La propiedad Objeto HTML en HTML DOM se usa para representar o acceder al elemento HTML <html> dentro del objeto. El elemento <html> se utiliza para devolver el documento HTML como un objeto de elemento.
Sintaxis:
- Se utiliza para acceder a un elemento <html>.
var x = document.getElementsByTagName("HTML")[0]; - También se puede utilizar para acceder a un elemento <html>.
var x = document.documentElement;
Valores de propiedad:
- getElementsByTagName(): se utiliza para devolver una colección de todos los elementos secundarios con el nombre de etiqueta especificado.
- innerHTML: Se utiliza para establecer o devolver el contenido de un elemento.
- getElementsById(): se utiliza para devolver una colección de todos los elementos secundarios con el Id especificado.
Ejemplo-1: acceda al elemento HTML usando document.getElementsByTagName(“HTML”)[0];
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<title>
HTML | DOM HTML Object Property
</title>
<style>
body {
text-align: center;
width: 70%;
}
h1 {
color: green;
}
h1,
h2 {
text-align: center;
}
</style>
<body>
<h1>GeeksforGeeks</h1>
<h2> HTML Object</h2>
<p>Click the button to get the
HTML content of the html element.</p>
<button onclick="GFG()">Click</button>
<p id="Geeks"></p>
<script>
function GFG() {
// Access html element and
return using "innerHTML"
var x =
document.getElementsByTagName(
"HTML")[0].innerHTML;
document.getElementById("Geeks").innerHTML = x;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Producción:
Antes de hacer clic en el botón:
Después de hacer clic en el botón: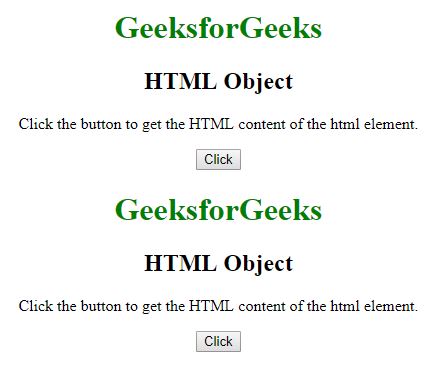
Ejemplo-2: Acceder al elemento html y devolver el elemento es primero o segundo .
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<title>
HTML | DOM HTML Object Property
</title>
<style>
body {
text-align: center;
width: 70%;
}
h1 {
color: green;
}
h1,
h2 {
text-align: center;
}
</style>
<body>
<h1>GeeksforGeeks</h1>
<h2> HTML Object</h2>
<p>Click the button to get the
HTML content of the html element.</p>
<p>Using the document.documentElement</p>
<button onclick="GFG()">Click</button>
<p id="Geeks"></p>
<script>
function GFG() {
// Access html element and return html
// with position value of html element.
var x =
document.documentElement.innerHTML;
document.getElementById(
"Geeks").innerHTML = "first" + x;
var y =
document.documentElement.innerHTML;
document.getElementById(
"Geeks").innerHTML = y + "second";
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Producción:
Antes de hacer clic en el botón:
Después de hacer clic en el botón: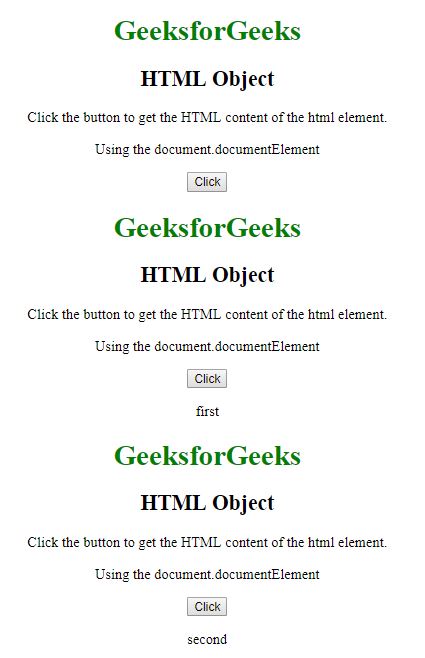
Ejemplo-3: acceda al elemento html y devuelva todos los elementos secundarios con el nombre de etiqueta especificado.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<title>
HTML | DOM HTML Object Property
</title>
<style>
body {
text-align: center;
width: 70%;
}
h1 {
color: green;
}
h1,
h2 {
text-align: center;
}
</style>
<body>
<h1>GeeksforGeeks</h1>
<h2> HTML Object</h2>
<p>Click the button to get the
HTML content of the html element.</p>
<p>Using the getElementsByTagName("HTML")[0]
and documentElement</p>
<button onclick="GFG()">Click</button>
<p id="Geeks"></p>
<script>
function GFG() {
// access and return html element
var x =
document.getElementsByTagName(
"HTML")[0].innerHTML;
document.getElementById("Geeks").innerHTML =
"getElementsByTagName" + x;
var y =
document.documentElement.innerHTML;
document.getElementById("Geeks").innerHTML =
y + "documentElement";
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Producción:
Antes de hacer clic en el botón:
Después de hacer clic en el botón:
Navegadores compatibles: los navegadores compatibles con la propiedad DOM HTML Object se enumeran a continuación:
- Google Chrome
- explorador de Internet
- Firefox
- Ópera
- Safari
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por SHUBHAMSINGH10 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA