La propiedad DOM innerText se utiliza para establecer o devolver el contenido de texto de un Node específico y sus descendientes. Esta propiedad es muy similar a la propiedad de contenido de texto, pero devuelve el contenido de todos los elementos, excepto los elementos <script> y <style>.
Sintaxis: Se utiliza para establecer la propiedad innerText.
node.innerText = text
Valor devuelto: Devuelve un valor de string que representa el contenido de texto del elemento junto con sus descendientes.
Ejemplo 1:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>
HTML DOM innerText Property
</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>GeeksforGeeks</h1>
<h2>HTML DOM textContent Property</h2>
<button id="geeks" onclick="MyGeeks()">
Submit
</button>
<p id="sudo"></p>
<script>
function MyGeeks() {
var text =
document.getElementById("geeks").innerText;
document.getElementById("sudo").innerHTML = text;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Salida:
antes de hacer clic en el botón: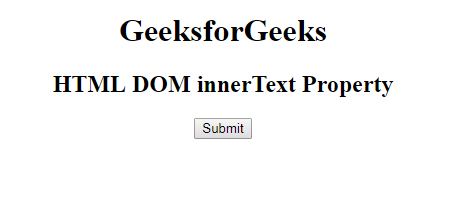
Después de hacer clic en el botón: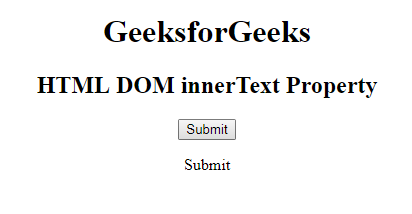
Ejemplo-2:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>
HTML DOM innerText Property
</title>
</head>
<body>
<center>
<h1>GeeksforGeeks</h1>
<h2>HTML DOM innerText Property</h2>
<p id="geeks" style="font-size:20px;">Hello Geeks!</p>
<button onclick="MyGeeks()">
Submit
</button>
<!-- MyGeeks function replace the inner text-->
<script>
function MyGeeks() {
document.getElementById("geeks").innerText =
"Welcome to GeeksforGeeks!";
}
</script>
</center>
</body>
</html>
Salida:
antes de hacer clic en el botón: 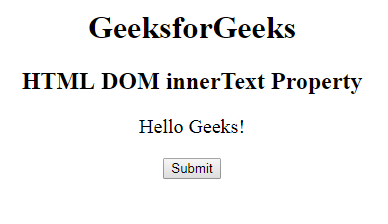
después de hacer clic en el botón: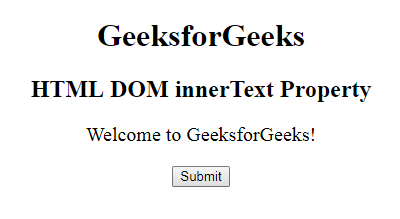
Navegadores compatibles: los navegadores compatibles con la propiedad DOM innerText se enumeran a continuación:
- Google Chrome 1.0
- Internet Explorer 4.0
- Firefox 1.0
- Ópera 3.5
- Safari 1.0
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por ManasChhabra2 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA