Beta(), betaf () y betal() son funciones integradas en C++ STL que se utilizan para calcular la función beta de dos valores reales positivos. La función toma dos variables x e y como entrada y devuelve la función beta de x e y. La función beta (también conocida como integral de Euler de primer tipo) de x e y se puede definir como:
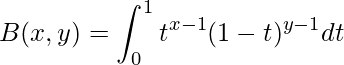
Sintaxis
double beta(double x, double y) or long double betal(long double x, long double y) or float betaf(float x, float y)
Parámetros: la función acepta dos parámetros obligatorios x e y que especifican los valores de un tipo de coma flotante o integral. Los parámetros pueden ser de tipo de datos double, double o float, float o long double, long double.
Valor devuelto: la función devuelve el valor de la función beta de x e y. El tipo de retorno depende de los parámetros pasados. Es el mismo que el del parámetro.
Nota : la función se ejecuta en y por encima de C++ 17 (7.1).
El siguiente programa ilustra las funciones beta(), betaf() y betal():
CPP
// C++ program to illustrate the three functions
// Being a special function, beta is only guaranteed
// to be in cmath if the user defines
// __STDCPP_WANT_MATH_SPEC_FUNCS__ before including
// any standard library headers.
#define __STDCPP_WANT_MATH_SPEC_FUNCS__ 1
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// Computes the beta function of 5 and 4 and print it
// If provided arguments are not of type double
// they are implicitly type-casted to the higher type.
// first example of beta()
cout << beta(5, 4) << "\n";
// second example of betaf()
cout << betaf(10.0, 4.0) << "\n";
// third example of betal()
cout << betal(10.0, 6.7) << "\n";
return 0;
}
Producción:
0.00357143 0.00034965 1.65804e-005
Aplicación de la función Beta: se utiliza para calcular coeficientes binomiales. El coeficiente binomial en términos de función beta se puede expresar como:

La relación anterior se puede utilizar para calcular el coeficiente binomial. A continuación se muestra una ilustración:
CPP
// C++ program to print the pascal triangle
// Being a special function, beta is only guaranteed
// to be in cmath if the user defines
// __STDCPP_WANT_MATH_SPEC_FUNCS__ before including
// any standard library headers.
#define __STDCPP_WANT_MATH_SPEC_FUNCS__ 1
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
// Function to return the value of binomial Coefficient
double binomialCoefficient(int n, int k)
{
// Calculate the value of nCr using above formula.
double ans = 1 / ((n + 1) * beta(n - k + 1, k + 1));
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Print the binomial Coefficient nCr where n=5 and r=2
cout << binomialCoefficient(5, 2) << "\n";
return 0;
}
Producción:
10