Dada una array booleana 2D, encuentre el número de islas.
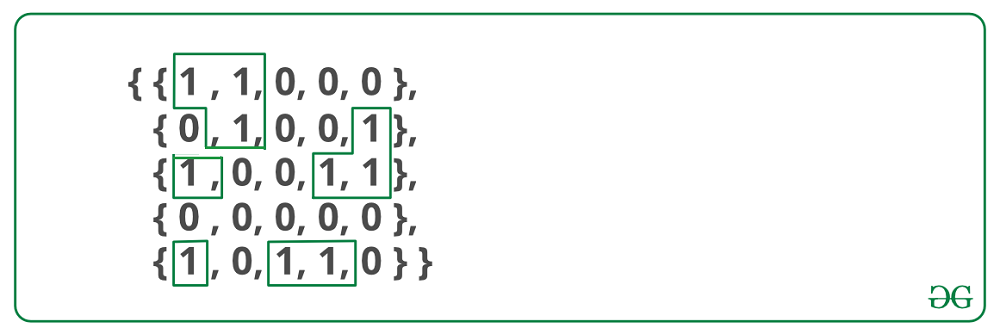
Un grupo de unos conectados forma una isla. Por ejemplo, la siguiente array contiene 5 islas
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 0, 1, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 1}
Una celda en la array 2D se puede conectar a 8 vecinos.
Esta es una variación del problema estándar: «Contar el número de componentes conectados en un gráfico no dirigido». Hemos discutido una solución basada en DFS en el siguiente conjunto 1.
Encuentre el número de islas
También podemos resolver la pregunta usando la estructura de datos de conjuntos disjuntos que se explica aquí . La idea es considerar todos los valores de 1 como conjuntos individuales. Atraviesa la array y haz una unión de todos los 1 vértices adyacentes. A continuación se detallan los pasos.
Enfoque:
1) Inicializar el resultado (recuento de islas) como 0
2) Recorrer cada índice de la array 2D.
3) Si el valor en ese índice es 1, verifique todos sus 8 vecinos. Si un vecino también es igual a 1, toma la unión del índice y su vecino.
4) Ahora defina una array de tamaño fila*columna para almacenar frecuencias de todos los conjuntos.
5) Ahora recorre la array nuevamente.
6) Si el valor en el índice es 1, encuentre su conjunto.
7) Si la frecuencia del conjunto en la array anterior es 0, incremente el resultado en 1.
A continuación se muestra la implementación en Java de los pasos anteriores.
C++
// C++ program to find number of islands
// using Disjoint Set data structure.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Class to represent
// Disjoint Set Data structure
class DisjointUnionSets
{
vector<int> rank, parent;
int n;
public:
DisjointUnionSets(int n)
{
rank.resize(n);
parent.resize(n);
this->n = n;
makeSet();
}
void makeSet()
{
// Initially, all elements
// are in their own set.
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
parent[i] = i;
}
// Finds the representative of the set
// that x is an element of
int find(int x)
{
if (parent[x] != x)
{
// if x is not the parent of itself,
// then x is not the representative of
// its set.
// so we recursively call Find on its parent
// and move i's node directly under the
// representative of this set
parent[x]=find(parent[x]);
}
return parent[x];
}
// Unites the set that includes x and the set
// that includes y
void Union(int x, int y)
{
// Find the representatives(or the root nodes)
// for x an y
int xRoot = find(x);
int yRoot = find(y);
// Elements are in the same set,
// no need to unite anything.
if (xRoot == yRoot)
return;
// If x's rank is less than y's rank
// Then move x under y so that
// depth of tree remains less
if (rank[xRoot] < rank[yRoot])
parent[xRoot] = yRoot;
// Else if y's rank is less than x's rank
// Then move y under x so that depth of tree
// remains less
else if (rank[yRoot] < rank[xRoot])
parent[yRoot] = xRoot;
else // Else if their ranks are the same
{
// Then move y under x (doesn't matter
// which one goes where)
parent[yRoot] = xRoot;
// And increment the result tree's
// rank by 1
rank[xRoot] = rank[xRoot] + 1;
}
}
};
// Returns number of islands in a[][]
int countIslands(vector<vector<int>>a)
{
int n = a.size();
int m = a[0].size();
DisjointUnionSets *dus = new DisjointUnionSets(n * m);
/* The following loop checks for its neighbours
and unites the indexes if both are 1. */
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < m; k++)
{
// If cell is 0, nothing to do
if (a[j][k] == 0)
continue;
// Check all 8 neighbours and do a Union
// with neighbour's set if neighbour is
// also 1
if (j + 1 < n && a[j + 1][k] == 1)
dus->Union(j * (m) + k,
(j + 1) * (m) + k);
if (j - 1 >= 0 && a[j - 1][k] == 1)
dus->Union(j * (m) + k,
(j - 1) * (m) + k);
if (k + 1 < m && a[j][k + 1] == 1)
dus->Union(j * (m) + k,
(j) * (m) + k + 1);
if (k - 1 >= 0 && a[j][k - 1] == 1)
dus->Union(j * (m) + k,
(j) * (m) + k - 1);
if (j + 1 < n && k + 1 < m &&
a[j + 1][k + 1] == 1)
dus->Union(j * (m) + k,
(j + 1) * (m) + k + 1);
if (j + 1 < n && k - 1 >= 0 &&
a[j + 1][k - 1] == 1)
dus->Union(j * m + k,
(j + 1) * (m) + k - 1);
if (j - 1 >= 0 && k + 1 < m &&
a[j - 1][k + 1] == 1)
dus->Union(j * m + k,
(j - 1) * m + k + 1);
if (j - 1 >= 0 && k - 1 >= 0 &&
a[j - 1][k - 1] == 1)
dus->Union(j * m + k,
(j - 1) * m + k - 1);
}
}
// Array to note down frequency of each set
int *c = new int[n * m];
int numberOfIslands = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < m; k++)
{
if (a[j][k] == 1)
{
int x = dus->find(j * m + k);
// If frequency of set is 0,
// increment numberOfIslands
if (c[x] == 0)
{
numberOfIslands++;
c[x]++;
}
else
c[x]++;
}
}
}
return numberOfIslands;
}
// Driver Code
int main(void)
{
vector<vector<int>>a = {{1, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 0, 1, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 1}};
cout << "Number of Islands is: "
<< countIslands(a) << endl;
}
// This code is contributed by ankush_953
Java
// Java program to find number of islands using Disjoint
// Set data structure.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException
{
int[][] a = new int[][] {{1, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 0, 1, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 1}
};
System.out.println("Number of Islands is: " +
countIslands(a));
}
// Returns number of islands in a[][]
static int countIslands(int a[][])
{
int n = a.length;
int m = a[0].length;
DisjointUnionSets dus = new DisjointUnionSets(n*m);
/* The following loop checks for its neighbours
and unites the indexes if both are 1. */
for (int j=0; j<n; j++)
{
for (int k=0; k<m; k++)
{
// If cell is 0, nothing to do
if (a[j][k] == 0)
continue;
// Check all 8 neighbours and do a union
// with neighbour's set if neighbour is
// also 1
if (j+1 < n && a[j+1][k]==1)
dus.union(j*(m)+k, (j+1)*(m)+k);
if (j-1 >= 0 && a[j-1][k]==1)
dus.union(j*(m)+k, (j-1)*(m)+k);
if (k+1 < m && a[j][k+1]==1)
dus.union(j*(m)+k, (j)*(m)+k+1);
if (k-1 >= 0 && a[j][k-1]==1)
dus.union(j*(m)+k, (j)*(m)+k-1);
if (j+1<n && k+1<m && a[j+1][k+1]==1)
dus.union(j*(m)+k, (j+1)*(m)+k+1);
if (j+1<n && k-1>=0 && a[j+1][k-1]==1)
dus.union(j*m+k, (j+1)*(m)+k-1);
if (j-1>=0 && k+1<m && a[j-1][k+1]==1)
dus.union(j*m+k, (j-1)*m+k+1);
if (j-1>=0 && k-1>=0 && a[j-1][k-1]==1)
dus.union(j*m+k, (j-1)*m+k-1);
}
}
// Array to note down frequency of each set
int[] c = new int[n*m];
int numberOfIslands = 0;
for (int j=0; j<n; j++)
{
for (int k=0; k<m; k++)
{
if (a[j][k]==1)
{
int x = dus.find(j*m+k);
// If frequency of set is 0,
// increment numberOfIslands
if (c[x]==0)
{
numberOfIslands++;
c[x]++;
}
else
c[x]++;
}
}
}
return numberOfIslands;
}
}
// Class to represent Disjoint Set Data structure
class DisjointUnionSets
{
int[] rank, parent;
int n;
public DisjointUnionSets(int n)
{
rank = new int[n];
parent = new int[n];
this.n = n;
makeSet();
}
void makeSet()
{
// Initially, all elements are in their
// own set.
for (int i=0; i<n; i++)
parent[i] = i;
}
// Finds the representative of the set that x
// is an element of
int find(int x)
{
if (parent[x] != x)
{
// if x is not the parent of itself,
// then x is not the representative of
// its set.
// so we recursively call Find on its parent
// and move i's node directly under the
// representative of this set
parent[x]=find(parent[x]);
}
return parent[x];
}
// Unites the set that includes x and the set
// that includes y
void union(int x, int y)
{
// Find the representatives (or the root nodes)
// for x an y
int xRoot = find(x);
int yRoot = find(y);
// Elements are in the same set, no need
// to unite anything.
if (xRoot == yRoot)
return;
// If x's rank is less than y's rank
// Then move x under y so that depth of tree
// remains less
if (rank[xRoot] < rank[yRoot])
parent[xRoot] = yRoot;
// Else if y's rank is less than x's rank
// Then move y under x so that depth of tree
// remains less
else if(rank[yRoot]<rank[xRoot])
parent[yRoot] = xRoot;
else // Else if their ranks are the same
{
// Then move y under x (doesn't matter
// which one goes where)
parent[yRoot] = xRoot;
// And increment the result tree's
// rank by 1
rank[xRoot] = rank[xRoot] + 1;
}
}
}
Python3
# Python3 program to find
# the number of islands using
# Disjoint Set data structure.
# Class to represent
# Disjoint Set Data structure
class DisjointUnionSets:
def __init__(self, n):
self.rank = [0] * n
self.parent = [0] * n
self.n = n
self.makeSet()
def makeSet(self):
# Initially, all elements are in their
# own set.
for i in range(self.n):
self.parent[i] = i
# Finds the representative of the set that x
# is an element of
def find(self, x):
if (self.parent[x] != x):
# if x is not the parent of itself,
# then x is not the representative of
# its set.
# so we recursively call Find on its parent
# and move i's node directly under the
# representative of this set
self.parent[x]=self.find(self.parent[x])
return self.parent[x]
# Unites the set that includes x and
# the set that includes y
def Union(self, x, y):
# Find the representatives(or the root nodes)
# for x an y
xRoot = self.find(x)
yRoot = self.find(y)
# Elements are in the same set,
# no need to unite anything.
if xRoot == yRoot:
return
# If x's rank is less than y's rank
# Then move x under y so that depth of tree
# remains less
if self.rank[xRoot] < self.rank[yRoot]:
parent[xRoot] = yRoot
# Else if y's rank is less than x's rank
# Then move y under x so that depth of tree
# remains less
elif self.rank[yRoot] < self.rank[xRoot]:
self.parent[yRoot] = xRoot
else:
# Else if their ranks are the same
# Then move y under x (doesn't matter
# which one goes where)
self.parent[yRoot] = xRoot
# And increment the result tree's
# rank by 1
self.rank[xRoot] = self.rank[xRoot] + 1
# Returns number of islands in a[][]
def countIslands(a):
n = len(a)
m = len(a[0])
dus = DisjointUnionSets(n * m)
# The following loop checks for its neighbours
# and unites the indexes if both are 1.
for j in range(0, n):
for k in range(0, m):
# If cell is 0, nothing to do
if a[j][k] == 0:
continue
# Check all 8 neighbours and do a Union
# with neighbour's set if neighbour is
# also 1
if j + 1 < n and a[j + 1][k] == 1:
dus.Union(j * (m) + k,
(j + 1) * (m) + k)
if j - 1 >= 0 and a[j - 1][k] == 1:
dus.Union(j * (m) + k,
(j - 1) * (m) + k)
if k + 1 < m and a[j][k + 1] == 1:
dus.Union(j * (m) + k,
(j) * (m) + k + 1)
if k - 1 >= 0 and a[j][k - 1] == 1:
dus.Union(j * (m) + k,
(j) * (m) + k - 1)
if (j + 1 < n and k + 1 < m and
a[j + 1][k + 1] == 1):
dus.Union(j * (m) + k, (j + 1) *
(m) + k + 1)
if (j + 1 < n and k - 1 >= 0 and
a[j + 1][k - 1] == 1):
dus.Union(j * m + k, (j + 1) *
(m) + k - 1)
if (j - 1 >= 0 and k + 1 < m and
a[j - 1][k + 1] == 1):
dus.Union(j * m + k, (j - 1) *
m + k + 1)
if (j - 1 >= 0 and k - 1 >= 0 and
a[j - 1][k - 1] == 1):
dus.Union(j * m + k, (j - 1) *
m + k - 1)
# Array to note down frequency of each set
c = [0] * (n * m)
numberOfIslands = 0
for j in range(n):
for k in range(n):
if a[j][k] == 1:
x = dus.find(j * m + k)
# If frequency of set is 0,
# increment numberOfIslands
if c[x] == 0:
numberOfIslands += 1
c[x] += 1
else:
c[x] += 1
return numberOfIslands
# Driver Code
a = [[1, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 1]]
print("Number of Islands is:", countIslands(a))
# This code is contributed by ankush_953
C#
// C# program to find number of islands using Disjoint
// Set data structure.
using System;
class GFG
{
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int[,] a = new int[,] {{1, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 0, 1, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 1}
};
Console.WriteLine("Number of Islands is: " +
countIslands(a));
}
// Returns number of islands in[,]a
static int countIslands(int[,]a)
{
int n = a.GetLength(0);
int m = a.GetLength(1);
DisjointUnionSets dus = new DisjointUnionSets(n * m);
/* The following loop checks for its neighbours
and unites the indexes if both are 1. */
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < m; k++)
{
// If cell is 0, nothing to do
if (a[j, k] == 0)
continue;
// Check all 8 neighbours and do a union
// with neighbour's set if neighbour is
// also 1
if (j + 1 < n && a[j + 1, k] == 1)
dus.union(j * (m) + k, (j + 1) * (m) + k);
if (j - 1 >= 0 && a[j - 1, k] == 1)
dus.union(j * (m) + k, (j - 1) * (m) + k);
if (k + 1 < m && a[j, k + 1] == 1)
dus.union(j * (m) + k, (j) * (m) + k + 1);
if (k-1 >= 0 && a[j,k-1]==1)
dus.union(j * (m) + k, (j) * (m) + k - 1);
if (j + 1 < n && k + 1 < m && a[j + 1, k + 1] == 1)
dus.union(j * (m) + k, (j + 1) * (m) + k + 1);
if (j + 1 < n && k - 1 >= 0 && a[j + 1,k - 1] == 1)
dus.union(j * m + k, (j + 1) * (m) + k - 1);
if (j - 1 >= 0 && k + 1 < m && a[j - 1, k + 1] == 1)
dus.union(j * m + k, (j - 1) * m + k + 1);
if (j - 1 >= 0 && k - 1 >= 0 && a[j - 1, k - 1] == 1)
dus.union(j * m + k, (j - 1) * m + k - 1);
}
}
// Array to note down frequency of each set
int[] c = new int[n*m];
int numberOfIslands = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < m; k++)
{
if (a[j, k] == 1)
{
int x = dus.find(j * m + k);
// If frequency of set is 0,
// increment numberOfIslands
if (c[x] == 0)
{
numberOfIslands++;
c[x]++;
}
else
c[x]++;
}
}
}
return numberOfIslands;
}
}
// Class to represent Disjoint Set Data structure
class DisjointUnionSets
{
int[] rank, parent;
int n;
public DisjointUnionSets(int n)
{
rank = new int[n];
parent = new int[n];
this.n = n;
makeSet();
}
public void makeSet()
{
// Initially, all elements are in their
// own set.
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
parent[i] = i;
}
// Finds the representative of the set that x
// is an element of
public int find(int x)
{
if (parent[x] != x)
{
// if x is not the parent of itself,
// then x is not the representative of
// its set.
// so we recursively call Find on its parent
// and move i's node directly under the
// representative of this set
parent[x]=find(parent[x]);
}
return parent[x];
}
// Unites the set that includes x and the set
// that includes y
public void union(int x, int y)
{
// Find the representatives (or the root nodes)
// for x an y
int xRoot = find(x);
int yRoot = find(y);
// Elements are in the same set, no need
// to unite anything.
if (xRoot == yRoot)
return;
// If x's rank is less than y's rank
// Then move x under y so that depth of tree
// remains less
if (rank[xRoot] < rank[yRoot])
parent[xRoot] = yRoot;
// Else if y's rank is less than x's rank
// Then move y under x so that depth of tree
// remains less
else if(rank[yRoot] < rank[xRoot])
parent[yRoot] = xRoot;
else // Else if their ranks are the same
{
// Then move y under x (doesn't matter
// which one goes where)
parent[yRoot] = xRoot;
// And increment the result tree's
// rank by 1
rank[xRoot] = rank[xRoot] + 1;
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992
Producción:
Number of Islands is: 5
Complejidad temporal: O(N * M), donde N es el número de filas y M es el número de columnas de la array.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(N * M)
Nikhil Tekwani contribuye con este artículo . Si te gusta GeeksforGeeks y te gustaría contribuir, también puedes escribir un artículo usando write.geeksforgeeks.org o enviar tu artículo por correo a review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA