Dada una array cuadrada, gírela 90 grados en el sentido de las agujas del reloj sin usar ningún espacio extra.
Ejemplos:
Input: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Output: 7 4 1 8 5 2 9 6 3 Input: 1 2 3 4 Output: 3 1 4 2
Método 1
Enfoque: El enfoque es similar a Inplace rotar array cuadrada en 90 grados | conjunto 1 . Lo único que es diferente es imprimir los elementos del ciclo en el sentido de las agujas del reloj, es decir, una array N x N tendrá ciclos cuadrados de suelo (N/2).
Por ejemplo, una array de 3 X 3 tendrá 1 ciclo. El ciclo está formado por su 1ra fila, última columna, última fila y 1ra columna.
Para cada ciclo cuadrado, intercambiamos los elementos involucrados con la celda correspondiente en la array en el sentido de las agujas del reloj. Solo necesitamos una variable temporal para esto.
Explicación:
Deje que el tamaño de fila y columna sea 3.
Durante la primera iteración:
a[i][j] = Elemento en el primer índice (esquina superior izquierda)= 1.
a[j][n-1-i]= Esquina superior derecha Elemento = 3.
a[n-1-i][n-1-j] = Elemento inferior de la esquina más a la derecha = 9.
a[n-1-j][i] = Elemento inferior de la esquina más a la izquierda = 7.
Mueva estos elementos en el sentido de las agujas del reloj dirección.
Durante la segunda iteración –
a[i][j] = 2.
a[j][n-1-i] = 6.
a[n-1-i][n-1-j] = 8.
a[n- 1-j][i] = 4.
De manera similar, mueva estos elementos en el sentido de las agujas del reloj.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation of above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 4
// Function to rotate the matrix 90 degree clockwise
void rotate90Clockwise(int a[N][N])
{
// Traverse each cycle
for (int i = 0; i < N / 2; i++) {
for (int j = i; j < N - i - 1; j++) {
// Swap elements of each cycle
// in clockwise direction
int temp = a[i][j];
a[i][j] = a[N - 1 - j][i];
a[N - 1 - j][i] = a[N - 1 - i][N - 1 - j];
a[N - 1 - i][N - 1 - j] = a[j][N - 1 - i];
a[j][N - 1 - i] = temp;
}
}
}
// Function for print matrix
void printMatrix(int arr[N][N])
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
cout << arr[i][j] << " ";
cout << '\n';
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[N][N] = { { 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 5, 6, 7, 8 },
{ 9, 10, 11, 12 },
{ 13, 14, 15, 16 } };
rotate90Clockwise(arr);
printMatrix(arr);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation of above approach
import java.io.*;
class GFG
{
static int N = 4;
// Function to rotate the matrix 90 degree clockwise
static void rotate90Clockwise(int a[][])
{
// Traverse each cycle
for (int i = 0; i < N / 2; i++)
{
for (int j = i; j < N - i - 1; j++)
{
// Swap elements of each cycle
// in clockwise direction
int temp = a[i][j];
a[i][j] = a[N - 1 - j][i];
a[N - 1 - j][i] = a[N - 1 - i][N - 1 - j];
a[N - 1 - i][N - 1 - j] = a[j][N - 1 - i];
a[j][N - 1 - i] = temp;
}
}
}
// Function for print matrix
static void printMatrix(int arr[][])
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
System.out.print( arr[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int arr[][] = { { 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 5, 6, 7, 8 },
{ 9, 10, 11, 12 },
{ 13, 14, 15, 16 } };
rotate90Clockwise(arr);
printMatrix(arr);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by inder_verma.
Python
# Function to rotate the matrix # 90 degree clockwise def rotate90Clockwise(A): N = len(A[0]) for i in range(N // 2): for j in range(i, N - i - 1): temp = A[i][j] A[i][j] = A[N - 1 - j][i] A[N - 1 - j][i] = A[N - 1 - i][N - 1 - j] A[N - 1 - i][N - 1 - j] = A[j][N - 1 - i] A[j][N - 1 - i] = temp # Function to print the matrix def printMatrix(A): N = len(A[0]) for i in range(N): print(A[i]) # Driver code A = [[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12], [13, 14, 15, 16]] rotate90Clockwise(A) printMatrix(A) # This code was contributed # by pk_tautolo
C#
// C# implementation of above approach
using System;
class GFG
{
static int N = 4;
// Function to rotate the matrix
// 90 degree clockwise
static void rotate90Clockwise(int[,] a)
{
// Traverse each cycle
for (int i = 0; i < N / 2; i++)
{
for (int j = i; j < N - i - 1; j++)
{
// Swap elements of each cycle
// in clockwise direction
int temp = a[i, j];
a[i, j] = a[N - 1 - j, i];
a[N - 1 - j, i] = a[N - 1 - i, N - 1 - j];
a[N - 1 - i, N - 1 - j] = a[j, N - 1 - i];
a[j, N - 1 - i] = temp;
}
}
}
// Function for print matrix
static void printMatrix(int[,] arr)
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
Console.Write( arr[i, j] + " ");
Console.Write("\n");
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main ()
{
int [,]arr = {{1, 2, 3, 4},
{5, 6, 7, 8},
{9, 10, 11, 12},
{13, 14, 15, 16}};
rotate90Clockwise(arr);
printMatrix(arr);
}
}
// This code is contributed
// by ChitraNayal
PHP
<?php
// PHP implementation of above approach
$N = 4;
// Function to rotate the matrix
// 90 degree clockwise
function rotate90Clockwise(&$a)
{
global $N;
// Traverse each cycle
for ($i = 0; $i < $N / 2; $i++)
{
for ($j = $i;
$j < $N - $i - 1; $j++)
{
// Swap elements of each cycle
// in clockwise direction
$temp = $a[$i][$j];
$a[$i][$j] = $a[$N - 1 - $j][$i];
$a[$N - 1 - $j][$i] =
$a[$N - 1 - $i][$N - 1 - $j];
$a[$N - 1 - $i][$N - 1 - $j] =
$a[$j][$N - 1 - $i];
$a[$j][$N - 1 - $i] = $temp;
}
}
}
// Function for print matrix
function printMatrix(&$arr)
{
global $N;
for ($i = 0; $i < $N; $i++)
{
for ($j = 0; $j < $N; $j++)
echo $arr[$i][$j] . " ";
echo "\n";
}
}
// Driver code
$arr = array(array(1, 2, 3, 4),
array(5, 6, 7, 8),
array(9, 10, 11, 12),
array(13, 14, 15, 16));
rotate90Clockwise($arr);
printMatrix($arr);
// This code is contributed
// by ChitraNayal
?>
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript implementation of above approach
var N = 4;
// Function to rotate the matrix 90 degree clockwise
function rotate90Clockwise(a) {
// Traverse each cycle
for (i = 0; i < parseInt(N / 2); i++) {
for (j = i; j < N - i - 1; j++) {
// Swap elements of each cycle
// in clockwise direction
var temp = a[i][j];
a[i][j] = a[N - 1 - j][i];
a[N - 1 - j][i] = a[N - 1 - i][N - 1 - j];
a[N - 1 - i][N - 1 - j] = a[j][N - 1 - i];
a[j][N - 1 - i] = temp;
}
}
}
// Function for print matrix
function printMatrix(arr) {
for (i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < N; j++)
document.write(arr[i][j] + " ");
document.write("<br/>");
}
}
// Driver code
var arr = [ [ 1, 2, 3, 4 ],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8 ],
[ 9, 10, 11, 12 ],
[ 13, 14, 15, 16 ] ];
rotate90Clockwise(arr);
printMatrix(arr);
// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji
</script>
13 9 5 1 14 10 6 2 15 11 7 3 16 12 8 4
Análisis de Complejidad:
Complejidad del tiempo – O(n*n)
Espacio Auxiliar – O(1)
Método 2:
Enfoque: El enfoque se basa en el patrón formado por los índices después de rotar la array. Considere la siguiente ilustración para tener una idea clara de ella.
Considere una array de 3 x 3 con índices (i, j) de la siguiente manera.
00 01 02
10 11 12
20 21 22
Después de girar la array 90 grados en el sentido de las agujas del reloj, los índices se transforman en
20 10 00 índice_fila_actual = 0, i = 2, 1, 0
21 11 01 índice_fila_actual = 1, i = 2, 1, 0
22 12 02 índice_fila_actual = 2, i = 2, 1, 0
Observación: En cualquier fila, por cada índice de fila decreciente i , existe un índice de columna constante j , tal que j = índice_fila_actual .
Este patrón se puede imprimir usando 2 bucles anidados.
(Este patrón de escritura de índices se logra escribiendo los índices exactos de los elementos deseados de
donde realmente existían en la array original).
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation of above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 4
// Function to rotate the matrix 90 degree clockwise
void rotate90Clockwise(int arr[N][N])
{
// printing the matrix on the basis of
// observations made on indices.
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
for (int i = N - 1; i >= 0; i--)
cout << arr[i][j] << " ";
cout << '\n';
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[N][N] = { { 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 5, 6, 7, 8 },
{ 9, 10, 11, 12 },
{ 13, 14, 15, 16 } };
rotate90Clockwise(arr);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by yashbeersingh42
Java
// Java implementation of above approach
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
static int N = 4;
// Function to rotate the matrix 90 degree clockwise
static void rotate90Clockwise(int arr[][])
{
// printing the matrix on the basis of
// observations made on indices.
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
for (int i = N - 1; i >= 0; i--)
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[][] = { { 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 5, 6, 7, 8 },
{ 9, 10, 11, 12 },
{ 13, 14, 15, 16 } };
rotate90Clockwise(arr);
}
}
// This code is contributed by yashbeersingh42
Python3
# Python3 implementation of above approach N = 4 # Function to rotate the matrix 90 degree clockwise def rotate90Clockwise(arr) : global N # printing the matrix on the basis of # observations made on indices. for j in range(N) : for i in range(N - 1, -1, -1) : print(arr[i][j], end = " ") print() # Driver code arr = [ [ 1, 2, 3, 4 ], [ 5, 6, 7, 8 ], [ 9, 10, 11, 12 ], [ 13, 14, 15, 16 ] ] rotate90Clockwise(arr); # This code is contributed by divyesh072019.
C#
// C# implementation of above approach
using System;
class GFG {
static int N = 4;
// Function to rotate the matrix 90 degree clockwise
static void rotate90Clockwise(int[,] arr)
{
// printing the matrix on the basis of
// observations made on indices.
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
for (int i = N - 1; i >= 0; i--)
Console.Write(arr[i, j] + " ");
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// Driver code
static void Main() {
int[,] arr = { { 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 5, 6, 7, 8 },
{ 9, 10, 11, 12 },
{ 13, 14, 15, 16 } };
rotate90Clockwise(arr);
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07.
Javascript
<script>
// javascript implementation of above approach
var N = 4;
// Function to rotate the matrix 90 degree clockwise
function rotate90Clockwise(arr) {
// printing the matrix on the basis of
// observations made on indices.
for (j = 0; j < N; j++) {
for (i = N - 1; i >= 0; i--)
document.write(arr[i][j] + " ");
document.write("<br/>");
}
}
var arr = [ [ 1, 2, 3, 4 ],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8 ],
[ 9, 10, 11, 12 ],
[ 13, 14, 15, 16 ] ];
rotate90Clockwise(arr);
// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji
</script>
13 9 5 1 14 10 6 2 15 11 7 3 16 12 8 4
Análisis de Complejidad:
Complejidad del tiempo – O(n*n)
Espacio Auxiliar – O(1)
Método 3:
Enfoque: El enfoque es rotar la array dada dos veces, la primera vez con respecto a la diagonal principal, la próxima vez rotar la array resultante con respecto a la columna del medio. Considere la siguiente ilustración para tener una idea clara de ella.
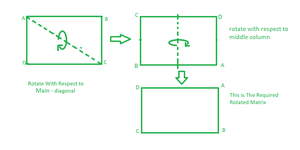
Gira la array cuadrada 90 grados en el sentido de las agujas del reloj
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 4
void print(int arr[N][N])
{
for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
for(int j = 0; j < N; ++j)
cout << arr[i][j] << " ";
cout << '\n';
}
}
void rotate(int arr[N][N])
{
// First rotation
// with respect to main diagonal
for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
for(int j = 0; j < i; ++j)
{
int temp = arr[i][j];
arr[i][j] = arr[j][i];
arr[j][i] = temp;
}
}
// Second rotation
// with respect to middle column
for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
for(int j = 0; j < N / 2; ++j)
{
int temp = arr[i][j];
arr[i][j] = arr[i][N - j - 1];
arr[i][N - j - 1] = temp;
}
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[N][N] = { { 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 5, 6, 7, 8 },
{ 9, 10, 11, 12 },
{ 13, 14, 15, 16 } };
rotate(arr);
print(arr);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Rahul Verma
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
static void rotate(int[][] arr) {
int n=arr.length;
// first rotation
// with respect to main diagonal
for(int i=0;i<n;++i)
{
for(int j=0;j<i;++j)
{
int temp = arr[i][j];
arr[i][j]=arr[j][i];
arr[j][i]=temp;
}
}
// Second rotation
// with respect to middle column
for(int i=0;i<n;++i)
{
for(int j=0;j<n/2;++j)
{
int temp =arr[i][j];
arr[i][j] = arr[i][n-j-1];
arr[i][n-j-1]=temp;
}
}
}
// to print matrix
static void printMatrix(int arr[][])
{
int n=arr.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
System.out.print( arr[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main (String[] args) {
int arr[][] = { { 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 5, 6, 7, 8 },
{ 9, 10, 11, 12 },
{ 13, 14, 15, 16 } };
rotate(arr);
printMatrix(arr);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rahul Verma
Python3
# Python3 implementation of above approach N = 4 # Function to rotate the matrix 90 degree clockwise def rotate(arr): global N # First rotation # with respect to main diagonal for i in range(N): for j in range(i): temp = arr[i][j] arr[i][j] = arr[j][i] arr[j][i] = temp # Second rotation # with respect to middle column for i in range(N): for j in range(int(N/2)): temp = arr[i][j] arr[i][j] = arr[i][N-j-1] arr[i][N-j-1] = temp # Driver code arr = [[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12], [13, 14, 15, 16]] rotate(arr) for i in range(N): for j in range(N): print(arr[i][j], end=" ") print() # This code is contributed by Aarti_Rathi
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG {
static void rotate(int[,] arr) {
int n=arr.GetLength(0);
// first rotation
// with respect to main diagonal
for(int i=0;i<n;++i)
{
for(int j=0;j<i;++j)
{
int temp = arr[i,j];
arr[i,j]=arr[j,i];
arr[j,i]=temp;
}
}
// Second rotation
// with respect to middle column
for(int i=0;i<n;++i)
{
for(int j=0;j<n/2;++j)
{
int temp =arr[i,j];
arr[i,j] = arr[i,n-j-1];
arr[i,n-j-1]=temp;
}
}
}
// to print matrix
static void printMatrix(int [,]arr)
{
int n=arr.GetLength(0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
Console.Write( arr[i,j] + " ");
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args) {
int [,]arr = { { 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 5, 6, 7, 8 },
{ 9, 10, 11, 12 },
{ 13, 14, 15, 16 } };
rotate(arr);
printMatrix(arr);
}
}
// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji
Javascript
<script>
let N = 4
function print(arr)
{
for(let i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
for(let j = 0; j < N; ++j)
document.write(arr[i][j] + " ");
document.write("<br>");
}
}
function rotate(arr)
{
// First rotation
// with respect to main diagonal
for(let i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
for(let j = 0; j < i; ++j)
{
let temp = arr[i][j];
arr[i][j] = arr[j][i];
arr[j][i] = temp;
}
}
// Second rotation
// with respect to middle column
for(let i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
for(let j = 0; j < N / 2; ++j)
{
let temp = arr[i][j];
arr[i][j] = arr[i][N - j - 1];
arr[i][N - j - 1] = temp;
}
}
}
// Driver code
let arr = [ [ 1, 2, 3, 4 ],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8 ],
[ 9, 10, 11, 12 ],
[ 13, 14, 15, 16 ] ];
rotate(arr);
print(arr);
//This code is contributed by Mayank Tyagi
</script>
13 9 5 1 14 10 6 2 15 11 7 3 16 12 8 4
Análisis de Complejidad:
Complejidad del tiempo – O(n*n)
Espacio Auxiliar – O(1)
Método 4:
Enfoque: Este enfoque es similar al método 3, la única diferencia es que en la primera rotación giramos sobre la diagonal secundaria y luego sobre la fila central.
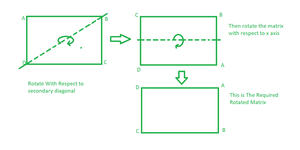
Gira la array cuadrada 90 grados en el sentido de las agujas del reloj
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 4
void print(int arr[N][N])
{
for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
for(int j = 0; j < N; ++j)
cout << arr[i][j] << " ";
cout << '\n';
}
}
void rotate(int arr[N][N])
{
// First rotation
// with respect to Secondary diagonal
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < N - i; j++)
{
int temp = arr[i][j];
arr[i][j] = arr[N - 1 - j][N - 1 - i];
arr[N - 1 - j][N - 1 - i] = temp;
}
}
// Second rotation
// with respect to middle row
for(int i = 0; i < N / 2; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
int temp = arr[i][j];
arr[i][j] = arr[N - 1 - i][j];
arr[N - 1 - i][j] = temp;
}
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[N][N] = { { 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 5, 6, 7, 8 },
{ 9, 10, 11, 12 },
{ 13, 14, 15, 16 } };
rotate(arr);
print(arr);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Rahul Verma
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
static void rotate(int[][] arr)
{
int n = arr.length;
// first rotation
// with respect to Secondary diagonal
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n - i; j++) {
int temp = arr[i][j];
arr[i][j] = arr[n - 1 - j][n - 1 - i];
arr[n - 1 - j][n - 1 - i] = temp;
}
}
// Second rotation
// with respect to middle row
for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
int temp = arr[i][j];
arr[i][j] = arr[n - 1 - i][j];
arr[n - 1 - i][j] = temp;
}
}
}
// to print matrix
static void printMatrix(int arr[][])
{
int n = arr.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[][] = { { 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 5, 6, 7, 8 },
{ 9, 10, 11, 12 },
{ 13, 14, 15, 16 } };
rotate(arr);
printMatrix(arr);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rahul Verma
Python3
# Python3 implementation of above approach N = 4 def display(arr): for i in range(N) : for j in range(N) : print(arr[i][j],end=" ") print() # Function to rotate the matrix 90 degree clockwise def rotate90Clockwise(arr) : global N # First rotation # with respect to Secondary diagonal for i in range(N) : for j in range(N-i) : arr[i][j],arr[N - 1 - j][N - 1 - i]=arr[N - 1 - j][N - 1 - i],arr[i][j] # Second rotation # with respect to middle row for i in range(N//2) : for j in range(N) : arr[i][j],arr[N - 1 - i][j]=arr[N - 1 - i][j],arr[i][j] # Driver code arr = [ [ 1, 2, 3, 4 ], [ 5, 6, 7, 8 ], [ 9, 10, 11, 12 ], [ 13, 14, 15, 16 ] ] rotate90Clockwise(arr) display(arr) # This code is contributed by Aarti_Rathi
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static void rotate(int[,] arr)
{
int n = arr.GetLength(0);
// First rotation
// with respect to Secondary diagonal
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < n - i; j++)
{
int temp = arr[i, j];
arr[i, j] = arr[n - 1 - j, n - 1 - i];
arr[n - 1 - j, n - 1 - i] = temp;
}
}
// Second rotation
// with respect to middle row
for(int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
int temp = arr[i, j];
arr[i, j] = arr[n - 1 - i, j];
arr[n - 1 - i, j] = temp;
}
}
}
// To print matrix
static void printMatrix(int [,]arr)
{
int n = arr.GetLength(0);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
Console.Write(arr[i, j] + " ");
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int [,]arr = { { 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 5, 6, 7, 8 },
{ 9, 10, 11, 12 },
{ 13, 14, 15, 16 } };
rotate(arr);
printMatrix(arr);
}
}
// This code is contributed by aashish1995
Javascript
<script>
function rotate(arr) {
var n = arr.length;
// first rotation
// with respect to Secondary diagonal
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < n - i; j++) {
var temp = arr[i][j];
arr[i][j] = arr[n - 1 - j][n - 1 - i];
arr[n - 1 - j][n - 1 - i] = temp;
}
}
// Second rotation
// with respect to middle row
for (i = 0; i < n / 2; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < n; j++) {
var temp = arr[i][j];
arr[i][j] = arr[n - 1 - i][j];
arr[n - 1 - i][j] = temp;
}
}
}
// to print matrix
function printMatrix(arr) {
var n = arr.length;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
document.write(arr[i][j] + " ");
document.write("<br/>");
}
}
// Driver code
var arr = [ [ 1, 2, 3, 4 ],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8 ],
[ 9, 10, 11, 12 ],
[ 13, 14, 15, 16 ] ];
rotate(arr);
printMatrix(arr);
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
</script>
13 9 5 1 14 10 6 2 15 11 7 3 16 12 8 4
Análisis de Complejidad:
Complejidad del tiempo – O(n*n)
Espacio Auxiliar – O(1)
Método 5:
Enfoque: primero transponemos la array dada y luego invertimos el contenido de las filas individuales para obtener la array resultante girada 90 grados en el sentido de las agujas del reloj.
1 2 3 1 4 7 7 4 1
4 5 6 ——Transponer——> 2 5 8 —-Invertir filas individuales—-> 8 5 2 (Array resultante)
7 8 9 3 6 9 9 6 3
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int n = 4;
void print(int mat[n][n])
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
cout << mat[i][j] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
void rotate90clockwise(int mat[n][n])
{
// Transpose of matrix
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
swap(mat[i][j], mat[j][i]);
// Reverse individual rows
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int low = 0, high = n - 1;
while (low < high) {
swap(mat[i][low], mat[i][high]);
low++;
high--;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int mat[n][n]
= { { 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 5, 6, 7, 8 },
{ 9, 10, 11, 12 },
{ 13, 14, 15, 16 } };
rotate90clockwise(mat);
print(mat);
}
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static int n = 4;
static void print(int mat[][]) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
System.out.print(mat[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
static void rotate90clockwise(int mat[][])
{
// Transpose of matrix
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
int t = mat[i][j];
mat[i][j] = mat[j][i];
mat[j][i] = t;
}
// Reverse individual rows
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int low = 0, high = n - 1;
while (low < high) {
int t = mat[i][low];
mat[i][low] = mat[i][high];
mat[i][high] = t;
low++;
high--;
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args) {
int mat[][] = { { 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 5, 6, 7, 8 },
{ 9, 10, 11, 12 },
{ 13, 14, 15, 16 } };
rotate90clockwise(mat);
print(mat);
}
}
// This code is contributed by umadevi9616
Python3
# Python3 implementation of above approach N = 4 def display(arr): for i in range(N) : for j in range(N) : print(arr[i][j],end=" ") print() # Function to rotate the matrix 90 degree clockwise def rotate90Clockwise(arr) : global N # Transpose of matrix for i in range(N) : for j in range(i+1,N) : arr[i][j],arr[j][i]=arr[j][i],arr[i][j] # Reverse individual rows for i in range(N//2) : low = 0 high = N-1 while (low<high) : arr[i][low],arr[i][high]=arr[i][high],arr[i][low] low = low + 1 high = high - 1 # Driver code arr = [ [ 1, 2, 3, 4 ], [ 5, 6, 7, 8 ], [ 9, 10, 11, 12 ], [ 13, 14, 15, 16 ] ] rotate90Clockwise(arr) display(arr) # This code is contributed by Aarti_Rathi
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static void rotate90clockwise(int[,] arr)
{
int n = arr.GetLength(0);
// Transpose of matrix
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = i+1; j < n; j++)
{
int temp = arr[i, j];
arr[i, j] = arr[j, i];
arr[j, i] = temp;
}
}
/// Reverse individual rows
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int low = 0, high = n - 1;
while (low < high) {
int temp = arr[i, low];
arr[i, low] = arr[i, high];
arr[i, high] = temp;
low++;
high--;
}
}
}
// To print matrix
static void printMatrix(int [,]arr)
{
int n = arr.GetLength(0);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
Console.Write(arr[i, j] + " ");
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int [,]arr = { { 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 5, 6, 7, 8 },
{ 9, 10, 11, 12 },
{ 13, 14, 15, 16 } };
rotate90clockwise(arr);
printMatrix(arr);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Aarti_Rathi
Javascript
<script>
function rotate(arr) {
var n = arr.length;
// Transpose of matrix
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (j = i+1; j < n; j++) {
var temp = arr[i][j];
arr[i][j] = arr[j][i];
arr[j][i] = temp;
}
}
// Reverse individual rows
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
var low = 0, high = n-1;
while (low < high) {
var temp = arr[i][low];
arr[i][low] = arr[i][high];
arr[i][high] = temp;
low++;
high--;
}
}
}
// to print matrix
function printMatrix(arr) {
var n = arr.length;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
document.write(arr[i][j] + " ");
document.write("<br/>");
}
}
// Driver code
var arr = [ [ 1, 2, 3, 4 ],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8 ],
[ 9, 10, 11, 12 ],
[ 13, 14, 15, 16 ] ];
rotate(arr);
printMatrix(arr);
// This code is contributed by Aarti_Rathi
</script>
13 9 5 1 14 10 6 2 15 11 7 3 16 12 8 4
Análisis de Complejidad:
Complejidad del tiempo – O(n*n)
Espacio Auxiliar – O(1)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por Rahul Singh_8868 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA