type as c, d i.e, Type I - a, b Type II - c, d Ways to arrange one pair at a time 1. a --- c 2. a --- d 3. b --- c 4. b --- d Ways to arrange two pairs at a time 5. a --- c, b --- d 6. a --- d, b --- c Input: 2 3 Output: 12 Input: 1 2 Output: 2
El enfoque es simple, solo necesitamos la combinación de elegir elementos ‘ i ‘ del tipo ‘ n ‘ y elementos ‘ i ‘ del tipo ‘ m ‘ y multiplicarlos ( Regla del producto ) donde ‘ i ‘ varía de 1 a ‘ n ‘ . Pero también podemos permutar el producto resultante en formas ‘i’, por lo tanto, ¡necesitamos multiplicar con i! . Después de eso, tome la suma ( Regla de la suma ) de todos los productos resultantes para obtener la respuesta final.
C++
// C++ program to find total no. of ways
// to form a pair in two different set
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// initialize global variable so that
// it can access by preCalculate() and
// nCr() function
int* fact, *inverseMod;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
/* Iterative Function to calculate (x^y)%p in O(log y) */
int power(int x, int y, int p)
{
int res = 1; // Initialize result
x = x % p; // Update x if it is more than or
// equal to p
while (y) {
// If y is odd, multiply x with result
if (y & 1)
res = (1LL * res * x) % p;
// y must be even now
y = y >> 1; // y = y/2
x = (1LL * x * x) % p;
} // trace(res);
return res;
}
// Pre-calculate factorial and
// Inverse of number
void preCalculate(int n)
{
fact[0] = inverseMod[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
fact[i] = (1LL * fact[i - 1] * i) % mod;
inverseMod[i] = power(fact[i], mod - 2, mod);
}
}
// utility function to calculate nCr
int nPr(int a, int b)
{
return (1LL * fact[a] * inverseMod[a - b]) % mod;
}
int countWays(int n, int m)
{
fact = new int[m + 1];
inverseMod = new int[m + 1];
// Pre-calculate factorial and
// inverse of number
preCalculate(m);
// Initialize answer
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
ans += (1LL * ((1LL * nPr(n, i)
* nPr(m, i)) % mod)
* inverseMod[i]) % mod;
if (ans >= mod)
ans %= mod;
}
return ans;
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
int n = 2, m = 2;
cout << countWays(n, m);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to find total
// no. of ways to form a pair
// in two different set
public class Test
{
static long[] fact;
static long[] inverseMod;
static int mod=1000000007;
/* Iterative Function to calculate
(x^y)%p in O(log y) */
static long power(long x, int y, int p)
{
// Initialize result
long res = 1;
// Update x if it is more than or
// equal to p
x = x % p;
while (y!=0)
{
// If y is odd, multiply
// x with result
if ((y & 1)!=0)
res = (1 * res * x) % p;
}
// y must be even now
y = y >> 1;
x = (1 * x * x) % p;
}
return res;
}
// Pre-calculate factorial and
// Inverse of number
public static void preCalculate(int n)
{
//int fact[]=new long[n];
// int inverseMod[]=new long[n];
fact[0] = 1;
inverseMod[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
fact[i] = (1 * fact[i - 1] * i)
% mod;
inverseMod[i] = power(fact[i],
mod - 2, mod);
}
}
// utility function to calculate nCr
public static long nPr(int a, int b)
{
return (1 * fact[a] * inverseMod[a - b])
% (long)mod;
}
public static int countWays(int n, int m)
{
fact = new long[m + 1];
inverseMod = new long[m + 1];
// Pre-calculate factorial and
// inverse of number
preCalculate(m);
// Initialize answer
long ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
ans = ans+(1 * ((1 * nPr(n, i)*
nPr(m, i)) % mod)*
(inverseMod[i])) % mod;
if (ans >= mod)
ans %= mod;
}
return (int)ans;
}
/* Driver program */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 2, m = 2;
System.out.println(countWays(n, m));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Gitanjali
Producción:
6
Complejidad temporal: O(m*log(mod))
Espacio auxiliar: O(m)
Este artículo es una contribución de Shubham Bansal . Si le gusta GeeksforGeeks y le gustaría contribuir, también puede escribir un artículo usando contribuya.geeksforgeeks.org o envíe su artículo por correo a contribuya@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA