La función pie.padAngle() en D3.js se usa para establecer el ángulo de relleno entre arcos consecutivos. Cuando se especifica un ángulo, establece el ángulo de la almohadilla en el ángulo o función dados y devuelve un generador circular. Cuando no se especifica el ángulo, devuelve el descriptor de acceso de ángulo de pad actual, que por defecto es sin padding.
Sintaxis:
pie.padAngle( angle )
Parámetros: esta función acepta un solo parámetro como se mencionó anteriormente y se describe a continuación:
- ángulo: Es un número o función que especifica el ángulo del pad en radianes. Es un parámetro opcional.
Valores devueltos: esta función no devuelve nada.
A continuación se muestran algunos ejemplos de la función pie.padAngle() en D3.js;
Ejemplo 1:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script src="https://d3js.org/d3.v6.min.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div style="width:300px; height:300px;">
<center>
<h1 style="color:green">
GeeksforGeeks
</h1>
<h2>
pie.padAngle()
</h2>
</center>
<svg width="300" height="250">
</svg>
</div>
<script>
// Data to be added in the pie chart
var data = [
{ "property": "p5", "value": 19 },
{ "property": "p5", "value": 12 },
{ "property": "p4", "value": 11 },
{ "property": "p3", "value": 10 },
{ "property": "p2", "value": 9 },
]
// Selecting SVG using d3.select()
var svg = d3.select("svg");
// Creating Pie generator
var pie = d3.pie()
.value((d) => { return d.value })
// Use of pie.padAngle() Function
.padAngle(0.5)
(data);
// Creating arc
var arc = d3.arc()
.innerRadius(0)
.outerRadius(80);
let g = svg.append("g")
.attr("transform", "translate(150,120)");
// Grouping different arcs
var arcs = g.selectAll("arc")
.data(pie)
.enter()
.append("g");
// Appending path
arcs.append("path")
.attr("fill", (data, i) => {
return d3.schemeSet3[i];
})
.attr("d", arc);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Producción:
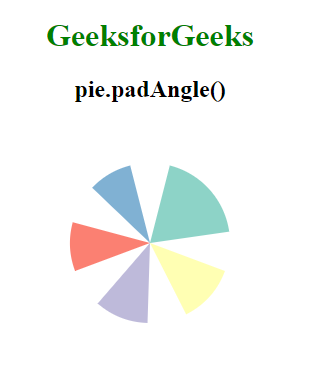
Ejemplo 2:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script src="https://d3js.org/d3.v6.min.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div style="width:300px; height:300px;">
<center>
<h1 style="color:green">
GeeksforGeeks
</h1>
<h2>
pie.padAngle()
</h2>
</center>
<svg width="300" height="250">
</svg>
</div>
<script>
// Data to be added in the pie chart
var data = [
{ "property": "p5", "value": 19 },
{ "property": "p5", "value": 12 },
{ "property": "p4", "value": 11 },
{ "property": "p3", "value": 10 },
{ "property": "p2", "value": 9 },
]
// Selecting SVG using d3.select()
var svg = d3.select("svg");
// Creating Pie generator
var pie = d3.pie()
.value((d) => { return d.value })
// Use of pie.padAngle() Function
.padAngle(0.1)
(data);
// Creating arc
var arc = d3.arc()
.innerRadius(40)
.outerRadius(80);
let g = svg.append("g")
.attr("transform", "translate(150,120)");
// Grouping different arcs
var arcs = g.selectAll("arc")
.data(pie)
.enter()
.append("g");
// Appending path
arcs.append("path")
.attr("fill", (data, i) => {
return d3.schemeSet3[i];
})
.attr("d", arc);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Producción:
